Abstract
Background
A family history of completed suicide and psychiatric illness has been identified as risk factors for suicide.
Aims
To examine the risk of offspring suicide in relation to parental history of suicide and other parental risk factors.
Method
The study population consisted of 7,177 adult offspring born 1959–1961 and their parents from the Copenhagen Perinatal Cohort. Cohort members and their parents who had committed suicide were identified in the Danish Causes of Death Registry (follow-up until December 31, 2005), while information on psychiatric hospitalisation history was obtained from the Danish Psychiatric Central Research Register.
Results
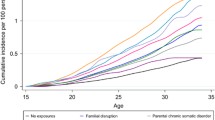
Forty-eight cohort members, 77 mothers and 133 fathers had committed suicide during the follow-up. Independent of parental psychiatric illness and social status, parental suicide significantly increased suicide risk in offspring (hazard ratio 4.40 with 95% CI 1.81–10.69). A stronger effect of parental suicide was observed in offspring without a history of psychiatric hospitalisation.
Conclusion
Parental history of suicide is a risk factor for suicide in offspring, but primarily in offspring without psychiatric hospitalisation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldessarini RJ, Hennen J (2004) Genetics of suicide: an overview. Harv Rev Psychiatry 12:1–13
Brent DA, Perper JA, Moritz G, Liotus L, Schweers J, Balach L, Roth C (1994) Familial risk factors for adolescent suicide: a case–control study. Acta Psychiatr Scand 89:52–58
Cheng AT (1995) Mental illness and suicide: a case–control study in east Taiwan. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:594–603
Cheng AT, Chen TH, Chen CC, Jenkins R (2000) Psychosocial and psychiatric risk factors for suicide: case–control psychological autopsy study. Br J Psychiatry 177:360–365
Glowinski AL, Bucholz KK, Nelson EC, Fu Q, Madden PA, Reich W, Heath AC (2001) Suicide attempts in an adolescent female twin sample. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40:1300–1307
Gould MS, Fisher P, Parides M, Flory M, Shaffer D (1996) Psychosocial risk factors of child and adolescent completed suicide. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:1155–1162
Johnson BA, Brent DA, Bridge J, Connolly J (1998) The familial aggregation of adolescent suicide attempts. Acta Psychiatr Scand 97:18–24
Juel K, Helweg-Larsen K (1999) The Danish registers of causes of death. Dan Med Bull 46:354–357
Kim CD, Seguin M, Therrien N, Riopel G, Chawky N, Lesage AD, Turecki G (2005) Familial aggregation of suicidal behavior: a family study of male suicide completers from the general population. Am J Psychiatry 162:1017–1019
Mittendorfer-Rutz E, Rasmussen F, Wasserman D (2008) Familial clustering of suicidal behaviour and psychopathology in young suicide attempters: a register-based nested case control study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 43:28–36
Munk-Jorgensen P, Mortensen PB (1997) The Danish psychiatric central register. Dan Med Bull 44:82–84
Murphy GE, Wetzel RD (1982) Family history of suicidal behavior among suicide attempters. J Nerv Ment Dis 170:86–90
Qin P, Agerbo E, Mortensen PB (2002) Suicide risk in relation to family history of completed suicide and psychiatric disorders: a nested case–control study based on longitudinal registers. Lancet 360:1126–1130
Qin P, Agerbo E, Mortensen PB (2003) Suicide risk in relation to socioeconomic, demographic, psychiatric, and familial factors: a national register-based study of all suicides in Denmark, 1981–1997. Am J Psychiatry 160:765–772
Roy A, Segal NL, Centerwall BS, Robinette CD (1991) Suicide in twins. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48:29–32
Silverton L, Mednick SA, Holst C, John R (2008) High social class and suicide in persons at risk for schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 117:192–197
Stenager K, Qin P (2008) Individual and parental psychiatric history and risk for suicide among adolescents and young adults in Denmark. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 43(11):920–926
Villumsen AL (1970) Environmental factors in congenital malformations: a prospective study of 9,006 human pregnancies. FADL’s Forlag, Copenhagen
Wender PH, Kety SS, Rosenthal D, Schulsinger F, Ortmann J, Lunde I (1986) Psychiatric disorders in the biological and adoptive families of adopted individuals with affective disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 43:923–929
Zachau-Christiansen B (1972) Development during the first year of life: a prospective study of 9,006 pregnancies. Poul A. Andersens Forlag, Helsingør
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sørensen, H.J., Mortensen, E.L., Wang, A.G. et al. Suicide and mental illness in parents and risk of suicide in offspring. Soc Psychiat Epidemiol 44, 748–751 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-009-0495-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-009-0495-5