Abstract
Key message
Two QTLs were identified to control panicle length in rice backcross lines, and one QTL qPL6 was finely mapped with potential in high yield breeding.
Abstract
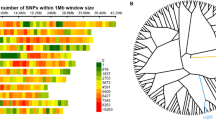
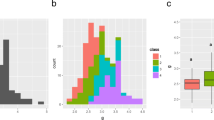
Panicle length (PL) is the key determinant of panicle architecture in rice, and strongly affects yield components, such as grain number per panicle. However, this trait has not been well studied genetically nor its contribution to yield improvement. In this study, we performed quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis for PL in four backcross populations derived from the cross of Nipponbare (japonica) and WS3 (indica), a new plant type (NPT) variety. Two QTLs were identified on chromosome 6 and 8, designated as qPL6 and qPL8, respectively. Near-isogenic lines (NILs) were developed to evaluate their contribution to important agronomic traits. We found that qPL6 and qPL8 had additive effects on PL trait. For the qPL6 locus, the WS3 allele also increased panicle primary and secondary branches and grain number per panicle. Moreover, this allele conferred wide and strong culms, a character of lodging resistance. By analyzing key recombinants in two steps, the qPL6 locus was finely mapped to a 25-kb interval, and 3 candidate genes were identified. According to the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within candidate genes, 5 dCaps markers were designed and used to get haplotypes of 96 modern Chinese varieties, which proved that qPL6 locus is differentiated between indica and temperate japonica varieties. Taken together, the superior qPL6 allele can be applied in rice breeding programs for large sink size, particularly for japonica varieties that originally lack the allele.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho YG, Kang HJ, Lee JS, Lee YT, Lim SJ, Gauch H, Eun MY, McCouch SR (2007) Identification of quantitative trait loci in rice for yield, yield components, and agronomic traits across years and locations. Crop Sci 47:2403–2417
Chung CL, Poland J, Kump K, Benson J, Longfellow J, Walsh E, Balint-Kurti P, Nelson R (2011) Targeted discovery of quantitative trait loci for resistance to northern leaf blight and other diseases of maize. Theor Appl Genet 123:307–326
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Craig KL, Tyers M (1999) The F-box: a new motif for ubiquitin dependent proteolysis in cell cycle regulation and signal transduction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 72:299–328
Ding XP, Li XK, Xiong LH (2011) Evaluation of near-isogenic lines for drought resistance QTL and fine mapping of a locus affecting flag leaf width, spikelet number, and root volume in rice. Theor Appl Genet 123:815–826
Hittalmani S, Shashidhar HE, Bagali PG, Huang N, Sidhu JS, Singh VP, Khush GS (2002) Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci for plant growth, yield and yield related traits across three diverse locations in a doubled haploid rice population. Euphytica 125:207–214
Hittalmani S, Huang N, Courtois B, Venuprasad R, Shashidhar HE, Zhuang JY, Zheng KL, Liu GF, Wang GC, Sidhu JS, Srivantaneeyakul S, Singh VP, Bagali PG, Prasanna HC, McLaren G, Khush GS (2003) Identification of QTL for growth- and grain yield-related traits in rice across nine locations of Asia. Theor Appl Genet 107:679–690
Huang X, Qian Q, Liu Z, Sun H, He S, Luo D, Xia G, Chu C, Li J, Fu X (2009) Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice. Nat Genet 41:494–497
Huang X, Kurata N, Wei X, Wang ZX, Wang A, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Liu K, Lu H, Li W, Guo Y, Lu Y, Zhou C, Fan D, Weng Q, Zhu C, Huang T, Zhang L, Wang Y, Feng L, Furuumi H, Kubo T, Miyabayashi T, Yuan X, Xu Q, Dong G, Zhan Q, Li C, Fujiyama A, Toyoda A, Lu T, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li J, Han B (2012) A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice. Nature 490:497–501
Ikeda K, Sunohara H, Nagato Y (2004) Developmental course of inflorescence and spikelet in rice. Breed Sci 54:147–156
Jurado S, Diaz-Trivino S, Abraham Z, Manzano C, Gutierrez C, del Pozo C (2008) SKP2A, an F-box protein that regulates cell division, is degraded via the ubiquitin pathway. Plant J 53:828–841
Kashiwagi T, Togawa E, Hirotsu N, Ishimaru K (2008) Improvement of lodging resistance with QTLs for stem diameter in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 117:749–757
Khush GS (1997) Origin, dispersal, cultivation and variation of rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:25–34
Kobayashi S, Fukuta Y, Sato T, Osaki M, Khush GS (2003) Molecular marker dissection of rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant architecture under temperate and tropical climates. Theor Appl Genet 107:1350–1356
Kovach MJ, Sweeney MT, McCouch SR (2007) New insights into the history of rice domestication. Trends Genet 23:578–587
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newberg LA (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lee SJ, Oh CS, Suh JP, McCouch SR, Ahn SN (2005) Identification of QTLs for domestication-related and agronomic traits in an Oryza sativa x O-rufipogon BC1F7 population. Plant Breed 124:209–219
