Abstract
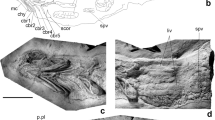
Fossilized soft tissues, occasionally found together with skeletal remains, provide insights to the physiology and functional morphology of extinct organisms. Herein, we present unusual fossilized structures from the cortical region of bone identified in isolated skeletal remains of Middle Triassic nothosaurs from Upper Silesia, Poland. The ribbed or annuli-shaped structures have been found in a sample of partially demineralized coracoid and are interpreted as either giant red blood cells or as blood vessel walls. The most probable function is reinforcing the blood vessels from changes of nitrogen pressure in air-breathing diving reptiles. These structures seem to have been built of extensible muscle layers which prevent the vessel damage during rapid ascent. Such suspected function presented here is parsimonious with results of previous studies, which indicate rarity of the pathological modification of bones associated with decompression syndrome in Middle Triassic nothosaurs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertazzo S, Maidment SCR, Kallepitis C, Fearn S, Stevens MM, Xie H (2015) Fibres and cellular structures preserved in 75-million-year-old dinosaur specimens. Nat Commun 6:7352. doi:10.1038/ncomms8352
Brachaniec T, Niedźwiedzki R, Surmik D, Krzykawski T, Szopa K, Gorzelak P, Salamon MA (2015) Coprolites of marine vertebrate predators from the Lower Triassic of southern Poland. Palaeogeog Palaeocl Palaeoec 435:118–126. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.06.005
Cadena E (2016) Microscopical and elemental FESEM and Phenom ProX-SEM-EDS analysis of osteocyte- and blood vessel-like microstructures obtained from fossil vertebrates of the Eocene Messel Pit, Germany. PeerJ 4:e1618. doi:10.7717/peerj.1618
Danise S, Higgs ND (2015) Bone-eating Osedax worms lived on Mesozoic marine reptile deadfalls. Biol Lett 11:20150072–20150072. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2015.0072
Eroschenko VP (2008) DiFioreʼs atlas of histology with functional correlations, 11th edn. Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Glover AG, Källström B, Smith CR, Dahlgren TG (2005) World-wide whale worms? A new species of Osedax from the shallow north Atlantic. Proc R Soc B 272:2587–2592. doi:10.1098/rspb.2005.3275
Goodman RM, Heah TP (2010) Temperature-induced plasticity at cellular and organismal levels in the lizard Anolis carolinensis. Integr Zool 5:208–217. doi:10.1111/j.1749-4877.2010.00206.x
Greenwalt DE, Goreva YS, Siljeström SM, Rose T, Harbach RE (2013) Hemoglobin-derived porphyrins preserved in a Middle Eocene blood-engorged mosquito. PNAS. doi:10.1073/pnas.1310885110
Gürich G (1884) Über einige Saurier des Oberschlesischen Muschelkalkes. Zeitschr. der Deutsch. Geologisch. Gesellsch. 36:125–144
Jans MME (2008) Microbial bioerosion of bone—a review. In: Wisshak M, Tapanila L (eds) Current developments in bioerosion. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 397–414
Ji C, Jiang D-Y, Rieppel O et al (2014) A new specimen of Nothosaurus youngi from the middle Triassic of Guizhou, China. J Vertebr Paleontol 34:465–470. doi:10.1080/02724634.2013.808204
Klein N (2010) Long bone histology of Sauropterygia from the Lower Muschelkalk of the Germanic Basin provides unexpected implications for phylogeny. PLoS One 5:e11613. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011613
Klein N, Albers PC (2009) A new species of the sauropsid reptile Nothosaurus from the Lower Muschelkalk of the western Germanic Basin, Winterswijk, the Netherlands. Acta Palaeontol Pol 54:589–598. doi:10.4202/app.2008.0083
Klein N, Sander PM, Krahl A, Scheyer TM, Houssaye A (2016) Diverse aquatic adaptations in Nothosaurus spp. (Sauropterygia)—inferences from humeral histology and microanatomy. PLoS One 11:e0158448. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0158448
Kowal-Linka M (2008) Formalizacja litostratygrafii formacji gogolińskiej (trias środkowy) na Śląsku Opolskim Geologos 14: 125–161
Kunisch H (1888) Über eine Saurierplatte aus dem Oberschlesischen Muschelkalke. Zeitschr der Deutsch Geologisch Gesellsch 40:671–693
Liu J, Hu S, Rieppel O et al (2014) A gigantic nothosaur (Reptilia: Sauropterygia) from the Middle Triassic of SW China and its implication for the Triassic biotic recovery. Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep07142
Lundsten L, Schlining KL, Frasier K, Johnson SB, Kuhnz LA, Harvey JBJ, Clague G, Vrijenhoek RC (2010) Time-series analysis of six whale-fall communities in Monterey Canyon, California. USA Deep Sea Res I 57:1573–1584. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2010.09.003
Pawlicki R (1995) Histochemical demonstration of DNA in Osteocytes from dinosaur bones. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 33:183–186
Pawlicki R, Nowogrodzka-Zagórska M (1998) Blood vessels and red blood cells preserved in dinosaur bones. Annals of Anatomy – Anatom Anz 180:73–77. doi:10.1016/S0940-9602(98)80140-4
