Abstract
Aims/hypothesis
Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake are processes that rely on regulated intracellular vesicle transport and vesicle fusion with the plasma membrane. DOC2A and DOC2B are calcium-sensitive proteins that were identified as key components of vesicle exocytosis in neurons. Our aim was to investigate the role of DOC2 isoforms in glucose homeostasis, insulin secretion and insulin action.
Methods
DOC2 expression was measured by RT-PCR and western blotting. Body weight, glucose tolerance, insulin action and GSIS were assessed in wild-type (WT), Doc2a −/− (Doc2aKO), Doc2b −/− (Doc2bKO) and Doc2a −/−/Doc2b −/− (Doc2a/Doc2bKO) mice in vivo. In vitro GSIS and glucose uptake were assessed in isolated tissues, and exocytotic proteins measured by western blotting. GLUT4 translocation was assessed by epifluorescence microscopy.
Results
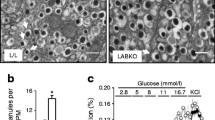
Doc2b mRNA was detected in all tissues tested, whereas Doc2a was only detected in islets and the brain. Doc2aKO and Doc2bKO mice had minor glucose intolerance, while Doc2a/Doc2bKO mice showed pronounced glucose intolerance. GSIS was markedly impaired in Doc2a/Doc2bKO mice in vivo, and in isolated Doc2a/Doc2bKO islets in vitro. In contrast, Doc2bKO mice had only subtle defects in insulin secretion in vivo. Insulin action was impaired to a similar degree in both Doc2bKO and Doc2a/Doc2bKO mice. In vitro insulin-stimulated glucose transport and GLUT4 vesicle fusion were defective in adipocytes derived from Doc2bKO mice. Surprisingly, insulin action was not altered in muscle isolated from DOC2-null mice.
Conclusions/interpretation
Our study identifies a critical role for DOC2B in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in adipocytes, and for the synergistic regulation of GSIS by DOC2A and DOC2B in beta cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DOC2:
-
Double C2 domain protein
- Doc2aKO:
-
Doc2a −/−
- Doc2bKO:
-
Doc2b −/−
- DXA:
-
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
- GSIS:
-
Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion
- ITT:
-
Insulin tolerance test
- [Ca2+]i :
-
Intracellular calcium
- MEFs:
-
Mouse embryonic fibroblasts
- PM:
-
Plasma membrane
- SNARE:
-
Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor
- WT:
-
Wild-type
References
Kahn SE (2003) The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of Type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 46:3–19
Ashcroft FM, Rorsman P (2012) Diabetes mellitus and the beta cell: the last ten years. Cell 148:1160–1171
Burgoyne RD, Morgan A (2003) Secretory granule exocytosis. Physiol Rev 83:581–632
Jahn R, Fasshauer D (2012) Molecular machines governing exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. Nature 490:201–207
Jewell JL, Oh E, Thurmond DC (2010) Exocytosis mechanisms underlying insulin release and glucose uptake: conserved roles for Munc18c and syntaxin 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298:R517–R531
Stöckli J, Fazakerley DJ, James DE (2011) GLUT4 exocytosis. J Cell Sci 124:4147–4159
Whitehead JP, Molero JC, Clark S, Martin S, Meneilly G, James DE (2001) The role of Ca2+ in insulin-stimulated glucose transport in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem 276:27816–27824
Lanner JT, Bruton JD, Katz A, Westerblad H (2008) Ca(2+) and insulin-mediated glucose uptake. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:339–345
Orita S, Sasaki T, Naito A et al (1995) Doc2: a novel brain protein having two repeated C2-like domains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 206:439–448
Sakaguchi G, Orita S, Maeda M, Igarashi H, Takai Y (1995) Molecular cloning of an isoform of Doc2 having two C2-like domains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 217:1053–1061
Kojima T, Fukuda M, Aruga J, Mikoshiba K (1996) Calcium-dependent phospholipid binding to the C2A domain of a ubiquitous form of double C2 protein (Doc2 beta). J Biochem 120:671–676
Verhage M, de Vries KJ, Roshol H, Burbach JP, Gispen WH, Sudhof TC (1997) DOC2 proteins in rat brain: complementary distribution and proposed function as vesicular adapter proteins in early stages of secretion. Neuron 18:453–461
