Abstract
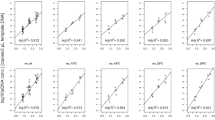
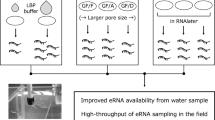
Environmental RNA (eRNA) analysis is conventionally expected to infer physiological information about organisms within their ecosystems, whereas environmental DNA (eDNA) analysis only infers their presence and abundance. Despite the promise of eRNA application, basic research on eRNA characteristics and dynamics is limited. The present study conducted aquarium experiments using zebrafish (Danio rerio) to estimate the particle size distribution (PSD) of eRNA in order to better understand the persistence state of eRNA particles. Rearing water samples were sequentially filtered using different pore-size filters, and the resulting size-fractioned mitochondrial cytochrome b (CytB) eDNA and eRNA data were modeled with the Weibull complementary cumulative distribution function (CCDF) to estimate the parameters characterizing the PSDs. It was revealed that the scale parameter (α) was significantly higher (i.e., the mean particle size was larger) for eRNA than eDNA, while the shape parameter (β) was not significantly different between them. This result supports the hypothesis that most eRNA particles are likely in a protected, intra-cellular state, which mitigates eRNA degradation in water. Moreover, these findings also imply the heterogeneous dispersion of eRNA relative to eDNA and suggest an efficient method of eRNA collection using a larger pore-size filter. Further studies on the characteristics and dynamics of eRNA particles should be pursued in the future.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the raw data of qPCR can be found in the Supplemental information.
References
Barnes MA, Turner CR (2016) The ecology of environmental DNA and implications for conservation genetics. Conserv Genet 17(1):1–17
Barnes MA, Chadderton WL, Jerde CL, Mahon AR, Turner CR, Lodge DM (2021) Environmental conditions influence eDNA particle size distribution in aquatic systems. Environmental DNA 3(3):643–653
Bauer M (2007) RNA in forensic science. Forensic Sci Int Genet 1(1):69–74
Bayat H, Rastgo M, Zadeh MM, Vereecken H (2015) Particle size distribution models, their characteristics and fitting capability. J Hydrol 529:872–889
Brandão-Dias PF, Hallack DM, Snyder ED, Tank JL, Bolster D, Volponi S, Egan SP (2023a) Particle size influences decay rates of environmental DNA in aquatic systems. Mol Ecol Resour 23(4):756–770
Brandão-Dias PF, Tank JL, Snyder ED, Mahl UH, Peters B, Bolster D, Egan SP (2023b) Suspended materials affect particle size distribution and removal of environmental DNA in flowing waters. Environ Sci Technol 57(35):13161–13171
Budovskaya YV, Wu K, Southworth LK, Jiang M, Tedesco P, Johnson TE, Kim SK (2008) An elt-3/elt-5/elt-6 GATA transcription circuit guides aging in C. elegans. Cell 134(2):291–303
Chambert T, Pilliod DS, Goldberg CS, Doi H, Takahara T (2018) An analytical framework for estimating aquatic species density from environmental DNA. Ecol Evol 8(6):3468–3477
Cristescu ME (2019) Can environmental RNA revolutionize biodiversity science? Trends Ecol Evol 34(8):694–697
Ellison SL, English CA, Burns MJ, Keer JT (2006) Routes to improving the reliability of low-level DNA analysis using real-time PCR. BMC Biotechnol 6(1):1–11
Ernster L, Schatz G (1981) Mitochondria: a historical review. J Cell Biol 91(3):227s–255s
Furlan EM, Gleeson D, Hardy CM, Duncan RP (2016) A framework for estimating the sensitivity of eDNA surveys. Mol Ecol Resour 16(3):641–654
Hechler RM, Yates MC, Chain FJ, Cristescu ME (2023) Environmental transcriptomics under heat stress: can environmental RNA reveal changes in gene expression of aquatic organisms? Mol Ecol Press. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.17152
Hiki K, Yamagishi T, Yamamoto H (2023) Environmental RNA as a noninvasive tool for assessing toxic effects in fish: a proof-of-concept study using Japanese Medaka exposed to pyrene. Environ Sci Technol 57(34):12654–12662
Jo TS (2023a) Methodological considerations for aqueous environmental RNA collection, preservation, and extraction. Anal Sci 39:1711–1718