Pawlicki R, Korbel A, Kubiak H (1966) Cells, collagen fibrils and vessels in dinosaur bone. Nature 211:655–657
Resnick D (2002) Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia
Rieppel O (1998) The status of the sauropterygian reptile genera Ceresiosaurus, Lariosaurus, and Silvestrosaurus from the Middle Triassic of Europe. Chicago, Ill.: Field Museum of Natural History
Rieppel O (2000) Sauropterygia I. Placodontia, Pachypleurosauria, Nothosauroidea, Pistosauroidea. Handbuch Der Paläoherpetologie, 134
Rieppel O, Wild R (1996) A revision of the genus Nothosaurus (Reptilia: Sauropterygia) from the Germanic Triassic, with comments on the status of Conchiosaurus clavatus. Fieldiana 1(34):1–82
Rieppel O, Mazin J-M, Tchernov E (1997) Speciation along rifting continental margins: a new Nothosaur from the Negev (Israël). C R Acad Sci Ser IIA Earth Planet Sci 325:991–997. doi:10.1016/S1251-8050(97)82380-4
Rothschild BM (1987) Decompression syndrome in fossil marine turtles. Annals of the Carnegie Museum 56:253–358
Rothschild BM, Martin LD (1987) Avascular necrosis: occurrence in diving cretaceous mosasaurs. Science 236:75–77. doi:10.1126/science.236.4797.75
Rothschild BM, Martin LD (2006) Skeletal impact of disease. New Mexico Museum of Natural History, Albuquerque
Rothschild BM, Naples V (2015) Decompression syndrome and diving behavior in Odontochelys, the first turtle. Acta Pal Pol 60:163–167. doi:10.4202/app.2012.0113
Rothschild BM, Storrs GW (2003) Decompression syndrome in plesiosaurs (Sauropterygia: Reptilia). J Vertebr Paleontol 23:324–328. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2003)023(0324:DSIPSR)2.0.CO;2
Rothschild BM, Xiaoting Z, Martin LD (2012) Adaptations for marine habitat and the effect of Triassic and Jurassic predator pressure on development of decompression syndrome in ichthyosaurs. Naturwissenschaften 299:443–448. doi:10.1007/s00114-012-0918-0
Rouse GW, Goffredi SK, Vrijenhoek RC (2004) Osedax: bone-eating marine worms with dwarf males. Science 305:668–671. doi:10.1126/science.1098650
Schweitzer MH, Suo Z, Avci R, Asara JM, Allen MA, Arce FT, Horner JR (2007) Analyses of soft tissue from tyrannosaurus rex suggest the presence of protein. Science 316:277–280. doi:10.1126/science.1138709
Schweitzer MH, Avci R, Collier T, Goodwin MB (2008) Microscopic, chemical and molecular methods for examining fossil preservation. Compt Rend Palevol 7:159–184
Schweitzer MH, Zheng W, Cleland TP, Goodwin MB, Boatman E, Theil E et al (2014) A role for iron and oxygen chemistry in preserving soft tissues, cells and molecules from deep time. Proc R Soc B 281:20132741. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.2741
Starostová Z, Konarzewski M, Kozłowski J, Kratochvíl L (2013) Ontogeny of metabolic rate and red blood cell size in eyelid geckos: species follow different paths. PLoS One 8:e64715. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064715
Surmik D, Boczarowski A, Balin K, Dulski M, Szade J, Kremer B, Pawlicki R (2016) Spectroscopic studies on organic matter from Triassic reptile bones, upper Silesia, Poland. PLoS One 11:e0151143. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0151143
Vijendravarma RK, Narasimha S, Kawecki TJ (2011) Plastic and evolutionary responses of cell size and number to larval malnutrition in Drisophila melanogaster. J. Evol Biol 24:897–903
von Meyer H (1847–1855) Die Saurier des Muschelkalkes mit Rücksicht auf die Saurier aus Buntem Sandstein und Keuper (in) Zur Fauna Der Vorwelt. Frankfurt A. Main
Wagner C, Steffen P, Svetina S (2013) Aggregation of red blood cells: from rouleaux to clot formation. Comptes rendus – Physique 14:459–469. doi:10.1016/j.crhy.2013.04.004
Wintrobe MM (1933) Variations in the size and hemoglobin content of erythrocytes in the blood of various vertebrates. Folia haematol 51:32–49
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Katarzyna Balin (Silesian Centre for Education and Interdisciplinary Research, Chorzów, Poland) for performing the mass spectrometry measurements and Aleksandra Pikuła (Sosnowiec, Poland) for making the three-dimensional idealized restoration of ribbed vessel. This research project is supported by National Science Center, Poland (www.ncn.gov.pl) grant no. 2011/01/N/ST10/06989.
Author contributions
DS conceived and designed the project with contribution of BMR. RP with DS prepared samples to scanning electron microscopy and mass spectra analyses. RP performed SEM images. DS with BMR wrote the paper with consultation of RP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Sven Thatje
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surmik, D., Rothschild, B.M. & Pawlicki, R. Unusual intraosseous fossilized soft tissues from the Middle Triassic Nothosaurus bone. Sci Nat 104, 25 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-017-1451-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-017-1451-y