Abstract
Key message
A first set of 25 NILs carrying ten BPH resistance genes and their pyramids was developed in the background of indica variety IR24 for insect resistance breeding in rice.
Abstract
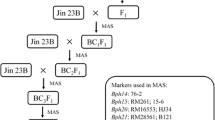
Brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal.) is one of the most destructive insect pests in rice. Development of near-isogenic lines (NILs) is an important strategy for genetic analysis of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance (R) genes and their deployment against diverse BPH populations. A set of 25 NILs with 9 single R genes and 16 multiple R gene combinations consisting of 11 two-gene pyramids and 5 three-gene pyramids in the genetic background of the susceptible indica rice cultivar IR24 was developed through marker-assisted selection. The linked DNA markers for each of the R genes were used for foreground selection and confirming the introgressed regions of the BPH R genes. Modified seed box screening and feeding rate of BPH were used to evaluate the spectrum of resistance. BPH reaction of each of the NILs carrying different single genes was variable at the antibiosis level with the four BPH populations of the Philippines. The NILs with two- to three-pyramided genes showed a stronger level of antibiosis (49.3–99.0%) against BPH populations compared with NILs with a single R gene NILs (42.0–83.5%) and IR24 (10.0%). Background genotyping by high-density SNPs markers revealed that most of the chromosome regions of the NILs (BC3F5) had IR24 genome recovery of 82.0–94.2%. Six major agronomic data of the NILs showed a phenotypically comparable agronomic performance with IR24. These newly developed NILs will be useful as new genetic resources for BPH resistance breeding and are valuable sources of genes in monitoring against the emerging BPH biotypes in different rice-growing countries.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng JA, Zhu ZR (2006) Analysis on the key factors causing the outbreak of brown planthopper in Yangtze area China in 2005. Plant Prot 32:1–4
Cruz PA, Arida A, Heong KL, Horgan FG (2011) Aspects of brown planthopper adaptation to resistant rice varieties with the BPH3 gene. Entomol Exp Appl 141:245–257
Du B, Zhang WL, Liu BF, Hu J, Wei Z, Shi ZY, He RF, Zhu LL, Chen RZ, Han B et al (2009) Identification and characterization of BPH14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:22163–22168
Fujita D, Yoshimura A, Yasui H (2010) Development of near isogenic lines and pyramided lines carrying resistance genes to green rice leafhopper (Nephotettix cincticeps Uhler) with the Taichung 65 genetic background in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci 60:18–27
Hao P, Liu C, Wang Y, Chen R, Tang M, Du B, Zhu L, He G (2008) Herbivore-induced callose deposition on the sieve plates of rice: an important mechanism for host resistance. Plant Physiol 146:1810–1820
He J, Liu Y, Liu Y, Jiang L, Wu H, Kang H, Liu S, Chen L, Liu X, Cheng X, Wan J (2013) High-resolution mapping of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene BPH27(t) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 31:549–557
Hirabayashi H, Angeles ER, Kaji R, Ogawa T, Brar DS, Khush GS (1998) Identification of brown planthopper resistance gene derived from O. officinalis using molecular markers in rice. Breed Sci 48(Suppl):82
Hirabayashi H, Ideta O, Sato H, Takeuchi Y, Ando I, Nemoto H, Imbe T, Brar DS, Ogawa T (2004) Identification of a resistance gene to brown planthopper derived from Oryza minuta in rice (in Japanese). Breed Res 6(suppl 1):285
Hittalmani S, Parco A, Mew TV, Zeigler RS, Huang N (2000) Fine mapping and DNA marker-assisted pyramiding of the three major genes for blast resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 100:1121–1128
Horgan FG, Naik BS, Iswanto EH, Almazan MLP, Ramal AF, Bernal CC (2016) Responses by the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, to conspecific density on resistant and susceptible rice varieties. Entomol Exp Appl 158:284–294
Hu J, Li X, Wu C, Yang C, Hua H, Gao G, Xiao J, He Y (2012) Pyramiding and evaluation of the brown planthopper resistance genes BPH14 and BPH15 in hybrid rice. Mol Breed 29:61–69
Hu J, Xiao C, Cheng M, Gao G, Zhang Q, He Y (2015) Fine mapping and pyramiding of brown planthopper resistance genes QBPH3 and QBPH4 in an introgression line from wild rice O. officinalis. Mol Breed 35:3. doi:10.1007/s11032-015-0228-2
Hu J, Xiao C, He C (2016) Recent progress on the genetics and molecular breeding of brown planthopper resistance in rice. Rice 9:30. doi:10.1186/s12284-016-0099-0
