Abstract
Key message
A major gene conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak was mapped to chromosome 5R in triticale.
Abstract
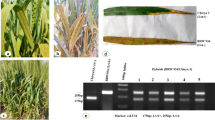
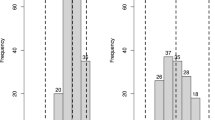
Bacterial leaf streak (BLS), caused by Xanthomonas translucens pv. undulosa (Xtu), is an important disease of wheat and triticale around the world. Although resistance to BLS is limited in wheat, several triticale accessions have high levels of resistance. To characterize the genetic basis of this resistance, we developed triticale mapping populations using a resistant accession (Siskiyou) and two susceptible accessions (UC38 and Villax St. Jose). Bulked segregant analysis in an F2 population derived from the cross of Siskiyou × UC38 led to the identification of a simple sequence repeat (SSR) marker (XSCM138) on chromosome 5R that co-segregated with the resistance gene. The cross of Siskiyou × Villax St. Jose was advanced into an F2:5 recombinant inbred line population and evaluated for BLS reaction. Genetic linkage maps on this population were assembled with markers generated using genotyping-by-sequencing as well as several SSR markers previously identified on 5R. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping revealed a single major QTL on chromosome 5R, underlined by the same SSR marker as in the Siskiyou × UC38 population. The F1 hybrids of the two crosses were highly resistant to BLS, indicating that resistance is largely dominant. This work will facilitate introgression of this rye-derived BLS resistance gene into the wheat genome by molecular marker-mediated chromosome engineering.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BLS:
-
Bacterial leaf streak
- BSA:
-
Bulked segregant analysis
- GBS:
-
Genotyping-by-sequencing
- LOD:
-
Log of odds ratio
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- MIM:
-
Multiple interval mapping
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- REMS:
-
Rye expressed microsatellite sites
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- SSD:
-
Single seed descent
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- SCM:
-
Secale cereale microsatellite
- Xtu :
-
Xanthomonas translucens pv. undulosa
References
Adhikari TB, Hansen JM, Gurung S, Bonman JM (2011) Identification of new sources of resistance in winter wheat to multiple strains of Xanthomonas translucens pv. undulosa. Plant Dis 95:582–588
Adhikari TB, Gurung S, Hansen JM, Bonman JM (2012a) Pathogenic and genetic diversity of Xanthomonas translucens pv. undulosa in North Dakota. Phytopathology 102:390–402
Adhikari TB, Gurung S, Hansen JM, Jackson EW, Bonman JM (2012b) Association mapping of quantitative trait loci in spring wheat landraces conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak and spot blotch. Plant Genome 5:1–16
Bauer E, Schmutzer T, Barilar I, Mascher M, Gundlach H, Martis MM, So Twardziok, Hackauf B, Gordillo A, Wilde P, Schmidt M, Korzun V, Mayer KF, Schmid K, Schön CC, Scholz U (2017) Towards a whole-genome sequence for rye (Secale cereale L.). Plant J 89:853–869
Bragard C, Singer E, Alizadeh A, Vauterin L, Maraite H, Swings J (1997) Xanthomonas translucens from small grains: diversity and phytopathological relevance. Phytopathology 87:1111–1117
Charkhabi NF, Shams-bakhsh M, Rahimian H (2015) Reaction of Iranian cereal genotype to multiple strains of Xanthomonas translucens pv. cerealis. J Agric Sci Technol 17:241–248
Charkhabi NF, Booher NJ, Peng Z, Wang L, Rahimian H, Shams-Bakhsh M, Liu Z, Liu S, White FF, Bogdanove AJ (2017) Complete genome sequencing and targeted mutagenesis reveal virulence contributions of Tal2 and Tal4b of Xanthomonas translucens pv. undulosa ICMP11055 in bacterial leaf streak of wheat. Front Microbiol 8:1488. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01488
Cunfer BM, Scolari BL (1982) Xanthomonas campestris pv. translucens on triticale and other small grains. Phytopathology 72:683–686
Duveiller E, van Ginkel M, Thijssen M (1993) Genetic analysis of resistance to bacterial leaf streak caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. undulosa in bread wheat. Euphytica 66:35–43
Duveiller E, Bragard C, Maraite H (1997) Bacterial leaf streak and black chaff caused by Xanthomonas translucens. In: Duveiller E, Fucikovsky L, Rudolph K (eds) The bacterial diseases of wheat: concepts and methods of disease management. CIMMYT, Mexico, pp 25–47
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
El Attari H, Sarrafi A, Alizadeh A, Dechamp-Guillaume G, Barrault G (1996) Genetic analysis of partial resistance to bacterial leaf streak (Xanthomonas campestris pv. cerealis) in wheat. Plant Pathol 45:736–741
Forster RL, Schaad NW (1988) Control of black chaff of wheat with seed treatment and a foundation seed health program. Plant Dis 72:935–938
