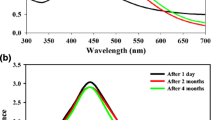
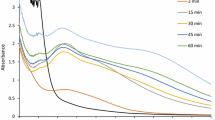
Abstract
Metallic nanoparticles of different compositions have already found numerous applications in various branches of industry, agriculture, and medicine. Given the well-known antibacterial activity of Ag, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are constantly being investigated for their promising ability to fight antibiotic-resistant pathogens. A promising candidate for AgNPs biosynthesis is chili pepper Capsicum annuum, cultivated worldwide and known for accumulating significant amounts of active substances. Phytochemical screening of aqueous extract of C. annuum pericarps demonstrated accumulation of 4.38 mg/g DW of total capsaicinoids, 14.56 mg GAE/g DW of total phenolic compounds, 1.67 mg QE/g DW of total flavonoids, and 1.03 mg CAE/g DW of total phenolic acids. All determined aromatic compounds carry various active functional groups, which effectively participate in the biosynthesis of AgNPs and are characterized by high antioxidant potential. Therefore, the present research focused on the facile, quick, and effective procedure for the biosynthesis of AgNPs, which were analyzed for their morphology such as shape and size through UV–visible, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) assays, and scanning electron microscopy. We found that the AgNPs biosynthesis resulted in changes in FTIR spectra, depicting the rearrangement of numerous functional groups, while the nanoparticles themselves were shown to be stable, spherical, 10–17 nm in size. Also we investigated the antibacterial properties of biosynthesized AgNPs, obtained with C. annuum fruit extracts, against a common phytopathogen Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis. As was shown by zone inhibition assay, AgNPs showed dose-dependent 5.13–6.44 cm antibacterial activity, greatly exceeding the 4.98 cm inhibition area, produced by the precursor salt, AgNO3.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- AgNPs:
-
Silver nanoparticles
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- Cmm:
-
Clavibacter michiganensis Subsp. michiganensis
- DPPH:
-
2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl
- DW:
-
Dry weight
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- GAE:
-
Gallic acid equivalents
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- SPR:
-
Surface plasmon resonance
- TCC:
-
Total capsaicinoids content
- TPC:
-
Total phenolic content
- TFC:
-
Total flavonoids content
- TPAC:
-
Total phenolic acids content
- UV-vis:
-
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy
References
Ahn EY, Jin H, Park Y (2019) Assessing the antioxidant, cytotoxic, apoptotic and wound healing properties of silver nanoparticles green-synthesized by plant extracts. Mater Sci Eng, C 101:204–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.03.095
Akhtar A, Asghar W, Khalid N (2021) Phytochemical constituents and biological properties of domesticated capsicum species: a review. Bioact Compd Health Dis 4(9):201–225. https://doi.org/10.31989/bchd.v4i9.837
Ali A, Sattar M, Hussain F, Tareen MHK, Militky J, Noman MT (2021) Single-step green synthesis of highly concentrated and stable colloidal dispersion of core-shell silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial and ultra-high catalytic properties. Nanomaterials 11(4):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11041007
Amruthraj NJ, Preetam Raj JP, Lebel A (2015) Capsaicin-capped silver nanoparticles: its kinetics, characterization and biocompatibility assay. Appl Nanosci 5(4):403–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-014-0330-5
Armstrong JM (1964) The molar extinction coefficient of 2, 6-dichlorophenol indophenol. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 86(1):194–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4165(64)90180-1
Balachandar R, Navaneethan R, Biruntha M, Kumar KKA, Govarthanan M, Karmegam N (2022) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles phytosynthesized from Glochidion candolleanum leaves. Mater Lett 311:131572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131572
Batiha GES, Alqahtani A, Ojo OA, Shaheen HM, Wasef L, Elzeiny M, Hetta HF (2020) Biological properties, bioactive constituents, and pharmacokinetics of some Capsicum spp. and capsaicinoids. Int J Mol Sci 21(15):5179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155179
Bélteky P, Rónavári A, Igaz N, Szerencsés B, Tóth IY, Pfeiffer I, Kónya Z (2019) Silver nanoparticles: Aggregation behavior in biorelevant conditions and its impact on biological activity. Int J Nanomed 14:667. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S185965
