Abstract
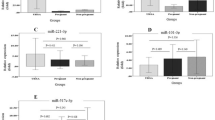
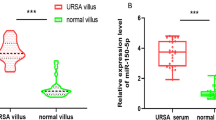
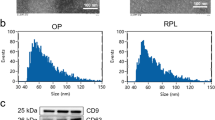
Unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion (URSA) is commonly observed, and seriously affects women’s reproductive health. Excessive interleukin-6 (IL-6) production has been shown to frequently occur and relate to URSA pathogenesis. In this study, the miRNA expression profile in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from URSA patients and normal pregnant (NP) women was assessed by miRNA microarray and real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). MiRNA target prediction tools and luciferase reporter assay were used to detect direct binding between miRNAs and IL6. Functional study of administering anti-IL-6 neutralizing antibody and miR-374c-5p mimics to an URSA animal model was performed to evaluate embryo resorption rates. In the results, compared with NP women, the expression of IL-6 increased markedly in PBMCs and decidual tissues at both mRNA and protein levels, while miR-374c-5p expression decreased significantly. Prediction software and luciferase reporter assay showed that miR-374c-5p binds with IL6 3′UTR via the complementary bases. Transfection of miR-374c-5p mimics into an in vitro HeLa cell line significantly downregulated the expression of IL-6, while transfection of the miR-374c-5p inhibitor induced an opposite result. In the URSA mouse model, miR-374c-5p overexpression reduced the embryo resorption rate significantly, accompanied with decreased expression of IL-6 in the decidua. To sum up, downregulated miR-374c-5p was involved in the pathogenesis of URSA by enhancing IL-6 expression. Modulation of miR-374c-5p expression may be used to regulate IL-6 production for the treatment of URSA.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article or on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
References
Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive M (2013) Definitions of infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss: a committee opinion. Fertil Steril 99:63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.09.023
Wu Z, You Z, Zhang C, Li Z, Su X, Zhang X, Li Y (2012) Association between functional polymorphisms of Foxp3 gene and the occurrence of unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion in a Chinese Han population. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:896458. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/896458
Wang WJ, Hao CF, Yi L, Yin GJ, Bao SH, Qiu LH, Lin QD (2010) Increased prevalence of T helper 17 (Th17) cells in peripheral blood and decidua in unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion patients. J Reprod Immunol 84:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jri.2009.12.003
Mei S, Tan J, Chen H, Chen Y, Zhang J (2010) Changes of CD4+CD25 high regulatory T cells and FOXP3 expression in unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion patients. Fertil Steril 94:0–2247
Bob P, Kanellopoulos-Langevin C, Bleux C, Kinsky R (2006) Antigen-specific modulation of graft-versus-host reactions by two distinct placental factors. Scand J Immunol 28:705–718
Hunter CA, Jones SA (2015) IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat Immunol 16:448–457
Li X, Wang B, Li Y, Wang L, Zhao X, Zhou X, Guo Y, Jiang G, Yao C (2013) The Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg paradigm induced by stachydrine hydrochloride reduces uterine bleeding in RU486-induced abortion mice. J Ethnopharmacol 145:241–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.10.059
Hattori Y, Nakanishi T, Ozaki Y, Nozawa K, Sato T, Sugiura-Ogasawara M (2007) Uterine cervical inflammatory cytokines, interleukin-6 and -8, as predictors of miscarriage in recurrent cases. Am J Reprod Immunol 58:350–357. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0897.2007.00516.x
Arruvito L, Billordo A, Capucchio M, Prada ME, Fainboim L (2009) IL-6 trans-signaling and the frequency of CD4+FOXP3+ cells in women with reproductive failure. J Reprod Immunol 82:158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jri.2009.04.010
Hemmatzadeh M, Shomali N, Yousefzadeh Y, Mohammadi H, Ghasemzadeh A, Yousefi M (2020) MicroRNAs: small molecules with a large impact on pre-eclampsia. J Cell Physiol 235:3235–3248. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29286
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Hympanova L, Krofta L (2016) Gestational hypertension, preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction induce dysregulation of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease associated microRNAs in maternal whole peripheral blood. Thromb Res 137:126–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2015.11.032