Jo TS (2023b) Utilizing the state of environmental DNA (eDNA) to incorporate time-scale information into eDNA analysis. Proc R Soc B 290(1999):20230979
Jo T, Arimoto M, Murakami H, Masuda R, Minamoto T (2019) Particle size distribution of environmental DNA from the nuclei of marine fish. Environ Sci Technol 53(16):9947–9956
Jo T, Fukuoka A, Uchida K, Ushimaru A, Minamoto T (2020a) Multiplex real-time PCR enables the simultaneous detection of environmental DNA from freshwater fishes: a case study of three exotic and three threatened native fishes in Japan. Biol Invasions 22:455–471
Jo T, Murakami H, Masuda R, Minamoto T (2020b) Selective collection of long fragments of environmental DNA using larger pore size filter. Sci Total Environ 735:139462
Jo T, Takao K, Minamoto T (2022) Linking the state of environmental DNA to its application for biomonitoring and stock assessment: targeting mitochondrial/nuclear genes, and different DNA fragment lengths and particle sizes. Environmental DNA 4(2):271–283
Jo T, Tsuri K, Hirohara T, Yamanaka H (2023) Warm temperature and alkaline conditions accelerate environmental RNA degradation. Environmental DNA 5(5):836–848
Kagzi K, Hechler RM, Fussmann GF, Cristescu ME (2022) Environmental RNA degrades more rapidly than environmental DNA across a broad range of pH conditions. Mol Ecol Resour 22(7):2640–2650
Kirtane A, Wieczorek D, Noji T, Baskin L, Ober C, Plosica R, Sassoubre L (2021) Quantification of Environmental DNA (eDNA) shedding and decay rates for three commercially harvested fish species and comparison between eDNA detection and trawl catches. Environ DNA 3(6):1142–1155
Kumar G, Farrell E, Reaume AM, Eble JA, Gaither MR (2022) One size does not fit all: tuning eDNA protocols for high-and low-turbidity water sampling. Environ DNA 4(1):167–180
Li Y, Breaker RR (1999) Kinetics of RNA degradation by specific base catalysis of transesterification involving the 2′-hydroxyl group. J Am Chem Soc 121(23):5364–5372
Littlefair JE, Rennie MD, Cristescu ME (2022) Environmental nucleic acids: a field-based comparison for monitoring freshwater habitats using eDNA and eRNA. Mol Ecol Resour 22(8):2928–2940
Lloyd HM, Jacobi JM, Cooke RA (1979) Nuclear diameter in parathyroid adenomas. J Clin Pathol 32(12):1278
Marshall NT, Vanderploeg HA, Chaganti SR (2021) Environmental (e)RNA advances the reliability of eDNA by predicting its age. Sci Rep 11:2769
Mauvisseau Q, Harper LR, Sander M, Hanner RH, Kleyer H, Deiner K (2022) The multiple states of environmental DNA and what is known about their persistence in aquatic environments. Environ Sci Technol 56(9):5322–5333
Miller CC (1924) The Stokes-Einstein law for diffusion in solution. Proceedings of the royal society of London. Series A, Containing Pap Math Phys Charact 106(740):724–749
Minamoto T, Yamanaka H, Takahara T, Honjo MN, Kawabata Z (2012) Surveillance of fish species composition using environmental DNA. Limnology 13:193–197
Misutka MD, Glover CN, Brush M, Goss GG, Veilleux HD (2023) A validated and optimized environmental DNA and RNA assay to detect Arctic grayling (Thymallus arcticus). Environmental DNA 5(6):1378–1392
Miyata K, Inoue Y, Amano Y, Nishioka T, Yamane M, Kawaguchi T, Honda H (2021) Fish environmental RNA enables precise ecological surveys with high positive predictivity. Ecol Indic 128:107796
Miyata K, Inoue Y, Amano Y, Nishioka T, Nagaike T, Kawaguchi T, Honda H (2022) Comparative environmental RNA and DNA metabarcoding analysis of river algae and arthropods for ecological surveys and water quality assessment. Sci Reports 12:19828
Moushomi R, Wilgar G, Carvalho G, Creer S, Seymour M (2019) Environmental DNA size sorting and degradation experiment indicates the state of Daphnia magna mitochondrial and nuclear eDNA is subcellular. Sci Rep 9:12500
Nevers MB, Byappanahalli MN, Morris CC, Shively D, Przybyla-Kelly K, Spoljaric AM, Roseman EF (2018) Environmental DNA (eDNA): a tool for quantifying the abundant but elusive round goby (Neogobius melanostomus). PLoS ONE 13(1):e0191720
Nielsen KM, Johnsen PJ, Bensasson D, Daffonchio D (2007) Release and persistence of extracellular DNA in the environment. Environ Biosaf Res 6(1–2):37–53