Huang N, Angeles ER, Domingo J, Magpantay G, Singh G, Zhang G, Kumaravadivel N, Bennett J, Khush GS (1997) Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice: marker assisted selection using RFLP and PCR. Theor Appl Genet 95:313–320
IRRI (2014) PBTools, version 1.4. Biometrics and Breeding Informatics, PBGB Division, International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños
Ishii T, Brar DS, Multani DS, Khush GS (1994) Molecular tagging of genes for brown planthopper resistance and earliness introgressed from Oryza australiensis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Genome 37:217–221
Jairin J, Phengrat K, Teangdeerith S, Vanavichit A, Toojinda T (2007a) Mapping of a broad-spectrum brown planthopper resistance gene, BPH3, on rice chromosome 6. Mol Breed 19:35–44
Jairin J, Teangdeerith S, Leelagud P, Phengrat K, Vanavichit A, Toojinda T (2007b) Physical mapping of BPH3, a brown planthopper resistance locus in rice. Mj Int J Sci Tech 01:166–177
Jairin J, Sansen K, Wongboon W, Kothcharerk J (2010) Detection of a brown planthopper resistance gene BPH4 at the same chromosomal position of BPH3 using two different genetic backgrounds of rice. Breed Sci 60:71–75
Jena KK, Kim SM (2010) Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics. Rice 3:161–171
Jena KK, Jeung JU, Lee JH, Choi HC, Brar DS (2006) High resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene, BPH18(t), and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:288–297
Ji H, Kim SR, Kim YH, Suh JP, Park HM, Sreenivasulu N, Misra G, Kim SM, Hechanova S, Kim H et al (2016) Map-based cloning and characterization of the BPH18 gene from wild rice conferring resistance to brown planthopper (BPH) insect pest. Sci Rep 6:34376. doi:10.1038/srep34376
Khush GS (2005) What it will take to feed 5.0 billion rice consumers in 2030. Plant Mol Biol 59(1):1–6
Liu YQ, Wu H, Chen H, Liu YL, He J, Kang HY, Sun ZG, Pan G et al (2015) A gene cluster encoding lectin receptor kinases confers broad-spectrum and durable insect resistance in rice. Nat Biotechnol 33(3):301–305
Liu Y, Chen L, Liu Y, Dai H, He J, Kang H, Pan G, Huang J, Qiu Z, Wang Q, Hu J, Liu L, Chen Y, Cheng X, Jiang L, Wan J (2016) Marker assisted pyramiding of two brown planthopper resistance genes, BPH3 and BPH27(t), into elite rice cultivars. Rice 9:27
McCouch SR (2008) Gene nomenclature system for rice. Rice 1:72–84
Murata K, Fujiwara M, Kaneda C, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C (1998) RFLP mapping of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal) resistance gene BPH2 of indica rice introgressed into a japonica breeding line ‘Norin-PL4’. Genes Genet Syst 7:359–364
Myint KKM, Matsumura M, Takagi M, Yasui H (2009) Demographic parameters of long-term laboratory strains of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stal (Homoptera: Delphacidae) on resistance genes, BPH20(t) and BPH21(t) in rice. J Fac Agric Kyushu Univ 54:159–164
Myint KKM, Fujita D, Matsumura M, Sonada T, Yoshimura A, Yasui H (2012) Mapping and pyramiding of two major genes for resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal) in the rice cultivar ADR52. Theor Appl Genet 124:495–504
Pathak PK, Heinrichs EA (1982) Selection of biotype populations 2 and 3 of Nilaparvata lugens by exposure to resistant rice varieties. Environ Entomol 11:85–90
Qiu YF, Guo JP, Jing SL, Zhu LL, He GC (2010) High-resolution mapping of the brown planthopper resistance gene BPH6 in rice and characterizing its resistance in the 9311 and Nipponbare near isogenic backgrounds. Theor Appl Genet 121:1601–1611
Qiu Y, Guo J, Jing S, Zhu L, He G (2012) Development and characterization of japonica rice lines carrying the brown planthopper-resistance genes BPH12 and BPH6. Theor Appl Genet 124:485–494
Rahman ML, Jiang WZ, Chu SH, Qiao YL, Ham TH, Woo MO, Lee J, Khanam MS, Chin JH, Jeung JU et al (2009) High-resolution mapping of two rice brown planthopper resistance genes, BPH20(t) and BPH21(t), originating from Oryza minuta. Theor Appl Genet 119(7):1237–1246
Ren J, Gao F, Wu X, Lu X, Zheng L, Lv J, Su X, Luo H, Ren G (2016) BPH32, a novel gene encoding an unknown SCR domain-containing protein, confer resistance against the brown planthopper in rice. Sci Rep 6:37645. doi:10.1038/srep37645
Sanchez AC, Brar DS, Huang N, Li Z, Khush GS (2000) Sequenced tagged site marker-assisted selection for three bacterial blight resistance genes in rice. Crop Sci 40:792–797
Sarao PS, Bentur JS (2016) Antixenosis and tolerance of rice genotypes against brown planthopper. Rice Sci 23(2):96–103
Sharma PN, Ketipearachchi Y, Murata K et al (2002) RFLP/AFLP mapping of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene BPH1 in rice. Euphytica 129:109–117
