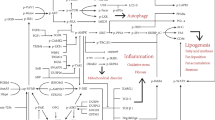
Abstract
SUMOylation is an important protein post-translational modification (PTM) process, in which the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) protein covalently binds to the target protein and regulates stability, subcellular localization, and protein–protein interaction of the target protein. Protein SUMOylation exerts crucial regulatory function in the liver, and its abnormalities are associated with various liver-related disease processes. This review focuses on the biological functions of protein SUMOylation in liver-related diseases in recent years, summarizes the molecular mechanisms of SUMOylation in the replication of hepatitis viruses and the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma, and discusses the significance of SUMOylation in liver-related disorders, which is essential for understanding liver biological processes and formulating therapeutic strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Chen Y, Peng W, Tao Q et al (2023) Increased small ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme SAE1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by enhancing mTOR SUMOylation. Lab Invest 103(1):100011
Ong JR, Bamodu OA, Khang NV et al (2021) SUMO-activating enzyme subunit 1 (SAE1) is a promising diagnostic cancer metabolism biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells 10(1):178
Tomasi ML, Ramani K, Ryoo M et al (2018) SUMOylation regulates cytochrome P450 2E1 expression and activity in alcoholic liver disease. Faseb j 32(6):3278–3288
Yang H, Gao S, Chen J et al (2020) UBE2I promotes metastasis and correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int 20:234
Tu J, Chen Y, Cai L et al (2015) Functional proteomics study reveals SUMOylation of TFII-I is involved in liver cancer cell proliferation. J Proteome Res 14(6):2385–2397
Li J, Xu Y, Long XD et al (2014) Cbx4 governs HIF-1α to potentiate angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by its SUMO E3 ligase activity. Cancer Cell 25(1):118–131
Yan L, Zhang T, Wang K et al (2022) SENP1 prevents steatohepatitis by suppressing RIPK1-driven apoptosis and inflammation. Nat Commun 13(1):7153
Tao Y, Li R, Shen C et al (2020) SENP1 is a crucial promotor for hepatocellular carcinoma through deSUMOylation of UBE2T. Aging (Albany NY) 12(2):1563–1576
Cui CP, Wong CC, Kai AK et al (2017) SENP1 promotes hypoxia-induced cancer stemness by HIF-1α deSUMOylation and SENP1/HIF-1α positive feedback loop. Gut 66(12):2149–2159
Liu Y, Dou X, Zhou WY et al (2021) Hepatic small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO)-specific protease 2 controls systemic metabolism through SUMOylation-dependent regulation of liver-adipose tissue crosstalk. Hepatology 74(4):1864–1883
Jin ZL, Pei H, Xu YH et al (2016) The SUMO-specific protease SENP5 controls DNA damage response and promotes tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20(17):3566–3573
Qian J, Luo Y, Gu X et al (2013) Inhibition of SENP6-induced radiosensitization of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by blocking radiation-induced NF-κB activation. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 28(3):196–200
Floris A, Chandla S, Lim Y et al (2023) Sumoylation of methionine adenosyltransferase alpha 1 promotes mitochondrial dysfunction in alcohol-associated liver disease. Hepatology. Epub ahead of print
Alfaro AJ, Dittner C, Becker J et al (2023) Fasting-sensitive SUMO-switch on Prox1 controls hepatic cholesterol metabolism. EMBO Rep 24(10):e55981
Lee GY, Jang H, Lee JH et al (2014) PIASy-mediated sumoylation of SREBP1c regulates hepatic lipid metabolism upon fasting signaling. Mol Cell Biol 34(6):926–938
Wang S, Yang M, Li P et al (2023) High-fat diet-Iinduced deSUMOylation of E4BP4 promotes lipid droplet biogenesis and liver steatosis in mice. Diabetes 72(3):348–361
Fan Y, Li X, Zhang L et al (2022) SUMOylation in viral replication and antiviral defense. Adv Sci (Weinh) 9(7):e2104126
Krump NA, You J (2018) Molecular mechanisms of viral oncogenesis in humans. Nat Rev Microbiol 16(11):684–698
Guo J, Chen D, Gao X et al (2017) Protein inhibitor of activated STAT2 restricts HCV replication by modulating viral proteins degradation. Viruses 9(10):285
