Abstract
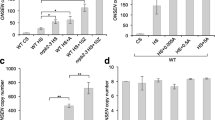
Tos17 is a copia-like, cryptic retrotransposon of rice, but can be activated by tissue culture. To study possible epigenetic mechanism controlling activity of Tos17, we subjected three rice lines (the parental line cv. Matsumae and two introgression lines, RZ2 and RZ35) that harbor different copies of the element to tissue culture. For each line, we investigated transcription and transposition of Tos17 in seed plants, calli and regenerated plants, cytosine-methylation status at CG and CNG positions within Tos17, effect of 5-azacytidine on methylation status and activity of Tos17, and cytosine-methylation states in genomic regions flanking original and some newly transposed copies of Tos17 in calli and regenerated plants. We found that only in introgression line RZ35 wasTos17 transcriptionally activated and temporarily mobilized by tissue culture, which was followed by repression before or upon plant regeneration. The activity and inactivity of Tos17 in calli and regenerated plants of RZ35 are accompanied by hypo- and hyper-CG methylation and hemi- and full CNG methylation, respectively, within the element, whereas immobilization of the element in the other two lines is concomitant with near-constant, full hypermethylation. Treatment with 5-azacytidine induced both CG and CNG partial hypomethylation of Tos17 in two lines (Matsumae and RZ35), which, however, was not accompanied by activation of Tos17 in any line. Heritable alteration in cytosine-methylation patterns occurred in three of seven genomic regions flanking Tos17 in calli and regenerated plants of RZ35, but in none of the five regions flanking dormant Tos17 in the other two lines.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amedeo O, Habu Y, Afsar K, Scheid, OM, Paszkowski J (2000) Disruption of the plant gene MOM releases transcriptional silencing of methylated genes. Nature 405:203–206
Banks JA, Masson P, Fedoroff N (1988) Molecular mechanisms in the developmental regulation of the maize Suppressor-mutator transposable element. Genes Dev 2:1364–1380
Barkan R, Martienssen A (1991) Inactivation of maize transposon Mu suppresses a mutant phenotype by activating an outward-reading promoter near the end of Mu1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3502–3506
Bennetzen JL (1996) The contributions of retroelements to plant genome organization, function and evolution. Trends Microbiol 4:347–353
Bennetzen JL (2000) Transposable element contributions to plant gene and genome evolution. Plant Mol Biol 42:251–269
Chandler VL, Walbot V (1986) DNA modification of a maize transposable element correlates with loss of activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:1767–1771
Colot V, Rossignol JL (1999) Eukaryotic DNA methylation as an evolutionary device. BioEssays 21:402–411
Cui H, Fedoroff NV (2002) Inducible DNA demethylation mediated by the maize Suppressor-mutator transposon-encoded TnpA protein. Plant Cell 14:2883–2899
Finnegan EJ, Dennis ES (1993) Isolation and identification by sequence homology of a putative cytosine methyltransferase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 21:2383–2388
Finnegan EJ, Genger PK, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES (1998) DNA methylation in plants. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:223–248
Grandibastien MA (1998) Activation of plant retrotransposons under stress conditions. Trends Plant Sci 3:181–187
Hirochika H (1997) Retrotransposons of rice: their regulation and use for genome analysis. Plant Mol Biol 35:231–240
Hirochika H (2001) Contribution of the Tos17 retrotransposon to rice functional genomics. Cur Opin Plant Biol 4:118–122
Hirochika H, Sugimoto K, Otsuki Y, Kanda M (1996) Retrotransposons of rice involved in mutations induced by tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7783–7787
Hirochika H, Okamoto J, Kakutani T (2000) Silencing of retrotransposons in Arabidopsis and reactivation by the ddm1 mutation. Plant Cell 12:357–368
Jeddeloh JA, Stokes TL, Richards EJ (1999) Maintenance of genomic methylation requires a SWI2/SNF2-like protein. Nat Genet 22:94–97
Kaeppler SM, Phillips RL (1993) Tissue culture-induced DNA methylation variation in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8773–8776
Kalendar R, Tanskanen J, Immonen S, Nevo E, Schulman AH (2000) Genome evolution in wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum) by BARE-1 retrotransposon dynamics in response to sharp microclimatic divergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6603–6607
Kashkush K, Feldman M, Levy AA (2003) Transcriptional activation of retrotransposons alters the expression of adjacent genes in wheat. Nat Genet 33:102–106
Kato M, Miura A, Bender J, Jacobsen SE, Kakutani T (2003) Role of CG and non-CG methylation in immobilization of transposons in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 13:421–426
Kidwell MG, Lisch DR (1997) Transposable elements as sources of variation in animals and plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7704–7711
Kidwell MG, Lisch DR (2000) Transposable elements and host genome evolution. Trends Ecol Evol 15:95–99
Kidwell MG, Lisch DR (2001) Perspective: transposable elements, parasitic DNA, and genome evolution. Evolution 55:1–24
Kitamura K, Hashida SN, Mikami T, Kishima Y (2001) Position effect of the excision frequency of the Antirrhinum transposon Tam3: implications for the degree of position-dependent methylation in the ends of the element. Plant Mol Biol 47:475–490