Gardnier DM, Upadhya NM, Slitter J, Ellis JG, Dodds PN, Kazan K, Manners JM (2014) Genomic analysis of Xanthomonas translucens pathogenic on wheat and barley reveals cross-kingdom gene transfer events and diverse protein delivery systems. PLoS One 9:e84995
Gustafson JP, Rupert EA, Qualset CO (1973) Registration of UC-38 triticale germplasm. Crop Sci 13:586
Gustafson JP, Ma XF, Korzun V, Snape JW (2009) A consensus map of rye integrating mapping data from five mapping populations. Theor Appl Genet 118(4):793–800
Hackauf B, Wehling P (2002) Identification of microsatellite polymorphisms in an expressed portion of the rye genome. Plant Breed 121:17–25
Hackauf B, Wehling P (2003) Development of microsatellite markers in rye: map construction. Plant Breed Seed Sci 48:143–151
Jaenicke S, Bunk B, Wibberg D, Spröer C, Hersemann L, Blom J, Winkler A, Schatschneider S, Albaum SP, Kölliker R, Goesmann A, Pühler A, Overmann J, Vorhölter F (2016) Complete genome sequence of the barley pathogen Xanthomonas translucens pv. translucens DSM 1874T (ATCC 19319T). Genome Announc 4:e01334-16
Joehanes R, Nelson JC (2008) QGene 4.0, an extensible Java QTL-analysis platform. Bioinformatics 24(23):2788–2789
Johnson JW, Cunfer BM, Morey DD (1987) Inheritance of resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. translucens in triticale. Euphytica 36:603–607
Johnson JW, Cunfer BM, Rothrock CS, Bruckner PL, Raymer PL, Roberts JJ (1989) Registration of GA21 and GA22 bacterial leaf streak resistant triticale germplasm line. Crop Sci 29:1585
Kandel YR, Glover KD, Tande CA, Osborne LE (2012) Evaluation of spring wheat germplasm for resistance to bacterial leaf streak caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. translucens. Plant Dis 96:1743–1748
Kandel YR, Glover KD, Osborne LE, Gonzalez-Hernandez JL (2015) Mapping quantitative resistance loci for bacterial leaf streak disease in hard red spring wheat using an identity by descent mapping approach. Euphytica 201:53–65
Kariyawasam GK, Carter AH, Rasmussen JB, Faris JD, Xu SS, Mergoum M, Liu ZH (2016) Genetic relationships between race-nonspecific and race-specific interactions in the wheat–Pyrenophora tritici-repentis pathosystem. Theor Appl Genet 129:897–908
Khlestkina EK, Than MH, Pestsova EG, Röder MS, Malyshev SV, Korzun V, Börner A (2004) Mapping of 99 new microsatellite-derived loci in rye (Secale cereale L.) including 39 expressed sequence tags. Theor Appl Genet 109:725–732
Korzun V, Malyshev S, Voylokov AV, Börner A (2001) A genetic map of rye (Secale cereale L.) combining RFLP, isozyme, protein, microsatellite and gene loci. Theor Appl Genet 102:709–717
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:592–597
Kuleung C, Baenziger PS, Kachman SD, Dweikat I (2006) Evaluating the genetic diversity of triticale with wheat and rye SSR markers. Crop Sci 46:1692–1700
Kumar S, Kumar N, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2003) 1BL.1RS translocation in some indian bread wheat genotypes and strategies for its use in future wheat breeding. Caryologia 56:23–30
Langlois PA, Snelling J, Hamilton JP, Bragard C, Koebnik R, Verdier V, Triplett LR, Blom J, Tisserat NA, Leach JE (2017) Characterization of the Xanthomonas translucens complex using draft genomes, comparative genomics, phylogenetic analysis and diagnostic LAMP assays. Phytopathology 107:519–527
Long YM, Chao WS, Ma GJ, Xu SS, Qi LL (2017) An innovative SNP genotyping method adapting to multiple platforms and throughputs. Theor Appl Genet 130:597–607
Lorieux M (2012) MapDisto: fast and efficient computation of genetic linkage maps. Mol Breeding 30(2):1231–1235
Lu F, Lipka AE, Glaubitz J, Elshire R, Cherney JH, Casler MD, Buckler ES, Costich DE (2013) Switchgrass genomic diversity, ploidy, and evolution: novel insights from a network-based SNP discovery protocol. PLoS Genet 9:e1003215
Matos M, Pérez-Flores V, Camacho MV, Pernaute B, Pinto-Carnide O, Benito C (2007) Detection and mapping of SSRs in rye ESTs from aluminum-stressed roots. Mol Breed 20:103–115
Milus EA, Mirlohi AF (1995) Survival of Xanthomonas campestris pv. translucens between successive wheat crops in Arkansas. Plant Dis 79:263–265
Pallotta MA, Warner P, Fox RL, Kuchel H, Jefferies SJ, Langridge P (2003) Marker assisted wheat breeding in the southern region of Australia. In: Pogna NE (ed) Proceedings of the 10th International Wheat Genetics Symposium, Paestum, Italy, 1-6 September 2003, Istituto Sperimentale per la Cerealicoltura, Rome, Paestum, Italy, pp 789–791
Peng Z, Hu Y, Xie Z, Potnis N, Akhunova A, Jones J, Liu Z, White F, Liu S (2016) Long read and single molecule DNA sequencing simplifies genome assembly and TAL effector gene analysis of Xanthomonas translucens. BMC Genom 17:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2348-9