Sharma PN, Torii A, Takumi S et al (2004) Marker-assisted pyramiding of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance genes BPH1 and BPH2 on rice chromosome 12. Hereditas 140:61–69
Su CC, Zhai HQ, Wang CM et al (2006) SSR mapping of brown planthopper resistance gene BPH9 in Kaharamana, an indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Genet Sin 33:262–268
Suh JP, Yang SJ, Jeung JU, Pamplona A, Kim JJ, Lee JH, Hong HC, Yang CI, Kim YG, Jena KK (2011) Development of elite breeding lines conferring BPH18 gene-derived resistance to brown planthopper (BPH) by marker-assisted selection and genome-wide background analysis in japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Field Crops Res 120:215–222
Suh JP, Jeung JU, Noh TH et al (2013) Development of breeding lines with three pyramided resistance genes that confer broad-spectrum bacterial blight resistance and their molecular analysis in rice. Rice 6:5
Sun LH, Su CC, Wang CM, Zai HQ, Wan JM (2005) Mapping of a major resistance gene to brown planthopper in the rice cultivar Rathu Heenati. Breed Sci 55:391–396
Tamura Y, Hattori M, Yoshioka H, Yoshioka M, Takahashi A, Wu J, Sentoku N, Yasui H (2014) Map-based cloning and characterization of a brown planthopper resistance gene BPH26 from Oryza sativa L. ssp. Indica cultivar ADR52. Sci Rep 4:5872. doi:10.1038/srep05872
Wang Y, Cao LM, Zhang YX et al (2015) Map-based cloning and characterization of BPH29, a B3 domain-containing recessive gene conferring brown planthopper resistance in rice. J Exp Bot 66:6035–6045
Wolfe D, Dudek S, Ritchie MD, Pendergrass SA (2013) Visualizing genomic information across chromosomes with Phenogram. Biodata Min 6:18
Xiao C, Hu J, Ao YT, Cheng MX, Gao GJ, Zhang QL, He GC, He YQ (2016) Development and evaluation of near-isogenic lines for brown planthopper resistance in rice cv. 9311. Sci Rep 6:38159. doi:10.1038/srep38159
Xue J, Zhou X, Zhang CX, Yu L, Fan HW, Wang Z, Xu HJ, Xi Y et al (2014) Genomes of the rice pest brownplanthopper and its endosymbionts reveal complex complementary contributions for host adaptation. Genome Biol 15:521
Yang HY, Ren X, Weng QM, Zhu LL, He GC (2002) Molecular mapping and genetic analysis of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal.) resistance gene. Hereditas 136:39–43
Yang HY, You AQ, Yang ZF, Zhang FT, He RF, Zhu LL, He GC (2004) High-resolution genetic mapping at the BPH15 locus for brown planthopper resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:182–191
Yanoria M, Koide Y, Fukuta Y, Imbe T, Tsunematsu H, Kato H, Ebron L, Nguyen T, Kobayashi N (2011) A set of near-isogenic lines of Indica-type rice variety CO-39 as differential varieties for blast resistance. Mol Breed 27(3):357–373
Yara A, Phi CN, Matsumura M, Yoshimura A, Yasui H (2010) Development of near-isogenic lines for BPH25(t) and BPH26(t), which confer resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål.) in indica rice ‘ADR52’. Breed Sci 60:639–647
Zhang G, Angeles ER, Abenes MLP, Khush GS, Huang N (1996) RAPD and RFLP mapping of the bacterial blight resistance gene xa13 in rice. Theor Appl Genet 93(1):65–70
Zhao Y, Huang J, Wang Z, Jing S, Wang Y, Ouyang Y, Cai B, Xin XF et al (2016) Allelic diversity in an NLR gene BPH9 enables rice to combat planthopper variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(45):12850–12855
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Mr. Rodante Abas for assistance in BPH bioassay experiments in the glasshouse and Mr. Allan Trinidad for providing excellent technical assistance during this study. We also thank all members of Novel Gene Resources team of the PB Division, IRRI, for their support during this study. We are grateful to the Global Rice Science Partnership (GRiSP) program of IRRI for financial support (Grant no.: DRPC 2011-134) to carry out this study. We are thankful to IRRI Communication team for carefully editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest in this study.
Ethical standards
This study complied with the ethical standards of the Philippines where this research work was conducted.
Additional information
Communicated by Dr. Lizhong Xiong.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jena, K.K., Hechanova, S.L., Verdeprado, H. et al. Development of 25 near-isogenic lines (NILs) with ten BPH resistance genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.): production, resistance spectrum, and molecular analysis. Theor Appl Genet 130, 2345–2360 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2963-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2963-8