Sorensen AE, Poppel MNM, van Desoye G, Damm P, Simmons D, Jensen SM, Dalgaard LT, Investigator G (2021) The predictive value of miR-16, -29a and -134 for early identification of gestational diabetes: a nested analysis of the DALI cohort. Cells 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010170
Tian S, Yu J, Zhang Y, Bian Y, Ma J, Yan J (2020) Overexpression of PTEN regulated by miR-19b and miR-494 in the villous of recurrent spontaneous abortion patients. J Reprod Immunol 140:103133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jri.2020.103133
Qin W, Tang Y, Yang N, Wei X, Wu J (2016) Potential role of circulating microRNAs as a biomarker for unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. Fertil Steril 105(1247–1254):e1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.01.028
Wang N, Chen FE, Long ZW (2017) Mechanism of microRNA-146a/Notch2 signaling regulating IL-6 in Graves ophthalmopathy. Cell Physiol Biochem 41:1285–1297. https://doi.org/10.1159/000464430
Huang HC, Yu HR, Hsu TY, Chen IL, Huang HC, Chang JC, Yang KD (2017) MicroRNA-142-3p and let-7g negatively regulates augmented IL-6 production in neonatal polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Int J Biol Sci 13:690–700. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.17030
He Q, Li F, Li J, Li R, Zhan G, Li G, Du W, Tan H (2017) MicroRNA-26a-interleukin (IL)-6-IL-17 axis regulates the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a murine model. Clin Exp Immunol 187:174–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12838
Zhu X, Liu H, Zhang Z, Wei R, Zhou X, Wang Z, Zhao L, Guo Q, Zhang Y, Chu C et al (2020) MiR-103 protects from recurrent spontaneous abortion via inhibiting STAT1 mediated M1 macrophage polarization. Int J Biol Sci 16:2248–2264. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.46144
Chaouat G, Assal Meliani A, Martal J, Raghupathy R, Elliott JF, Mosmann T, Wegmann TG (1995) IL-10 prevents naturally occurring fetal loss in the CBA x DBA/2 mating combination, and local defect in IL-10 production in this abortion-prone combination is corrected by in vivo injection of IFN-tau. J Immunol 154:4261–4268
Zenclussen AC, Blois S, Stumpo R, Olmos S, Arias K, Malan Borel I, Roux ME, Margni RA (2003) Murine abortion is associated with enhanced interleukin-6 levels at the feto-maternal interface. Cytokine 24:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2003.08.002
Markert UR, Morales-Prieto DM, Fitzgerald JS (2011) Understanding the link between the IL-6 cytokine family and pregnancy: implications for future therapeutics. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 7:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1586/eci.11.60
Tabibzadeh S, Kong QF, Babaknia A, May LT (1995) Progressive rise in the expression of interleukin-6 in human endometrium during menstrual cycle is initiated during the implantation window. Hum Reprod 10:2793–2799. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a135793
Vandermolen DT, Gu Y (1996) Human endometrial interleukin-6 (IL-6): in vivo messenger ribonucleic acid expression, in vitro protein production, and stimulation thereof by IL-1 beta. Fertil Steril 66:741–747
von Wolff M, Stieger S, Lumpp K, Bucking J, Strowitzki T, Thaler CJ (2002) Endometrial interleukin-6 in vitro is not regulated directly by female steroid hormones, but by pro-inflammatory cytokines and hypoxia. Mol Hum Reprod 8:1096–1102. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/8.12.1096
Saifi B, Rezaee SA, Tajik N, Ahmadpour ME, Ashrafi M, Vakili R, Soleimaniasl S, Aflatoonian R, Mehdizadeh M (2014) Th17 cells and related cytokines in unexplained recurrent spontaneous miscarriage at the implantation window. Reprod Biomed Online 29:481–489
Liang PY, Diao LH, Huang CY, Lian RC, Chen X, Li GG, Zhao J, Li YY, He XB, Zeng Y (2015) The pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine profile in peripheral blood of women with recurrent implantation failure. Reprod Biomed Online 31:823–826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2015.08.009
Fu B, Tian Z, Wei H (2014) TH17 cells in human recurrent pregnancy loss and pre-eclampsia. Cell Mol Immunol 11:564–570. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.54
Wang WJ, Hao CF, Qu QL, Wang X, Qiu LH, Lin QD (2010) The deregulation of regulatory T cells on interleukin-17-producing T helper cells in patients with unexplained early recurrent miscarriage. Hum Reprod 25:2591–2596. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deq198