Pesce C, Bolot S, Cunnac S, Portier P, Fischer-Le Saux M, Jacques MA, Gagnevin L, Arlat M, Noël LD, Carrère S, Bragard C, Koebnik R (2015) High quality draft genome sequence of the Xanthomonas translucens pv. cerealis pathotype strain CFBP 2541. Genome Announc 3:e01574-14
Poland JA, Brown PJ, Sorrells ME, Jannink JL (2012) Development of high-density genetic maps for barley and wheat using a novel two-enzyme genotyping-by-sequencing approach. PLoS One 7:e32253
Qualset CO, Vogt HE, Gustafson JP, Zillinsky FJ, Prato JD, Beatty KD (1985) Registration of Siskiyou triticale. Crop Sci 25:887
Rabinovich SV (1998) Importance of wheat–rye translocations for breeding modern cultivars of Triticum aestivum L. Euphytica 100:323–340
Saal B, Wricke G (1999) Development of simple sequence repeat markers in rye (Secale cereale L.). Genome 42:964–972
Sapkota S, Zhang Q, Mergoum M, Xu SS, Liu ZH (2017) Evaluation of triticale accessions for resistance to wheat bacterial leaf streak caused by Xanthomonas translucens pv. undulosa. Plant Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12768 (in press)
Sears ER (1982) A wheat mutation conditioning an intermediate level of homoeologous chromosome pairing. Can J Genet Cytol 24:715–719
Shane WW, Baumer JS, Teng PS (1987) Crop losses caused by Xanthomonas streak on spring wheat and barley. Plant Dis 71:927–930
Sun H (2016) Development and application of chromosome specific markers of Secale cereale cv. Jingzhouheimai. Master’s thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, China
Tenhola-Roininen T, Kalendar R, Schulman AH, Tanhuanpää P (2011) A double haploid rye linkage map with a QTL affecting α-amylase activity. J Appl Genet 52:299–304
Tillman BL, Harrison SA (1996) Heritability of resistance to bacterial streak in winter wheat. Crop Sci 36:412–418
Tillman BL, Harrison SA, Clark CA, Milus EA, Russin JS (1996) Evaluation of bread wheat germplasm for resistance to bacterial streak. Crop Sci 36:1063–1068
Tillman BL, Kursell WS, Harrison SA, Russin JS (1999) Yield loss caused by bacterial streak in winter wheat. Plant Dis 83:609–614
Vauterin L, Yang P, Hoste B, Pot B, Swings J, Kersters K (1992) Taxonomy of xanthomonads from cereals and grasses based on SDS-PAGE of proteins, fatty acid analysis and DNA hybridization. J Gen Microbiol 138:1467–1477
Vauterin L, Hoste B, Kersters K, Swings J (1995) Reclassification of Xanthomonas. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:472–489
Waldron LR (1929) The relationship of black chaff disease of wheat to certain physical and pathological characters. Science 70:268
Wichmann F, Vorholter FJ, Hersemann L, Widmer L, Bolm J, Niehaus K, Reinhard S, Conradin C, Kolliker R (2013) The noncanonical type III secretion system of Xanthomonas translucens pv. graminis is essential for forage grass infection. Mol Plant Pathol 14:576–588
Yang B, White FF (2004) Diverse members of the AvrBs3/PthA family of type III effectors are major virulence determinants in bacterial blight disease of rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17(11):1192–1200
Zeller FJ, Hsam SLK (1983) Broaden the genetic variability of cultivated wheat by utilizing rye chromatin. In: Proceedings of 6th international wheat genetic symposium. Kyoto, Japan, pp 161–173
Zhong S, Leng Y, Friesen TL, Faris JD, Szabo LJ (2009) Development and characterization of expressed sequence tag-derived microsatellite markers for the wheat stem rust fungus Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. Phytopathology 99:282–289
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. Justin Hestead for technical support, Drs. Xiwen Cai and Tim Friesen for critical review of the manuscript, and Drs. Andreas Börner (Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics and Crop Plant Research, Gatersleben, Germany) and Zengjun Qi (Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China) for providing the sequences of rye 5R SSR primers. This material is based upon work supported, in part, by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), under Hatch project number ND02224, the North Dakota Wheat Commission, and the US National Science Foundation research Grant 2012-1238189 (F.F.W).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this article.
Ethical standards
All experiments complied with the ethical standards of the university.
Additional information
Communicated by Thomas Miedaner.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, A., Jayawardana, M., Fiedler, J. et al. Genetic mapping of a major gene in triticale conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak. Theor Appl Genet 131, 649–658 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-3026-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-3026-x