Abstract
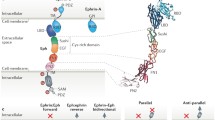
Recent studies of the large families of Eph-related receptor tyrosine kinases and their ligands suggest that they have key roles in embryonic development. These receptors mediate cell contact dependent signalling by binding to membrane-bound ligands, and certain ligands may themselves transduce signals. Functional studies indicate that in a number of tissues the receptors and ligands are expressed in complementary domains and mediate repulsive interactions that restrict cell and axon migration. In addition, they can also stimulate cell migration. Eph-related receptors and their ligands are therefore mediators of cell interactions required for tissue patterning and neuronal pathfinding during development. The potential clinical implications of these findings are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 January 1997 / Accepted: 17 March 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Wilkinson, D. Eph-related receptors and their ligands: mediators of contact dependent cell interactions. J Mol Med 75, 576–586 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090050142
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090050142