Boudghane LC, Bouabdellah N, Bouanane S, Ahmed FZB, Laroussi MA, Bendiaf Y, Merzouk H (2022) Phytochemical, antioxidant, and antimicrobial attributes of different extracts of seeds: the Algerian variety of dates ‘Deglet Nour’(Phoenix dactylifera L.). Vegetos, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-022-00413-3
Buda S, Shafie S, Rashid SA, Jaafar H, Sharif NFM (2017) Enhanced visible light absorption and reduced charge recombination in AgNP plasmonic photoelectrochemical cell. Results Phys 7:2311–2316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.07.009
Caicedo-Lopez LH, Guevara-Gonzalez RG, Ramirez-Jimenez AK, Feregrino-Perez AA, Contreras-Medina LM (2022) Eustress application trough-controlled elicitation strategies as an effective agrobiotechnology tool for capsaicinoids increase: a review. Phytochem Rev 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-022-09818-z
Dong C, Tao J, Fu Z (2021) Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Capsicum annuum L. Extract. Nanosci Nanotechnol-Asia 11(4):72–78. https://doi.org/10.2174/2210681210999200905130447
dos S Costa D, Alviano Moreno DS, Alviano CS, da Silva AJR (2021) Extension of Solanaceae Food Crops Shelf Life by the Use of Elicitors and Sustainable Practices During Postharvest Phase. Food Bioprocess Technol 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-021-02713-z
Dzhagan V, Smirnov O, Kovalenko M, Mazur N, Hreshchuk O, Taran N, Zahn DR (2022) Spectroscopic Study of Phytosynthesized Ag Nanoparticles and Their Activity as SERS Substrate. Chemosensors 10(4):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10040129
Fahmy HM, Mosleh AM, AbdElghany A, Shams-Eldin E, Serea ESA, Ali SA, Shalan AE (2019) Coated silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, cytotoxicity, and optical properties. RSC Adv 9(35):20118–20136. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA02907A
Huang J, Lin L, Li Q, Sun D, Wang Y, Lu Y, He N, Yang K, Yang X, Wang H (2008) Continuous-flow biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by lixivium of sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf in tubular microreactors. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:6081–6090. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie701698e
Khatoon A, Syed JA, Buledi JA, Shakeel S, Mallah A, Solangi AR, Shah MR (2022) Bio-green fabrication of bell pepper mediated silver nanoparticles: an efficient material for electrochemical sensing of arbutin in cosmetics. J Iran Chem Soc 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-022-02558-z
Kumar B, Smita K, Awasthi SK, Debut A, Cumbal L (2021) Capsicum baccatum (Andean Chilli)-assisted phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their H2O2 sensing ability. Part Sci Technol 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2021.2006381
La J, Kim MJ, Lee J (2021) Evaluation of solvent effects on the DPPH reactivity for determining the antioxidant activity in oil matrix. Food Sci Biotechnol 30(3):367–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-020-00874-9
Lee SH, Jun BH (2019) Silver nanoparticles: synthesis and application for nanomedicine. Int J Mol Sci 20(4):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040865
Lomelí-Rosales DA, Zamudio-Ojeda A, Reyes-Maldonado OK, López-Reyes ME, Basulto-Padilla GC, Lopez-Naranjo EJ, Velázquez-Juárez G (2022) Green Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Capsicum chinense Plant. Molecules 27(5):1692. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051692
Méndez-Andrade R, Vallejo-Perez MR, Loera-Alvarado E, de los Santos-Villarreal G, García-Cerda LA, Vera-Reyes I (2022) Efficacy of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles from Larrea tridentata against Clavibacter michiganensis. J Phytopathol 170(2):91–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/jph.13058
Nakagawa S, Ohmura R, Toshima S, Park H, Narasako Y, Hirano T, Kunitake H (2021) Changes in polyphenols, anthocyanins, and DPPH radical-scavenging activities in sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.) during tuber growth. Sci Hortic 284:110100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110100
Nayak S, Goveas LC, Kumar PS, Selvaraj R, Vinayagam R (2022) Plant-mediated gold and silver nanoparticles as detectors of heavy metal contamination. Food Chem Toxicol 113271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.113271
Neupane P, Lamichhane J (2020) Estimation of total phenolic content, total flavonoid content and antioxidant capacities of five medicinal plants from Nepal. Vegetos 33(2):360–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-020-00116-7
Nicolae-Maranciuc A, Chicea D, Chicea LM (2022) Ag Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications-Synthesis and Characterization – A Review. Int J Mol Sci 23(10):5778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105778