Barbagallo C, Passanisi R, Mirabella F, Cirnigliaro M, Costanzo A, Lauretta G, Barbagallo D, Bianchi C, Pagni F, Castorina S et al (2019) Upregulated microRNAs in membranous glomerulonephropathy are associated with significant downregulation of IL6 and MYC mRNAs. J Cell Physiol 234:12625–12636. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27851
Liu Y, Li C, Wu H, Xie X, Sun Y, Dai M (2018) Paeonol attenuated inflammatory response of endothelial cells via stimulating monocytes-derived exosomal microRNA-223. Front Pharmacol 9:1105. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01105
Gao N, Dong L (2017) MicroRNA-146 regulates the inflammatory cytokines expression in vascular endothelial cells during sepsis. Pharmazie 72:700–704. https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2017.7600
Zheng Q, Zhang D, Yang YU, Cui X, Sun J, Liang C, Qin H, Yang X, Liu S, Yan Q (2017) MicroRNA-200c impairs uterine receptivity formation by targeting FUT4 and alpha1,3-fucosylation. Cell Death Differ 24:2161–2172. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.136
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Wei R, Miao X, Sun S, Liang G, Chu C, Zhao L, Zhu X, Guo Q et al (2020) IL (interleukin)-6 contributes to deep vein thrombosis and is negatively regulated by miR-338-5p. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 40:323–334. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313137
Wang XQ, Li Y, Su X, Zhang L, Liu CM, Liu H, Ma X, Xia H (2018) Haplotype-based association of two SNPs in miR-323b with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion in a Chinese Han population. J Cell Physiol 233:6001–6017. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26415
Huang Y, Huang H, Li M, Zhang X, Liu Y, Wang Y (2017) MicroRNA-374c-5p regulates the invasion and migration of cervical cancer by acting on the Foxc1/snail pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 94:1038–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.150
Hao S, Tian W, Chen Y, Wang L, Jiang Y, Gao B, Luo D (2019) MicroRNA-374c-5p inhibits the development of breast cancer through TATA-box binding protein associated factor 7-mediated transcriptional regulation of DEP domain containing 1. J Cell Biochem 120:15360–15368. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28803
Kim YJ, Yeon Y, Lee WJ, Shin YU, Cho H, Sung YK, Kim DR, Lim HW, Kang MH (2019) Comparison of microRNA expression in tears of normal subjects and Sjogren syndrome patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 60:4889–4895. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.19-27062
Yu Y, Guo R, Zhang Y, Shi H, Sun H, Chu X, Wu X, Lu H, Sun C (2020) miRNA-mRNA profile and regulatory network in stearic acid-treated beta-cell dysfunction. J Endocrinol 246:13–27. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-20-0055
Acknowledgements
We thank Li Han and Guozhen Hei for experimental assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (81873337), the Project of Transformation in High-tech Achievements (2013ZHZX2A0405), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019MH039), Central Government Guides Local Science and Technology Development Fund Projects of Shandong Province (YDZX20203700001407), Research Leader Studio Project of Jinan Science and Technology Bureau (2020GXRC050), Taishan Scholars (Tsqn 201812125), the Academic Promotion Program of Shandong First Medical University (2019RC005), and the Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Project of Shandong Province (202005021490).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Lin Zhao and Li Han; methodology: Chu Chu, Xiaoxiao Fu, and Ke Xu; formal analysis and investigation: Ran Wei and Xiaoxiao Zhu; writing — original draft preparation: Lin Zhao and Guozhen Hei; writing — review and editing: Zhen Zhang and Xia Li; funding acquisition: Qiang Guo and Xia Li; resources: Xia Li; supervision: Xia Li. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key messages
• URSA has a serious impact on women’s reproductive health.
• IL-6 production has been shown to frequently occur and relate to URSA pathogenesis.
• Downregulated miR-374c-5p was involved in the pathogenesis of URSA by enhancing IL6 expression.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Han, L., Hei, G. et al. Diminished miR-374c-5p negatively regulates IL (interleukin)-6 in unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. J Mol Med 100, 1043–1056 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-022-02178-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-022-02178-3