Groffen AJ, Martens S, Diez Arazola R et al (2010) Doc2b is a high-affinity Ca2+ sensor for spontaneous neurotransmitter release. Science 327:1614–1618
Fukuda M, Mikoshiba K (2000) Doc2gamma, a third isoform of double C2 protein, lacking calcium-dependent phospholipid binding activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 276:626–632
Groffen AJ, Friedrich R, Brian EC, Ashery U, Verhage M (2006) DOC2A and DOC2B are sensors for neuronal activity with unique calcium-dependent and kinetic properties. J Neurochem 97:818–833
Friedrich R, Groffen AJ, Connell E et al (2008) DOC2B acts as a calcium switch and enhances vesicle fusion. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 28:6794–6806
Berghs CA, Korteweg N, Bouteiller A et al (1999) Co-expression in Xenopus neurons and neuroendocrine cells of messenger RNA homologues of exocytosis proteins DOC2 and munc18–1. Neuroscience 92:763–772
Ke B, Oh E, Thurmond DC (2007) Doc2beta is a novel Munc18c-interacting partner and positive effector of syntaxin 4-mediated exocytosis. J Biol Chem 282:21786–21797
Orita S, Naito A, Sakaguchi G et al (1997) Physical and functional interactions of Doc2 and Munc13 in Ca2+-dependent exocytotic machinery. J Biol Chem 272:16081–16084
Mochida S, Orita S, Sakaguchi G, Sasaki T, Takai Y (1998) Role of the Doc2 alpha-Munc13-1 interaction in the neurotransmitter release process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:11418–11422
Duncan RR, Betz A, Shipston MJ, Brose N, Chow RH (1999) Transient, phorbol ester-induced DOC2-Munc13 interactions in vivo. J Biol Chem 274:27347–27350
Nagano F, Orita S, Sasaki T et al (1998) Interaction of Doc2 with tctex-1, a light chain of cytoplasmic dynein. Implication in dynein-dependent vesicle transport. J Biol Chem 273:30065–30068
Sato M, Mori Y, Matsui T et al (2010) Role of the polybasic sequence in the Doc2alpha C2B domain in dense-core vesicle exocytosis in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 114:171–181
Miyazaki M, Emoto M, Fukuda N et al (2009) DOC2b is a SNARE regulator of glucose-stimulated delayed insulin secretion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384:461–465
Fukuda N, Emoto M, Nakamori Y et al (2009) DOC2B: a novel syntaxin-4 binding protein mediating insulin-regulated GLUT4 vesicle fusion in adipocytes. Diabetes 58:377–384
Yu H, Rathore SS, Davis EM, Ouyang Y, Shen J (2013) Doc2b promotes GLUT4 exocytosis by activating the SNARE-mediated fusion reaction in a calcium- and membrane bending-dependent manner. Mol Biol Cell 24:1176–1184
Ramalingam L, Oh E, Yoder SM et al (2012) Doc2b is a key effector of insulin secretion and skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 61:2424–2432
Sakaguchi G, Manabe T, Kobayashi K et al (1999) Doc2alpha is an activity-dependent modulator of excitatory synaptic transmission. Eur J Neurosci 11:4262–4268
Cantley J, Boslem E, Laybutt DR et al (2011) Deletion of protein kinase C delta in mice modulates stability of inflammatory genes and protects against cytokine-stimulated beta cell death in vitro and in vivo. Diabetologia 54:380–389
Cantley J, Choudhury AI, Asare-Anane H et al (2007) Pancreatic deletion of insulin receptor substrate 2 reduces beta and alpha cell mass and impairs glucose homeostasis in mice. Diabetologia 50:1248–1256
Sommer C, Straehle C, Koethe U, Hamprecht FA (2011) ilastik: Interactive Learning and Segmentation Toolkit. 8th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: 230–233
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to Image J: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Zhao P, Yang L, Lopez JA et al (2009) Variations in the requirement for v-SNAREs in GLUT4 trafficking in adipocytes. J Cell Sci 122:3472–3480
Burchfield JG, Lu J, Fazakerley DJ et al (2013) Novel systems for dynamically assessing insulin action in live cells reveals heterogeneity in the insulin response. Traffic 14:259–273
Nica AC, Ongen H, Irminger J-C et al (2013) Cell-type, allelic, and genetic signatures in the human pancreatic beta cell transcriptome. Genome Res 23:1554–1562