Noshad A, Iqbal M, Hetherington C, Wahab H (2020) Biogenic AgNPs – a nano weapon against bacterial canker of tomato (BCT). Adv Agric 2020:9630785. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9630785
Noshad A, Hetherington C, Iqbal M (2019) Impact of AgNPs on seed germination and seedling growth: A focus study on its antibacterial potential against Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis infection in Solanum lycopersicum. J Nanomater 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6316094
Rajam MV, Nandy S, Pandey R (2021) Biotechnology of Red Pepper. In Genetically Modified Crops (pp. 53–83). Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5932-7_3
Ryu WK, Kim HW, Kim GD, Rhee HI (2017) Rapid determination of capsaicinoids by colorimetric method. J Food Drug Anal 25(4):798–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2016.11.007
Salayová A, Bedlovičová Z, Daneu N, Baláž M, LukáčováBujňáková Z, Balážová Ľ, Tkáčiková Ľ (2021) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity using various medicinal plant extracts: Morphology and antibacterial efficacy. Nanomaterials 11(4):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11041005
Samrot AV, Shobana N, Jenna R (2018) Antibacterial and antioxidant activity of different staged ripened fruit of Capsicum annuum and its green synthesized silver nanoparticles. BioNanoScience 8(2):632–646
Shankar T, Karthiga P, Swarnalatha K, Rajkumar K (2017) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capsicum frutescence and its intensified activity against E. coli. Resour-Efficient Technol 3(3):303–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reffit.2017.01.004
Smirnov OE, Kalynovskyi VY, Yumyna YM, Zelena PP, Skoryk MA, Dzhagan VM, Taran NY (2021) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of hot chili pepper fruits and its antimicrobial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ukr Biochem J 93(5):102–110. https://doi.org/10.15407/ubj93.05.102
Solano-Alvarez N, Valencia-Hernández JA, Vergara-Pineda S, Millán-Almaraz JR, Torres-Pacheco I, Guevara-González RG (2022) Comparative Analysis of the NDVI and NGBVI as Indicators of the Protective Effect of Beneficial Bacteria in Conditions of Biotic Stress. Plants 11(7):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11070932
Türker-Kaya S, Huck CW (2017) A review of mid-infrared and near-infrared imaging: Principles, concepts and applications in plant tissue analysis. Molecules 22:168. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010168
Ulaeto SB, Mathew GM, Pancrecious JK, Nair JB, Rajan TPD, Maiti KK, Pai BC (2020) Biogenic Ag Nanoparticles from Neem Extract: Their Structural Evaluation and Antimicrobial Effects against Pseudomonas nitroreducens and Aspergillus unguis (NII 08123). ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01257
Valencia-Hernandez JA, Solano-Alvarez N, Rico-Rodriguez MA, Rodriguez-Ontiveros A, Torres-Pacheco I, Rico-Garcia E, Guevara-Gonzalez RG (2022) Eustressic Dose of Cadmium in Soil Induces Defense Mechanisms and Protection Against Clavibacter Michiganensis in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J Plant Growth Regul 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10559-0
Velgosova O, Veselovský L (2019) Synthesis of Ag nanoparticle using R. officinalis, U. dioica and V. vitisidaea extracts. Mater Lett 248:150–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.04.027
Vergun O, Svydenko L, Grygorieva O, Sedláčková VH, Šramková KF, Ivanišová E, Brindza J (2022) Polyphenol component and antioxidant activity of Thymus spp. Potravinarstvo 15(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.5219/1715
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. M.A. Skoryk from G.V. Kurdyumov Institute for Metal Physics, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine for the SEM investigation and Dr. M. Vuichyk from ISP NASU for IR measurements of biosynthesized solutions of AgNPs.
Funding
This work was not supported by any funding agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Oleksandr Smirnov and Vitalii Kalynovskyi project conceptualization and edited the manuscript, Pavlina Zelena and Yuliia Yumyna designed the experiments with microorganisms, Volodymyr Dzhagan performed the FTIR analysis, Mariia Kovalenko wrote the first draft of the manuscript, Yevheniia Konotop and Nataliya Taran analyzed the manuscript contents and made the manuscript corrections. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Lukasz Stepien
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Smirnov, O., Kalynovskyi, V., Zelena, P. et al. Bactericidal activity of Ag nanoparticles biosynthesized from Capsicum annuum pericarps against phytopathogenic Clavibacter michiganensis. Sci Nat 110, 15 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-023-01844-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-023-01844-x