Abstract
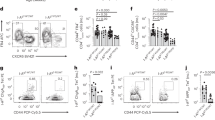
Upon allogeneic transplantation (Tx) of pancreatic islets under the kidney capsule of diabetic rats, cells from draining lymph nodes and, to a minor degree, bone marrow transiently upregulate CD44 splice variants as detected by RT-PCR using CD44 variant exon specific primers. Maximal expression was on day 5 post Tx in lymph nodes and thus precedes islet rejection sufficiently (in this model by 5 days) to still permit establishing rescue by immunosuppressive therapy. CD44 variant exon sequence could therefore serve as early markers of allograft rejection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milde, K., Herrlich, P. & Ponta, H. CD44 splice variants in draining lymph nodes precede allograft rejection of endocrine cells. J Mol Med 77, 67–69 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090050303
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090050303