Lee HS, Lim YS, Park EM et al (2014) SUMOylation of nonstructural 5A protein regulates hepatitis C virus replication. J Viral Hepat 21(10):e108–e117
Hofmann S, Plank V, Groitl P et al (2023) SUMO modification of hepatitis B virus core mediates nuclear entry, promyelocytic leukemia nuclear body association, and efficient formation of covalently closed circular DNA. Microbiol Spectr 11(3):e0044623
Xi R, Kadur Lakshminarasimha Murthy P, Tung KL et al (2019) SENP3-mediated host defense response contains HBV replication and restores protein synthesis. PLoS One 14(1):e0209179
Yen CJ, Yang ST, Chen RY et al (2019) Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) enhances centrosomal P4.1-associated protein (CPAP) expression to promote hepatocarcinogenesis. J Biomed Sci 26(1):44
Sengupta I, Das D, Singh SP et al (2017) Host transcription factor Speckled 110 kDa (Sp110), a nuclear body protein, is hijacked by hepatitis B virus protein X for viral persistence. J Biol Chem 292(50):20379–20393
Ha HL, Kwon T, Bak IS et al (2016) IGF-II induced by hepatitis B virus X protein regulates EMT via SUMO mediated loss of E-cadherin in mice. Oncotarget 7(35):56944–56957
Akil A, Wedeh G, Zahid Mustafa M et al (2016) SUMO1 depletion prevents lipid droplet accumulation and HCV replication. Arch Virol 161(1):141–148
Chen J, Zhou Y, Zhuang Y et al (2019) The metabolic regulator small heterodimer partner contributes to the glucose and lipid homeostasis abnormalities induced by hepatitis C virus infection. Metabolism 100:153954
Tseng CH, Cheng TS, Shu CY et al (2010) Modification of small hepatitis delta virus antigen by SUMO protein. J Virol 84(2):918–927
Wang Z, Pan B, Su L et al (2023) SUMOylation inhibitors activate anti-tumor immunity by reshaping the immune microenvironment in a preclinical model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). Epub ahead of print
Guo H, Xu J, Zheng Q et al (2019) NRF2 SUMOylation promotes de novo serine synthesis and maintains HCC tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett 466:39–48
Zubiete-Franco I, García-Rodríguez JL, Lopitz-Otsoa F et al (2019) SUMOylation regulates LKB1 localization and its oncogenic activity in liver cancer. EBioMedicine 40:406–421
Li W, Han Q, Zhu Y et al (2023) SUMOylation of RNF146 results in Axin degradation and activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling to promote the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 42(21):1728–1740
Bian XL, Chen HZ, Yang PB et al (2017) Nur77 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma via switching glucose metabolism toward gluconeogenesis through attenuating phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase sumoylation. Nat Commun 8:14420
Xu H, Wang H, Zhao W et al (2020) SUMO1 modification of methyltransferase-like 3 promotes tumor progression via regulating Snail mRNA homeostasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 10(13):5671–5686
Lin D, Fu Z, Yang G et al (2020) Exportin-5 SUMOylation promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Exp Cell Res 395(2):112219
Zhou Q, Yin Y, Yu M et al (2022) GTPBP4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis via the PKM2 dependent glucose metabolism. Redox Biol 56:102458
Wang Z, Pan B, Qiu J et al (2023) SUMOylated IL-33 in the nucleus stabilizes the transcription factor IRF1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells to promote immune escape. Sci Signal 16(776):eabq3362
Liu J, Sha M, Wang Q et al (2015) Small ubiquitin-related modifier 2/3 interacts with p65 and stabilizes it in the cytoplasm in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 15:675
Jiang C, Zhang C, Dai M et al (2024) Interplay between SUMO1-related SUMOylation and phosphorylation of p65 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1871(1):119595
You H, Yuan D, Li Q et al (2023) Hepatitis B virus X protein increases LASP1 SUMOylation to stabilize HER2 and facilitate hepatocarcinogenesis. Int J Biol Macromol 226:996–1009
Liu J, Wu Z, Han D et al (2020) Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor inhibits liver cancer through small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO)ylation-related suppression of NF-κB/Snail signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hepatology 71(4):1262–1278
