Abstract
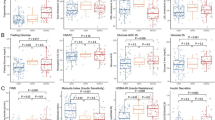
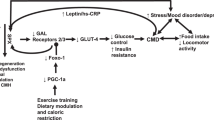
Obesity of children and adolescents (OCA) is often accompanied by metabolic syndrome (MetS), which often leads to adult obesity and subsequent complications, yet the entire pathophysiological response is not fully understood. The number and composition of circulating extracellular vesicles (EV) reflect overall patient condition; therefore, we investigated the pathophysiological condition of OCA, including MetS-associated dysmetabolism, using circulating EVs. In total, 107 children and adolescents with or without obesity (boys, n = 69; girls, n = 38; median age, 10 years) were enrolled. Circulating EV number and EV protein composition were assessed via flow cytometry and liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry, respectively. In a multivariate analysis, relative body weight (standardized partial regression coefficient (SPRC) 0.469, P = 0.012) and serum triglyceride level (SPRC 0.548, P < 0.001) were detected as independent parameters correlating with circulating EV number. Proteomic analysis identified 31 upregulated and 45 downregulated EV proteins in OCA. Gene ontology analysis revealed upregulated proteins to be involved in various biological processes, including intracellular protein transport, protein folding, stress response, leukocyte activation, innate immune response, and platelet degranulation, which can modulate lipid and glucose metabolism, skeletal and cardiac muscle development, inflammation, immune response, carcinogenesis, and cancer progression. Notably, several identified EV proteins are involved in neuro-development, neurotransmitter release, and neuro-protective agents in OCA. Circulating EVs were derived from adipocytes, hepatocytes, B cell lymphocytes, and neurons. Circulating EV number is significantly associated with MetS-related dysmetabolism and the EV protein cargo carries a special “signature” that reflects the alteration of various biological processes under the pathophysiological condition of OCA.
Key messages
-
Circulating EV number correlates with physical and laboratory parameters for obesity in children and adolescents.
-
Relative body weight and triglyceride are independent factors for increased circulating EVs.
-
EV composition is significantly changed in obesity of children and adolescents.
-
Identified EV composition changes associated with obesity and involves in metabolism, immune response, and cancer progression.
-
Circulating EVs are partially derived from adipocyte, hepatocytes, B cells, and neurons.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data will be available on reasonable request.
References
Di Cesare M, Soric M, Bovet P, Miranda JJ, Bhutta Z, Stevens GA, Laxmaiah A, Kengne AP, Bentham J (2019) The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: a worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med 17:212. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-019-1449-8
Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Mantzoros CS (2019) Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism 92:82–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.11.014
Alford S, Patel D, Perakakis N, Mantzoros CS (2018) Obesity as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: weighing the evidence. Obes Rev 19:269–280. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12629
Avgerinos KI, Spyrou N, Mantzoros CS, Dalamaga M (2019) Obesity and cancer risk: emerging biological mechanisms and perspectives. Metabolism 92:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.11.001
Skinner AC, Steiner MJ, Henderson FW, Perrin EM (2010) Multiple markers of inflammation and weight status: cross-sectional analyses throughout childhood. Pediatrics 125:e801-809. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-2182
Andersen CJ, Murphy KE, Fernandez ML (2016) Impact of obesity and metabolic syndrome on immunity. Adv Nutr 7:66–75. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.010207
de Oliveira Dos Santos AR, de Oliveira Zanuso B, Miola VFB, Barbalho SM, Santos Bueno PC, Flato UAP, Detregiachi CRP, Buchaim DV, Buchaim RL, Tofano RJ et al. (2021) Adipokines, myokines, and hepatokines: crosstalk and metabolic repercussions. Int J Mol Sci 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052639
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS (2020) The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 367. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977
Gurunathan S, Kang MH, Jeyaraj M, Qasim M, Kim JH (2019) Review of the isolation, characterization, biological function, and multifarious therapeutic approaches of exosomes. Cells 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8040307