Li SB, Qian Q, Fu ZM, Zeng DL, Meng XB, Kyozuka J, Maekawa M, Zhu XD, Zhang J, Li JY, Wang YH (2009) Short panicle1 encodes a putative PTR family transporter and determines rice panicle size. Plant J 58:592–605
Li XB, Yan WG, Agrama H, Jia LM, Shen XH, Jackson A, Moldenhauer K, Yeater K, McClung A, Wu DX (2011) Mapping QTLs for improving grain yield using the USDA rice mini-core collection. Planta 234:347–361
Liu TM, Li LZ, Zhang YS, Xu CG, Li XH, Xing YZ (2011a) Comparison of quantitative trait loci for rice yield, panicle length and spikelet density across three connected populations. J Genet 90:377–382
Liu Y, Zhu X, Zhang SH, Bernardo M, Edwards J, Galbraith DW, Leach J, Zhang GS, Liu B, Leung H (2011b) Dissecting quantitative resistance against blast disease using heterogeneous inbred family lines in rice. Theor Appl Genet 122:341–353
Loudet O, Gaudon V, Trubuil A, Daniel-Vedele F (2005) Quantitative trait loci controlling root growth and architecture in Arabidopsis thaliana confirmed by heterogeneous inbred family. Theor Appl Genet 110:742–753
Marathi B, Guleria S, Mohapatra T, Parsad R, Mariappan N, Kurungara VK, Atwal SS, Prabhu KV, Singh NK, Singh AK (2012) QTL analysis of novel genomic regions associated with yield and yield related traits in new plant type based recombinant inbred lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 12:137
Mei HW, Li ZK, Shu QY, Guo LB, Wang YP, Yu XQ, Ying C, Luo L (2005) Gene actions of QTLs affecting several agronomic traits resolved in a recombinant inbred rice population and two backcross populations. Theor Appl Genet 110:649–659
Shen YJ, Jiang H, Jin JP, Zhang ZB, Xi B, He YY, Wang G, Wang C, Qian L, Li X, Yu QB, Liu HJ, Chen DH, Gao JH, Huang H, Shi TL, Yang ZN (2004) Development of genome-wide DNA polymorphism database for map-based cloning of rice genes. Plant Physiol 135:1198–1205
Thomson MJ, Tai TH, McClung AM, Lai XH, Hinga ME, Lobos KB, Xu Y, Martinez CP, McCouch SR (2003) Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield, yield components and morphological traits in an advanced backcross population between Oryza rufipogon and the Oryza sativa cultivar Jefferson. Theor Appl Genet 107:479–493
Tian F, Zhu ZF, Zhang BS, Tan LB, Fu YC, Wang XK, Sun CQ (2006) Fine mapping of a quantitative trait locus for grain number per panicle from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon griff.). Theor Appl Genet 113:619–629
Tuinstra MR, Ejeta G, Goldsbrough PB (1997) Heterogeneous inbred family (HIF) analysis: a method for developing near-isogenic lines that differ at quantitative trait loci. Theor Appl Genet 95:1005–1011
Wang SC, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm. Accessed 01 Aug 2012
Xiao JH, Li JM, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, Yuan LP, Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1998) Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci alleles from a wild rice relative, Oryza rufipogon. Genetics 150:899–909
Xie XB, Jin FX, Song MH, Suh JP, Hwang HG, Kim YG, McCouch SR, Ahn SN (2008) Fine mapping of a yield-enhancing QTL cluster associated with transgressive variation in an Oryza sativa x O-rufipogon cross. Theor Appl Genet 116:613–622
Xing Y, Zhang Q (2010) Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:421–442
Xing Z, Tan F, Hua P, Sun L, Xu G, Zhang Q (2002) Characterization of the main effects, epistatic effects and their environmental interactions of QTLs on the genetic basis of yield traits in rice. Theor Appl Genet 105:248–257
Xu YH, Zhu YY, Zhou HC, Li Q, Sun ZX, Liu YG, Lin HX, He ZH (2004) Identification of a 98 kb DNA segment containing the rice Eui gene controlling uppermost internode elongation, and construction of a TAC transgene sublibrary. Mol Genet Genom 272:149–155
Yadav SK, Pandey P, Kumar B, Suresh BG (2011) Genetic architecture, inter-relationship and selection criteria for yield improvement in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Pak J Biol Sci: PJBS 14:540–545
Yamamoto T, Lin HX, Sasaki T, Yano M (2000) Identification of heading date quantitative trait locus Hd6 and characterization of its epistatic interactions with Hd2 in rice using advanced backcross progeny. Genetics 154:885–891
Zhang YS, Luo LJ, Liu TM, Xu CG, Xing YZ (2009) Four rice QTL controlling number of spikelets per panicle expressed the characteristics of single Mendelian gene in near isogenic backgrounds. Theor Appl Genet 118:1035–1044
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 91117018) and from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2012AA10A302).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Wissuwa.
L. Zhang, J. Wang and J. Wang contributed equally to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Wang, J., Wang, J. et al. Quantitative trait locus analysis and fine mapping of the qPL6 locus for panicle length in rice. Theor Appl Genet 128, 1151–1161 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2496-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2496-y