Abstract
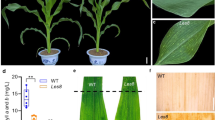
The Ragged leaves1 (Rg1) maize mutant frequently develops lesions on leaves, leaf sheaths, and ear bracts. Lesion formation is independent of biotic stress. High-level accumulation of H2O2 revealed by staining Rg1 leaves, with 3′,3′-diaminobenzidine and trypan blue, suggested that lesion formation appeared to be due to cell death. Rg1 was initially mapped to an interval around 70.5 Mb in bin 3.04 on the short arm of chromosome 3. Utilizing 15 newly developed markers, Rg1 was delimitated to an interval around 17 kb using 16,356 individuals of a BC1 segregating population. There was only one gene, rp3, predicted in this region according to the B73 genome. Analysis of transcriptome data revealed that 441 genes significantly up-regulated in Rg1 leaves were functionally over-represented. Among those genes, several were involved in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Our results suggested that lesions of Rg1 maize arose probably due to an aberrant rust resistance allele of Rp3, which elicited the accumulation of ROS independent of biotic stress.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399
Bindschedler LV, Dewdney J, Blee KA, Stone JM, Asai T, Plotnikov J, Denoux C, Hayes T, Gerrish C, Davies DR (2006) Peroxidase-dependent apoplastic oxidative burst in Arabidopsis required for pathogen resistance. Plant J 47:851–863
Bongard-Pierce DK, Evans M, Poethig RS (1996) Heteroblastic features of leaf anatomy in maize and their genetic regulation. Int J Plant Sci 157:331–340
Bowling SA, Clarke JD, Liu Y, Klessig DF, Dong X (1997) Thecpr5 mutant of Arabidopsis expresses both NPR1-dependent and NPR1-independent resistance. Plant Cell 9:1573–1584
Brink RA, Senn PH (1931) Heritable characters in maize. XL. Ragged, a dominant character, linked with A1Ts4 and D1. J Hered 22:155–161
Büschges R, Hollricher K, Panstruga R, Simons G, Wolter M, Frijters A, van Daelen R, van der Lee T, Diergaarde P, Groenendijk J (1997) The barley Mlo gene: a novel control element of plant pathogen resistance. Cell 88:695–705
Chintamanani S, Hulbert SH, Johal GS, Balint-Kurti PJ (2010) Identification of a maize locus that modulates the hypersensitive defense response, using mutant-assisted gene identification and characterization. Genetics 184:813–825
Daudi A, Cheng Z, O’Brien JA, Mammarella N, Khan S, Ausubel FM, Bolwell GP (2012) The apoplastic oxidative burst peroxidase in Arabidopsis is a major component of pattern-triggered immunity. Plant Cell 24:275–287
Dietrich RA, Delaney TP, Uknes SJ, Ward ER, Ryals JA, Dangl JL (1994) Arabidopsis mutants simulating disease resistance response. Cell 77:565–577
Dixon RA, Paiva NL (1995) Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7:1085–1097
Farkhari M, Lu Y, Shah T, Zhang S, Naghavi MR, Rong T, Xu Y (2011) Recombination frequency variation in maize as revealed by genomewide single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Plant Breeding 130:533–539
Feng YJ, Wang JW, Luo SM (2007) Effects of exogenous jasmonic acid on concentrations of direct-defense chemicals and expression of related genes in bt (Bacillus thuringiensis) corn (Zea mays). Agric Sci in China 6:1456–1462
Feuillet C, Travella S, Stein N, Albar L, Nublat A, Keller B (2003) Map-based isolation of the leaf rust disease resistance gene Lr10 from the hexaploid wheat (Triticumaestivum L.) genome. Proc NatI Acad Sci USA 100:15253–15258
Foreman J, Demidchik V, Bothwell JHF, Mylona P, Miedema H, Torres MA, Linstead P, Costa S, Brownlee C, Jones JDG (2003) Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase regulate plant cell growth. Nature 422:442–446
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Noutoshi Y, Takahashi F, Narusaka Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Crosstalk between abiotic and biotic stress responses: a current view from the points of convergence in the stress signaling networks. CurrOpin Plant Biol 9:436–442
Gray J, Close PS, Briggs SP, Johal GS (1997) A novel suppressor of cell death in plants encoded by the Lls1 gene of maize. Cell 89:25–31
Greenberg JT, Ausubel FM (1993) Arabidopsis mutants compromised for the control of cellular damage during pathogenesis and aging. Plant J 4:327–341
Greenberg JT, Guo A, Klessig DF, Ausubel FM (1994) Programmed cell death in plants: a pathogen-triggered response activated coordinately with multiple defense functions. Cell 77:551–563
Heldt H-W (1997) Plant Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Oxford University Press, New York