Kobayashi Y, Eguchi A, Tempaku M, Honda T, Togashi K, Iwasa M, Hasegawa H, Takei Y, Sumida Y, Taguchi O (2018) Circulating extracellular vesicles are associated with lipid and insulin metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 315:E574–E582. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00160.2018
Eguchi A, Lazic M, Armando AM, Phillips SA, Katebian R, Maraka S, Quehenberger O, Sears DD, Feldstein AE (2016) Circulating adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles are novel markers of metabolic stress. J Mol Med (Berl) 94:1241–1253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-016-1446-8
Kobayashi Y, Eguchi A, Tamai Y, Fukuda S, Tempaku M, Izuoka K, Iwasa M, Takei Y, Togashi K (2021) Protein composition of circulating extracellular vesicles immediately changed by particular short time of high-intensity interval training exercise. Front Physiol 12:693007. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.693007
Liu Y, Ji Y, Li M, Wang M, Yi X, Yin C, Wang S, Zhang M, Zhao Z, Xiao Y (2018) Integrated analysis of long noncoding RNA and mRNA expression profile in children with obesity by microarray analysis. Sci Rep 8:8750. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27113-w
Chen R, Xin G, Zhang X (2019) Long non-coding RNA HCP5 serves as a ceRNA sponging miR-17-5p and miR-27a/b to regulate the pathogenesis of childhood obesity via the MAPK signaling pathway. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 32:1327–1339. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2018-0432
Brandt S, Roos J, Inzaghi E, Kotnik P, Kovac J, Battelino T, Cianfarani S, Nobili V, Colajacomo M, Kratzer W et al (2018) Circulating levels of miR-122 and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in pre-pubertal obese children. Pediatr Obes 13:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijpo.12261
Ito Y, Fujieda K, Okuno A (2016) Weight-for-height charts for Japanese children based on the year 2000 Report of School Health Statistics Research. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 25:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1297/cpe.25.77
Kubo T (2014) Common approach to childhood obesity in Japan. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 27:581–592. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2014-0047
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280883
Chung J, Park HS, Kim YJ, Yu MH, Park S, Jung SI (2021) Association of hepatic steatosis index with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease diagnosed by non-enhanced CT in a screening population. Diagnostics (Basel) 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11122168
Lee DH (2017) Imaging evaluation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: focused on quantification. Clin Mol Hepatol 23:290–301. https://doi.org/10.3350/cmh.2017.0042
Lee SS, Park SH (2014) Radiologic evaluation of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 20:7392–7402. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7392
Rappsilber J, Ishihama Y, Mann M (2003) Stop and go extraction tips for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization, nanoelectrospray, and LC/MS sample pretreatment in proteomics. Anal Chem 75:663–670. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac026117i
Cox J, Mann M (2008) MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 26:1367–1372. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1511
Cox J, Neuhauser N, Michalski A, Scheltema RA, Olsen JV, Mann M (2011) Andromeda: a peptide search engine integrated into the MaxQuant environment. J Proteome Res 10:1794–1805. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr101065j
Hebert AS, Prasad S, Belford MW, Bailey DJ, McAlister GC, Abbatiello SE, Huguet R, Wouters ER, Dunyach JJ, Brademan DR et al (2018) Comprehensive single-shot proteomics with FAIMS on a hybrid orbitrap mass spectrometer. Anal Chem 90:9529–9537. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02233
Tyanova S, Temu T, Sinitcyn P, Carlson A, Hein MY, Geiger T, Mann M, Cox J (2016) The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat Methods 13:731–740. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3901
Babicki S, Arndt D, Marcu A, Liang Y, Grant JR, Maciejewski A, Wishart DS (2016) Heatmapper: web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W147-153. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw419
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos A, Tsafou KP et al (2015) STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D447-452. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1003
McLellan AD (2009) Exosome release by primary B cells. Crit Rev Immunol 29:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1615/critrevimmunol.v29.i3.20
Krautbauer S, Haberl EM, Eisinger K, Pohl R, Rein-Fischboeck L, Rentero C, Alvarez-Guaita A, Enrich C, Grewal T, Buechler C et al (2017) Annexin A6 regulates adipocyte lipid storage and adiponectin release. Mol Cell Endocrinol 439:419–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.09.033