Kumar A, Bennetzen JL (1999) Plant retrotransposons. Ann Rev Genet 33:479–532
Lindroth AM, Cao X, Jackson JP, Zilberman D, McCallum CM, Henikoff S, Jacobsen SE (2001) Requirement of CHROMOMETHYLASE3 for maintenance of CpXpG methylation. Science 292:2077–2080
Liu B, Wendel JF (2000) Retrotransposon activation followed by rapid repression in introgressed rice plants. Genome 43:874–880
Liu B, Piao HM, Zhao FS, Zhao JH, Zhao R (1999) Production and molecular characterization of rice lines with introgressed traits from a wild species of Zizania latifolia Griseb. J Genet Breed 53:279–284
Liu YG, Mitsukawa N, Oosumi T, Whittier RF (1995) Efficient isolation and mapping of Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA insert junctions by thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR. Plant J 8:457–463
Lucas H, Feuerbach F, Grandbastien MA, Caboche M (1995) The tobacco retrotransposon Tnt1 transposes in Arabidopsis thaliana. EMBO J 14:2364–2373
Martienssen RA (1996) Epigenetic phenomena: paramutation and gene silencing in plants. Curr Biol 6:810–813
Martienssen RA, Colot V (2001) DNA methylation and epigenetic inheritance in plants and filamentous fungi. Science 293:1070–1074
McClelland M, Nelson M, Raschke E (1994) Effect of site-specific modification on restriction endonucleases and DNA modification methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3640–3659
McClintock B (1984) The significance of responses of the genome to challenge. Science 226:792–801
Miura A, Yonebayashi S, Watanabe K, Toyama T, Shimada H, Kakutani T (2001) Mobilization of transposons by a mutation abolishing full DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Nature 411:212–214
Nakayashiki H, Ikeda K, Hashimoto Y, Tosa Y, Mayama S (2001) Methylation is not the main force repressing the retrotransposon MAGGY in Magnaporthe grisea. Nucleic Acids Res 29:1278–1284
O’Neill RJW, O’Neill MJ, Graves JAM (1998) Undermethylation associated with retroelement activation and chromosome remodeling in an interspecific mammalian hybrid. Nature 393:68–72
Phillips RL, Kaeppler SM, Olhoft P (1994) Genetic instability of plant tissue cultures: breakdown of normal controls. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5222–5226
Ros F, Kunze R (2001) Regulation of activator/dissociation transposition by replication and DNA methylation. Genetics 157:1723–1733
Schwartz D, Dennis E (1986) Transposase activity of the Ac-controlling element in maize is regulated by its degree of methylation. Mol Genet Genet 205:476–482
Singer T, Yordan C, Martienssen RA (2001) Robertson’s mutator transposons in A. thaliana are regulated by the chromatin-remodeling gene Decrease in DNA Methylation (DDM1). Genes Dev 15:591–602
Vicient CM, Jaaskelainen MJ, Kalendar R, Schulman AH (2001) Active retrotransposons are a common feature of grass genomes. Plant Physiol 125:1283–1292
Vongs A, Kakutani T, Martienssen RA, Richards EJ (1993) Arabidopsis thaliana DNA methylation mutants. Science 260:1926–1928
Wang L, Heinlein M, Kunze R (1996) Methylation pattern of Activator transposase binding sites in maize endosperm. Plant Cell 8:747–758
Wendel JF (2000) Genome evolution in polyploids. Plant Mol Biol 42:225–249
Wendel JF, Wessler SR (2000) Retrotransposon-mediated genome evolution on a local ecological scale. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6250–6252
Wessler SR (1996) Plant retrotransposons: turned on by stress. Curr Biol 6:959–961
White SE, Habear LF, Wessler SR (1994) Retrotransposons in the flanking regions of normal plant genes: a role for copia-like elements in the evolution of gene structure and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11792–11796
Whitelaw E, Martin DIK (2001) Retrotransposons as epigenetic mediators of phenotypic variation in mammals. Nat Genet 27:361–365
Yamazaki M, Tsugawa H, Miyao A, Yano M, Wu J, Yamamoto S, Matsumoto T, Sasaka T, Hirochika H (2001) The rice retrotransposon Tos17 prefers low-copy-number sequences as integration targets. Mol Genet Genomics 265:336–344
Yoder JA, Walsh CP, Bestor TH (1997) Cytosine methylation and the ecology of intragenomic parasites. Trends Genet 13:335–340
Zhou Y, Magill CW, Magill JM, Newton RJ (1998) An apparent case of nonsymmetrical and sustained strand-specific hemimethylation in the Dc8 gene of carrot. Genome 41:23–33
Zhou Y, Cambareri EB, Kinsey JA (2001) DNA methylation inhibits expression and transposition of the Neurospora Tad retrotransposon. Mol Genet Genomics 265:748–754
Acknowledgements
Authors Z.L. Liu and F.P. Han contributed equally to this work. This study was supported by the National Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (30225003) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30370768). We are grateful to Professor Jonathan F. Wendel of Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa, USA for constructive discussions pertinent to this work. This paper is dedicated to Professor Moshe Feldman of the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel, in honor of his 70th birthday.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Hagemann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z.L., Han, F.P., Tan, M. et al. Activation of a rice endogenous retrotransposon Tos17 in tissue culture is accompanied by cytosine demethylation and causes heritable alteration in methylation pattern of flanking genomic regions. Theor Appl Genet 109, 200–209 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1618-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1618-8