Abstract.
Objective:
Based on the increased prescription of antidepressants, the aim of this study was to analyse the changes in self-poisonings with antidepressants during the period 1987–1997.
Methods:
A total of 909 patients who were admitted to hospital after deliberate self-poisoning were investigated regarding psychiatric diagnoses and drugs ingested.
Results:
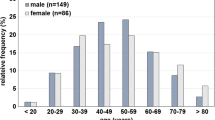
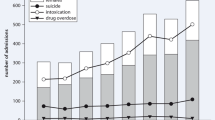
In the whole group, there was no significant change in the rate of antidepressant overdoses between 1987 and 1990 (20%) and 1995 and 1997 (17 %), but among females with a mood disorder overdoses decreased from 43% to 22% (p = 0.01). The proportion of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in self-poisonings was significantly lower than expected from sales figures.
Conclusion:
The increased antidepressant sales have not caused an increased use of antidepressants in self-poisonings. It is, therefore, tempting to assume that an increased use of antidepressants for appropriate indications causes decreased self-poisoning rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bäckman, J., Ekman, CJ., Alsén, M. et al. Use of antidepressants in deliberate self-poisoning. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 38, 684–689 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-003-0688-2
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-003-0688-2