O’Brien K, Breyne K, Ughetto S, Laurent LC, Breakefield XO (2020) RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21(10):585–606
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, Heisterkamp S, Van Willigen B, Maintainer R (2017) nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R Package 3(1):274
R Core Team (2022) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Rosin P, Rammler E (1933) Laws governing the fineness of powdered coal. J Inst Fuel 7:29–36
Schrader C, Schielke A, Ellerbroek L, Johne R (2012) PCR inhibitors–occurrence, properties and removal. J Appl Microbiol 113(5):1014–1026
Scriver M, Zaiko A, Pochon X, von Ammon U (2023) Harnessing decay rates for coastal marine biosecurity applications: a review of environmental DNA and RNA fate. Environ DNA 5(5):960–972
Tkach M, Théry C (2016) Communication by extracellular vesicles: where we are and where we need to go. Cell 164(6):1226–1232
Tom M, Auslander M (2005) Transcript and protein environmental biomarkers in fish—a review. Chemosphere 59(2):155–162
Tsuri K, Ikeda S, Hirohara T, Shimada Y, Minamoto T, Yamanaka H (2021) Messenger RNA typing of environmental RNA (eRNA): a case study on zebrafish tank water with perspectives for the future development of eRNA analysis on aquatic vertebrates. Environ DNA 3(1):14–21
Turner CR, Barnes MA, Xu CC, Jones SE, Jerde CL, Lodge DM (2014) Particle size distribution and optimal capture of aqueous macrobial eDNA. Methods Ecol Evol 5(7):676–684
Veilleux HD, Misutka MD, Glover CN (2021) Environmental DNA and environmental RNA: current and prospective applications for biological monitoring. Sci Total Environ 782:146891
Warne RT (2014) A primer on multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) for behavioral scientists. Pract Assess Res Eval 19(17):1–10
Wood SA, Biessy L, Latchford JL, Zaiko A, von Ammon U, Audrezet F, Pochon X (2020) Release and degradation of environmental DNA and RNA in a marine system. Sci Total Environ 704:135314
Yao M, Zhang S, Lu Q, Chen X, Zhang SY, Kong Y, Zhao J (2022) Fishing for fish environmental DNA: ecological applications, methodological considerations, surveying designs, and ways forward. Mol Ecol 31(20):5132–5164
Yates MC, Derry AM, Cristescu ME (2021) Environmental RNA: a revolution in ecological resolution? Trends Ecol Evol 36(7):601–609
Yates MC, Gaudet-Boulay M, Garcia Machado E, Côté G, Gilbert A, Bernatchez L (2023) How much is enough Examining the sampling effort necessary to estimate mean eDNA concentrations in lentic systems. Environ DNA 5:1527. https://doi.org/10.1002/edn3.461
Zhao B, van Bodegom PM, Trimbos K (2021) The particle size distribution of environmental DNA varies with species and degradation. Sci Total Environ 797:149175
Zobeck TM, Gill TE, Popham TW (1999) A two-parameter Weibull function to describe airborne dust particle size distributions. Earth Surf Process Landf: J British Geomorphol Res Group 24(10):943–955
Acknowledgements
I thank Dr. Hiroki Yamanaka (Ryukoku University) for partially providing financial support for the study. I also thank an editor and anonymous reviewers whose comments significantly improved the manuscript and Alaina Eckert for proofreading the manuscript. The proofreading of the manuscript was also supported by Grammarly (https://app.grammarly.com).
Funding
This work was supported by the Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Research Fellows (Grant Numbers JP22J00439 and JP22KJ3043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.J.S. conceived the study, performed molecular and statistical analyses, and wrote and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Matjaž Gregorič
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, T.S. Larger particle size distribution of environmental RNA compared to environmental DNA: a case study targeting the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene in zebrafish (Danio rerio) using experimental aquariums. Sci Nat 111, 18 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-024-01904-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-024-01904-w