Naslavsky N, Rahajeng J, Rapaport D, Horowitz M, Caplan S (2007) EHD1 regulates cholesterol homeostasis and lipid droplet storage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:792–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.022
Mackness MI, Arrol S, Abbott C, Durrington PN (1993) Protection of low-density lipoprotein against oxidative modification by high-density lipoprotein associated paraoxonase. Atherosclerosis 104:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9150(93)90183-u
Diallo K, Oppong AK, Lim GE (2019) Can 14–3-3 proteins serve as therapeutic targets for the treatment of metabolic diseases? Pharmacol Res 139:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.11.021
Ma Y, Gao J, Yin J, Gu L, Liu X, Chen S, Huang Q, Lu H, Yang Y, Zhou H et al (2016) Identification of a novel function of adipocyte plasma membrane-associated protein (APMAP) in gestational diabetes mellitus by proteomic analysis of omental adipose tissue. J Proteome Res 15:628–637. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b01030
Guilherme A, Soriano NA, Furcinitti PS, Czech MP (2004) Role of EHD1 and EHBP1 in perinuclear sorting and insulin-regulated GLUT4 recycling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem 279:40062–40075. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M401918200
Xiong Y, Lei QY, Zhao S, Guan KL (2011) Regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis by acetylation of PKM and PEPCK. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 76:285–289. https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.2011.76.010942
D’Souza RF, Masson SWC, Woodhead JST, James SL, MacRae C, Hedges CP, Merry TL (2021) alpha1-Antitrypsin A treatment attenuates neutrophil elastase accumulation and enhances insulin sensitivity in adipose tissue of mice fed a high-fat diet. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 321:E560–E570. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00181.2021
Kubota A, Juanola-Falgarona M, Emmanuele V, Sanchez-Quintero MJ, Kariya S, Sera F, Homma S, Tanji K, Quinzii CM, Hirano M (2019) Cardiomyopathy and altered integrin-actin signaling in Fhl1 mutant female mice. Hum Mol Genet 28:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy299
Aratani Y (2018) Myeloperoxidase: its role for host defense, inflammation, and neutrophil function. Arch Biochem Biophys 640:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2018.01.004
Pruenster M, Vogl T, Roth J, Sperandio M (2016) S100A8/A9: from basic science to clinical application. Pharmacol Ther 167:120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.07.015
Nazari A, Khorramdelazad H, Hassanshahi G, Day AS, Sardoo AM, Fard ET, Abedinzadeh M, Nadimi AE (2017) S100A12 in renal and cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci 191:253–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.10.036
Crouch EC (2000) Surfactant protein-D and pulmonary host defense. Respir Res 1:93–108. https://doi.org/10.1186/rr19
Wang H, Liu B, Wei J (2021) Beta2-microglobulin(B2M) in cancer immunotherapies: biological function, resistance and remedy. Cancer Lett 517:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2021.06.008
Silva RG, Nunes JE, Canduri F, Borges JC, Gava LM, Moreno FB, Basso LA, Santos DS (2007) Purine nucleoside phosphorylase: a potential target for the development of drugs to treat T-cell- and apicomplexan parasite-mediated diseases. Curr Drug Targets 8:413–422. https://doi.org/10.2174/138945007780058997
Qi H, Liu S, Guo C, Wang J, Greenaway FT, Sun MZ (2015) Role of annexin A6 in cancer. Oncol Lett 10:1947–1952. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.3498
Kobayashi T, Shiozaki A, Nako Y, Ichikawa D, Kosuga T, Shoda K, Arita T, Konishi H, Komatsu S, Kubota T et al (2018) Chloride intracellular channel 1 as a switch among tumor behaviors in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 9:23237–23252. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.25296
Wilson MR, Zoubeidi A (2017) Clusterin as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets 21:201–213. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2017.1267142
Wei X, Zhang H (2020) Four and a half LIM domains protein 1 can be as a double-edged sword in cancer progression. Cancer Biol Med 17:270–281. https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0420
Hu Z, Zhou X, Zeng D, Lai J (2022) Shikonin induces cell autophagy via modulating the microRNA -545-3p/guanine nucleotide binding protein beta polypeptide 1 axis, thereby disrupting cellular carcinogenesis in colon cancer. Bioengineered 13:5928–5941. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.2024638