Hoisington DA, Neuffer MG, Walbot V (1982) Disease lesion mimics in maize I. effect of genetic background, temperature, developmental age, and wounding on necrotic spot formation with Les1. DevBiol 93:381–388
Hu G, Richter TE, Hulbert SH, Pryor T (1996) Disease lesion mimicry caused by mutations in the rust resistance gene rp1. Plant Cell 8:1367–1376
Hu G, Yalpani N, Briggs SP, Johal GS (1998) A porphyrin pathway impairment is responsible for the phenotype of a dominant disease lesion mimic mutant of maize. Plant Cell 10:1095–1106
Johal GS, Hulbert SH, Briggs SP (1995) Disease lesion mimics of maize: a model for cell death in plants. BioEssays 17:685–692
Kawano T (2003) Roles of the reactive oxygen species-generating peroxidase reactions in plant defense and growth induction. Plant Cell Rep 21:829–837
Kim JY, Park SC, Hwang I, Cheong H, Nah JW, Hahm KS, Park Y (2009) Protease inhibitors from plants with antimicrobial activity. Int J MolSci 10:2860–2872
Kombrink E, Schröder M, Hahlbrock K (1988) Several “pathogenesis-related” proteins in potato are1, 3-β-glucanases and chitinases. Proc NatI Acad Sci USA 85:782–786
Lanubile A, Bernardi J, Marocco A, Logrieco A, Paciolla C (2011) Differential activation of defense genes and enzymes in maize genotypes with contrasting levels of resistance to Fusariumverticillioides. EnvironExp Bot 78:39–46
Levine A, Tenhaken R, Dixon R, Lamb C (1994) H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Cell 79:583–593
Li T, Bai G (2009) Lesion mimic associates with adult plant resistance to leaf rust infection in wheat. Theoret Appl Genet 119:13–21
Li Q, Wan JM (2005) SSRHunter: development of a local searching software for SSR sites. Hereditas 27:808–810
Li AL, Wang ML, Zhou RH, Kong XY, Huo NX, Wang WS, Jia JZ (2005) Comparative analysis of early H2O2 accumulation in compatible and incompatible wheat powdery mildew interactions. Plant Pathol 54:308–316
Lorrain S, Vailleau F, Balagué C, Roby D (2003) Lesion mimic mutants: keys for deciphering cell death and defense pathways in plants? Trends Plant Sci 8:263–271
Mericle LW (1950) The developmental genetics of the Rg mutant in maize. Am J Bot 37:100–116
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498
Molina A, Segura A, Garcia-Olmedo F (1993) Lipid transfer proteins (nsLTPs) from barley and maize leaves are potent inhibitors of bacterial and fungal plant pathogens. FebsLett 316:119–122
Mori M, Tomita C, Sugimoto K, Hasegawa M, Hayashi N, Dubouzet JG, Ochiai H, Sekimoto H, Hirochika H, Kikuchi S (2007) Isolation and molecular characterization of a Spotted leaf 18 mutant by modified activation-tagging in rice. Plant Mol Biol 63:847–860
Naoumkina MA, Zhao Q, Gallego-Giraldo L, Dai X, Zhao PX, Dixon RA (2010) Genome-wide analysis of phenylpropanoid defence pathways. Molecular plant pathology 11:829–846
Qiao Y, Jiang W, Lee JH, Park BS, Choi MS, Piao R, Woo MO, Roh JH, Han L, Paek NC (2010) SPL28 encodes a clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1, medium subunit μ1 (AP1M1) and is responsible for spotted leaf and early senescence in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 185:258–274
Ramos-Onsins SE, Puerma E, Balañá-Alcaide D, Salguero D, Aguadé M (2008) Multilocus analysis of variation using a large empirical data set: phenylpropanoid pathway genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Ecol 17(5):1211–1223
Rohrmeier T, Lehle L (1993) WIP1, a wound-inducible gene from maize with homology to Bowman–Birk proteinase inhibitors. Plant Mol Biol 22:783–792
Rostoks N, Schmierer D, Mudie S, Drader T, Brueggeman R, Caldwell DG, Waugh R, Kleinhofs A (2006) Barley necrotic locus nec1 encodes the cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 4 homologous to the Arabidopsis HLM1. Mol Genet Genomics 275:159–168
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. ProcNatIAcadSci 81:8014–8018
Sandhu SS, Mazzafera P, Azini LE, Bastos CR, Colombo CA (2007) Lipoxygenase activity in Brazilian rice cultivars with variable resistance to leaf blast disease. Bragantia 66:27–30
Sanz-Alferez S, Richter TE, Hulbert SH, Bennetzen JL (1995) The Rp3 disease resistance gene of maize: mapping and characterization of introgressed alleles. Theoret Appl Genet 91:25–32
Schweizer P, Buchala A, Silverman P, Seskar M, Raskin I, Metraux JP (1997) Jasmonate-inducible genes are activated in rice by pathogen attack without a concomitant increase in endogenous jasmonic acid levels. Plant Physiol 114:79–88
