Abstract
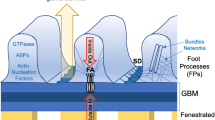
Nephrotic syndrome is a common kidney disease seen in both children and adults. The clinical syndrome includes massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and usually hypercholesterolemia. Development of these clinical changes is closely correlated with profound structural changes in glomerular epithelial cells, or podocytes, which together with the glomerular basement membrane and endothelium comprise the kidney’s blood filtration barrier. Although relatively little is known about the cellular or molecular changes which occur within podocytes during the development of nephrotic syndrome, cytoskeletal proteins very likely play a central role in these changes since they are primarily responsible for the maintenance of cell structure in almost all cells. This review focuses on: (a) the structure and function of podocytes in both the normal state and during nephrotic syndrome and (b) the potential roles of several cytoskeleton-associated proteins identified in podocytes in the development of and/or recovery from the pathophysiological cytoskeletal changes which occur in podocytes during nephrotic syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 April 1997 / Accepted: 18 July 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smoyer, W., Mundel, P. Regulation of podocyte structure during the development of nephrotic syndrome. J Mol Med 76, 172–183 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090050206
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090050206