Yu F, Wu W, Liang M, Huang Y, Chen C (2020) Prognostic significance of Rab27A and Rab27B expression in esophageal squamous cell cancer. Cancer Manag Res 12:6353–6361. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S258940
Lohmann K, Masuho I, Patil DN, Baumann H, Hebert E, Steinrucke S, Trujillano D, Skamangas NK, Dobricic V, Huning I et al (2017) Novel GNB1 mutations disrupt assembly and function of G protein heterotrimers and cause global developmental delay in humans. Hum Mol Genet 26:1078–1086. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx018
Li M, Oh TJ, Fan H, Diao J, Zhang K (2020) Syntaxin clustering and optogenetic control for synaptic membrane fusion. J Mol Biol 432:4773–4782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.07.005
Vieira M, Saraiva MJ (2014) Transthyretin: a multifaceted protein. Biomol Concepts 5:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmc-2013-0038
Malaspina A, Kaushik N, de Belleroche J (2000) A 14–3-3 mRNA is up-regulated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord. J Neurochem 75:2511–2520. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0752511.x
Melzer L, Freiman TM, Derouiche A (2021) Rab6A as a pan-astrocytic marker in mouse and human brain, and comparison with other glial markers (GFAP, GS, Aldh1L1, SOX9). Cells 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010072
Wang ZV, Scherer PE (2016) Adiponectin, the past two decades. J Mol Cell Biol 8:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjw011
Dateki S (2017) ACAN mutations as a cause of familial short stature. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 26:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1297/cpe.26.119
Yuan ZY, Cheng LT, Wang ZF, Wu YQ (2021) Desmoplakin and clinical manifestations of desmoplakin cardiomyopathy. Chin Med J (Engl) 134:1771–1779. https://doi.org/10.1097/CM9.0000000000001581
Akerstrom B, Logdberg L, Berggard T, Osmark P, Lindqvist A (2000) alpha(1)-Microglobulin: a yellow-brown lipocalin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1482:172–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-4838(00)00157-6
Schittek B (2012) The multiple facets of dermcidin in cell survival and host defense. J Innate Immun 4:349–360. https://doi.org/10.1159/000336844
Wei H, Wang JY (2021) Role of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor in IgA and IgM transcytosis. Int J Mol Sci 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052284
Kataoka H, Kawaguchi M (2010) Hepatocyte growth factor activator (HGFA): pathophysiological functions in vivo. FEBS J 277:2230–2237. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07640.x
Cnop M, Foufelle F, Velloso LA (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress, obesity and diabetes. Trends Mol Med 18:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2011.07.010
Kolb R, Sutterwala FS, Zhang W (2016) Obesity and cancer: inflammation bridges the two. Curr Opin Pharmacol 29:77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2016.07.005
Saltiel AR, Olefsky JM (2017) Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest 127:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI92035
Thommen DS, Schumacher TN (2018) T cell dysfunction in cancer. Cancer Cell 33:547–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.03.012
Franchina DG, Grusdat M, Brenner D (2018) B-cell metabolic remodeling and cancer. Trends Cancer 4:138–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2017.12.006
Van Grouw JM, Volpe SL (2013) Childhood obesity in America. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 20:396–400. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.med.0000433064.78799.0c
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the paramedical for technical assistance at National Hospital Organization Mie National Hospital.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 21K11572 to YK, and Japan Science and Technology Agency to AE and KI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YK and AE contributed to study concept and design, interpretation of data, and drafting of the manuscript. KI, MT, KI, TT, KK, MN, and NF contributed to the acquisition of data. MI, HN, TF, and KT contributed to study supervision. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Review Committee of Mie University Hospital (Approval No. 3201) and by the institutional ethics board of the National Hospital Organization Mie Hospital (Approval No. 2020-02). All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, Y., Eguchi, A., Imami, K. et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles are associated with pathophysiological condition including metabolic syndrome-related dysmetabolism in children and adolescents with obesity. J Mol Med 102, 23–38 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-023-02386-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-023-02386-5