Sebela M, Radová A, Angelini R, Tavladoraki P, Frébort I, Peè P (2001) FAD-containing polyamine oxidases: a timely challenge for researchers in biochemistry and physiology of plants. Plant Sci 160:197–207
Seevers PM, Daly JM, Catedral FF (1971) The role of peroxidase isozymes in resistance to wheat stem rust disease. Plant Physiol 48:353–360
Sels J, Mathys J, De Coninck B, Cammue B, De Bolle MFC (2008) Plant pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins: a focus on PR peptides. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:941–950
Shirano Y (2002) A gain-of-function mutation in an Arabidopsis toll Interleukin1 receptor-nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat type R gene triggers defense responses and results in enhanced disease resistance. Plant Cell 14:3149–3162
Shrestha CL, Ona I, Muthukrishnan S, Mew TW (2008) Chitinase levels in rice cultivars correlate with resistance to the sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctoniasolani. Eur J Plant Pathol 120:69–77
Tang J, Zhu X, Wang Y, Liu L, Xu B, Li F, Fang J, Chu C (2011) Semi-dominant mutations in the CC-NB-LRR-type R gene, NLS1, lead to constitutive activation of defense responses in rice. Plant J 66:996–1007
Thiel T, Kota R, Grosse I, Stein N, Graner A (2004) SNP2CAPS: a SNP and INDEL analysis tool for CAPS marker development. Nucleic Acids Res 32:e5
Torres MA, Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006) Reactive oxygen species signaling in response to pathogens. Plant Physiol 141:373–378
Van Der Luit AH, Piatti T, DoornA Van, Musgrave A, Felix G, Boller T, Munnik T (2000) Elicitation of suspension-cultured tomato cells triggers the formation of phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol pyrophosphate. Plant Physiol 123:1507–1516
Webb CA, Richter TE, Collins NC, Nicolas M, Trick HN, Pryor T, Hulbert SH (2002) Genetic and molecular characterization of the maize rp3 rust resistance locus. Genetics 162:381–394
Wilkinson DR, Hooker AL (1968) Genetics of reaction to Pucciniasorghi in ten corn inbred lines from Africa and Europe. Phytopathology 58:605–608
Wolter M, Hollricher K, Salamini F, Schulze-Lefert P (1993) The mlo resistance alleles to powdery mildew infection in barley trigger a developmentally controlled defence mimic phenotype. Mol Gen Genet 239:122–128
Wu C, Bordeos A, Madamba MRS, Baraoidan M, Ramos M, Wang G, Leach JE, Leung H (2008) Rice lesion mimic mutants with enhanced resistance to diseases. Mol Genet Genomics 279:605–619
Xu F, Fan C, He Y (2007) Chitinases in Oryza sativa ssp.japonica and Arabidopsis thaliana. J Genet Genomics 34:138–150
Yamanouchi U, Yano M, Lin H, Ashikari M, Yamada K (2002) A rice spotted leaf gene, Spl7, encodes a heat stress transcription factor protein. Proc NatI Acad Sci USA 99:7530–7535
Yao Q, Zhou R, Fu T, Wu W, Zhu Z, Li A, Jia J (2009) Characterization and mapping of complementary lesion-mimic genes lm1 and lm2 in common wheat. Theoret Appl Genet 119:1005–1012
Yin Z, Chen J, Zeng L, Goh M, Leung H, Khush GS, Wang GL (2000) Characterizing rice lesion mimic mutants and identifying a mutant with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:869–876
Yoda H, Yamaguchi Y, Sano H (2003) Induction of hypersensitive cell death by hydrogen peroxide produced through polyamine degradation in tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 132:1973–1981
Zeng LR, Qu S, Bordeos A, Yang C, Baraoidan M, Yan H, Xie Q, Nahm BH, Leung H, Wang GL (2004) Spotted leaf11, a negative regulator of plant cell death and defense, encodes a U-box/armadillo repeat protein endowed with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Plant Cell 16:2795–2808
Zhang Y, Goritschnig S, Dong X, Li X (2003) A gain-of-function mutation in a plant disease resistance gene leads to constitutive activation of downstream signal transduction pathways in suppressor of npr1-1, constitutive 1. Plant Cell 15:2636–2646
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2009CB11840).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Luebberstedt.
Haiying Guan and Chaoxian Liu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
###Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, H., Liu, C., Zhao, Y. et al. Characterization, fine mapping and expression profiling of Ragged leaves1 in maize. Theor Appl Genet 125, 1125–1135 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1899-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1899-2