Qin G, Tu X, Li H et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA p53-stabilizing and activating RNA promotes p53 signaling by inhibiting heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K deSUMOylation and suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 71(1):112–129
Qian L, Liang Z, Wang Z et al (2023) Cellular gp96 upregulates AFP expression by blockade of NR5A2 SUMOylation and ubiquitination in HCC. J Mol Cell Biol 15(5):mjad027
Li J, Zhou Y, Liu Y et al (2018) Sorafenib inhibits caspase-1 expression through suppressing TLR4/stat3/SUMO1 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 19(11):1057–1064
Qin Y, Bao H, Pan Y et al (2014) SUMOylation alterations are associated with multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep 9(3):877–881
Li Y, Chen J, Wang B et al (2023) FOXK2 affects cancer cell response to chemotherapy by promoting nucleotide de novo synthesis. Drug Resist Updat 67:100926
Dai J, Hao Y, Chen X et al (2023) miR-122/SENP1 axis confers stemness and chemoresistance to liver cancer through Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncol Lett 26(3):390
Zhang CY, Jiang ZM, Ma XF et al (2019) Saikosaponin-d inhibits the hepatoma cells and enhances chemosensitivity through SENP5-dependent inhibition of Gli1 SUMOylation under hypoxia. Front Pharmacol 10:1039
Jiang Z, Zhang C, Liu X et al (2020) Dexamethasone inhibits stemness maintenance and enhances chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells by inducing deSUMOylation of HIF-1α and Oct4. Int J Oncol 57(3):780–790
Wang J, Cong P, Jin Z et al (2023) A novel prognostic signature for hepatocellular carcinoma based on SUMOylation-related genes. Sci Rep 13(1):11233
Yang Y, Xia Z, Wang X et al (2018) Small-molecule inhibitors targeting protein SUMOylation as novel anticancer compounds. Mol Pharmacol 94(2):885–894
He X, Riceberg J, Soucy T et al (2017) Probing the roles of SUMOylation in cancer cell biology by using a selective SAE inhibitor. Nat Chem Biol 13(11):1164–1171
Langston SP, Grossman S, England D et al (2021) Discovery of TAK-981, a first-in-class inhibitor of SUMO-activating enzyme for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem 64(5):2501–2520
Kumar S, Schoonderwoerd MJA, Kroonen JS et al (2022) Targeting pancreatic cancer by TAK-981: a SUMOylation inhibitor that activates the immune system and blocks cancer cell cycle progression in a preclinical model. Gut 71(11):2266–2283
Guo WH, Yuan LH, Xiao ZH et al (2011) Overexpression of SUMO-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: a latent target for diagnosis and therapy of hepatoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137(3):533–541
Chen J, Chen C, Lin Y et al (2021) Downregulation of SUMO2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion. FEBS Open Bio 11(6):1771–1784
Zhang Z, Wen H, Peng B et al (2021) CDKN2A deregulation in fatty liver disease and its accelerative role in the process of lipogenesis. Faseb j 35(4):e21230
Liu Q, Zhou B, Liao R et al (2020) PIAS4, upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes tumorigenicity and metastasis. J Cell Biochem 121(5–6):3372–3381
Shen Y, Li Y, Ma X et al (2018) Connexin 43 SUMOylation improves gap junction functions between liver cancer stem cells and enhances their sensitivity to HSVtk/GCV. Int J Oncol 52(3):872–880
Ge H, Du J, Xu J et al (2017) SUMOylation of HSP27 by small ubiquitin-like modifier 2/3 promotes proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther 18(8):552–559
Mei L, Yuan L, Shi W et al (2017) SUMOylation of large tumor suppressor 1 at Lys751 attenuates its kinase activity and tumor-suppressor functions. Cancer Lett 386:1–11
Funding
This work was financially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82360389).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YYF wrote the manuscript and created schematic representations. YFX reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Yu, F. Abnormal protein SUMOylation in liver disease: novel target for therapy. J Mol Med (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-024-02440-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-024-02440-w