Purpose: To develop a superconducting magnetic resonance (MR) imager that provides direct access to the patient and permits interactive MR-guided interventional procedures.
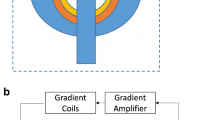
Materials and methods: A 0.5-T superconducting magnet that allows a region of vertical access to the patient was designed and constructed. This magnet was integrated with newly designed shielded gradient coils, flexible surface coils, nonmagnetic displays, position-monitoring probes and device-tracking instrumentation.
Results: The magnet homogeneity was 12.3 ppm or better, and the gradient field was linear to within 1 % over an imaging region of 30 cm in diameter. The signal-to-noise ratio was 10 % higher than in a comparable 0.5-T superconducting imager. Images were obtained in several anatomic regions with use of routine pulse sequences. Interactive image plane selection and near real-time imaging, with use of fast gradient-recalled echo sequences were demonstrated at a rate of one image every 1.5 s. More than 240 procedures (including open brain surgery) have been successfully performed within this environment.
Conclusions: MR-guided interventional and surgical procedures can be performed with full patient access using an open-configuration, superconducting MR magnet with near real-time imaging and interactive image plane control.
Zusammenfassung
Die Magnetresonanztomographie (MRT) eignet sich als nichtinvasives Verfahren mit hoher Auflösung besonders gut zur Bildgebung für minimal invasive, chirurgische oder interventionelle Eingriffe. Eine wesentliche Voraussetzung ist jedoch die Entwicklung offener MR-Systeme. Das hier beschriebene, offene MR-System mit supraleitendem 0,5-T-Magneten (SIGNA SP,GE) erlaubt den Zugang zum Patienten auch während der Bildaquisition und die interaktive Kontrolle der Bildebene durch den Benutzer. Die kontinuierliche Bildunterstützung ermöglicht neue Techniken zur Führung interventioneller oder chirurgischer Eingriffe, eine genauere Lokalisation von Instrumenten und die unmittelbare Verlaufskontrolle nahezu in Echtzeit. Klinische Anwendungen dieser Technologie werden dargestellt. Durch schnelle Rechentechniken für das Bildmanagement und intraoperative Bildgebung, ermöglicht das offene MR-System die Entwicklung neuer, besonders effizienter interventioneller und minimal invasiv chirurgischer Verfahren.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kettenbach, J., Silverman, S., Schwartz, R. et al. Composition, clinical suitability and future prospects of a 0.5-T MR system for interventional use. Radiologe 37, 825–834 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001170050289
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001170050289