Marselli L, Thorne J, Dahiya S et al (2010) Gene expression profiles of Beta-cell enriched tissue obtained by laser capture microdissection from subjects with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 5:e11499
Li H, Heilbronn LK, Hu D et al (2008) Islet-1: a potentially important role for an islet cell gene in visceral fat. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16:356–362
Cantley J, Burchfield JG, Pearson GL, Schmitz-Peiffer C, Leitges M, Biden TJ (2009) Deletion of PKCepsilon selectively enhances the amplifying pathways of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion via increased lipolysis in mouse beta-cells. Diabetes 58:1826–1834
Valenti G, Procino G, Tamma G, Carmosino M, Svelto M (2005) Minireview: aquaporin 2 trafficking. Endocrinology 146:5063–5070
Butterworth MB, Edinger RS, Frizzell RA, Johnson JP (2008) Regulation of the epithelial sodium channel by membrane trafficking. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 296:F10–F24
Gustavsson N, Lao Y, Maximov A et al (2008) Impaired insulin secretion and glucose intolerance in synaptotagmin-7-null mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:3992–3997
Gustavsson N, Wang X, Wang Y et al (2010) Neuronal calcium sensor synaptotagmin-9 is not involved in the regulation of glucose homeostasis or insulin secretion. PLoS One 5:e15414
Beauvois MC, Merezak C, Jonas J-C, Ravier MA, Henquin J-C, Gilon P (2006) Glucose-induced mixed [Ca2+]c oscillations in mouse beta-cells are controlled by the membrane potential and the SERCA3 Ca2+-ATPase of the endoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290:C1503–C1511
Dyachok O, Idevall-Hagren O, Sågetorp J et al (2008) Glucose-induced cyclic AMP oscillations regulate pulsatile insulin secretion. Cell Metab 8:26–37
Wuttke A, Idevall-Hagren O, Tengholm A (2013) P2Y(1) receptor-dependent diacylglycerol signaling microdomains in beta cells promote insulin secretion. FASEB J 27:1610–1620
Sheu L, Pasyk EA, Ji J et al (2003) Regulation of insulin exocytosis by Munc13-1. J Biol Chem 278:27556–27563
Kwan EP, Xie L, Sheu L et al (2006) Munc13-1 deficiency reduces insulin secretion and causes abnormal glucose tolerance. Diabetes 55:1421–1429
Kang L, He Z, Xu P et al (2006) Munc13-1 is required for the sustained release of insulin from pancreatic β cells. Cell Metab 3:463–468
Bruton JD, Katz A, Westerblad H (1999) Insulin increases near-membrane but not global Ca2+ in isolated skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:3281–3286
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Südhof (Stanford University, CA, USA) for providing antibodies. We thank M. van de Bunt and A. Gloyn (University of Oxford, UK) for assistance with RNA-seq data analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by a National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) program grant (DEJ) and project grant (JC), and by the Chinese Scholarship Council (JL). DEJ is an NHMRC Senior Principal Research Fellow.
Duality of interest
The authors declare they have no duality of interest associated with this manuscript.
Contribution statement
DEJ conceived the studies. JC wrote the manuscript, with critical input from all authors. DEJ, JC, JL, JGB and JS designed experiments and interpreted data. JC, JL, JGB, JS, CCM, PTW, HP and RC designed experiments, and acquired and analysed data. MV and AJAG contributed to the acquisition and interpretation of data. All authors approved the final manuscript. DEJ is the guarantor of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jia Li, James Cantley and James G. Burchfield contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM Methods
(PDF 273 kb)
ESM Data file
(XLS 31,905 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Cantley, J., Burchfield, J.G. et al. DOC2 isoforms play dual roles in insulin secretion and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. Diabetologia 57, 2173–2182 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-014-3312-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-014-3312-y