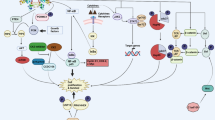
Abstract
Gene transcription is strictly controlled by transcriptional complexes, which are assemblies of transcription factors, transcriptional regulators, and co-regulators. Mammalian genomes encode two C-terminal-binding proteins (CtBPs), CtBP1 and CtBP2, which are both well-known transcriptional corepressors of oncogenic processes. Their overexpression in tumors is associated with malignant behavior, such as uncontrolled cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, as well as with an increase in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. CtBPs coordinate with other transcriptional regulators, such as histone deacetylases (HDACs) and histone acetyltransferases (p300 and CBP [CREBP-binding protein]) that contain the PXDLS motif, and with transcription factors to assemble transcriptional complexes that dock onto the promoters of genes to initiate gene transcription. Emerging evidence suggests that CtBPs function as both corepressors and coactivators in different biological processes ranging from apoptosis to inflammation and osteogenesis. Therapeutic targeting of CtBPs or the interactions required to form transcriptional complexes has also shown promising effects in preventing disease progression. This review summarizes the most recent progress in the study of CtBP functions and therapeutic inhibitors in different biological processes. This knowledge may enable a better understanding of the complexity of the roles of CtBPs, while providing new insights into therapeutic strategies that target CtBPs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dcona MM, Morris BL, Ellis KC, Grossman SR (2017) CtBP- an emerging oncogene and novel small molecule drug target: advances in the understanding of its oncogenic action and identification of therapeutic inhibitors. Cancer Biol Ther 18(6):379–391
Chinnadurai G (2007) Transcriptional regulation by C-terminal binding proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39(9):1593–1607
Blevins MA, Huang M, Zhao R (2017) The role of CtBP1 in oncogenic processes and its potential as a therapeutic target. Mol Cancer Ther 16(6):981–990
Wang Y, Che S, Cai G, He Y, Chen J, Xu W (2016) Expression and prognostic significance of CTBP2 in human gliomas. Oncol Lett 12(4):2429–2434
Hubler D, Rankovic M, Richter K, Lazarevic V, Altrock WD, Fischer KD et al (2012) Differential spatial expression and subcellular localization of CtBP family members in rodent brain. PLoS One 7(6):e39710
Hildebrand JD, Soriano P (2002) Overlapping and unique roles for C-terminal binding protein 1 (CtBP1) and CtBP2 during mouse development. Mol Cell Biol 22(15):5296–5307
Molloy DP, Barral PM, Gallimore PH, Grand RJ (2007) The effect of CtBP1 binding on the structure of the C-terminal region of adenovirus 12 early region 1A. Virology 363(2):342–356
Hilbert BJ, Grossman SR, Schiffer CA, Royer WE Jr (2014) Crystal structures of human CtBP in complex with substrate MTOB reveal active site features useful for inhibitor design. FEBS Lett 588(9):1743–1748
Stankiewicz TR, Gray JJ, Winter AN, Linseman DA (2014) C-terminal binding proteins: central players in development and disease. Biomol Concepts 5(6):489–511
Zhang Q, Piston DW, Goodman RH (2002) Regulation of corepressor function by nuclear NADH. Science 295(5561):1895–1897
Lin X, Sun B, Liang M, Liang YY, Gast A, Hildebrand J et al (2003) Opposed regulation of corepressor CtBP by SUMOylation and PDZ binding. Mol Cell 11(5):1389–1396
Zhang Q, Nottke A, Goodman RH (2005) Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 mediates CtBP phosphorylation and degradation in UV-triggered apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(8):2802–2807
Wang SY, Iordanov M, Zhang Q (2006) c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase promotes apoptosis by down-regulating the transcriptional co-repressor CtBP. J Biol Chem 281(46):34810–34815
Lee HJ, Zheng JJ (2010) PDZ domains and their binding partners: structure, specificity, and modification. Cell Commun Signal 8:8
Nardini M, Svergun D, Konarev PV, Spano S, Fasano M, Bracco C et al (2006) The C-terminal domain of the transcriptional corepressor CtBP is intrinsically unstructured. Protein Sci 15(5):1042–1050
Bellesis AG, Jecrois AM, Hayes JA, Schiffer CA, Royer WE Jr (2018) Assembly of human C-terminal binding protein (CtBP) into tetramers. J Biol Chem 293(23):9101–9112
Nichols JC, Schiffer CA, Royer Jr WE (2021) NAD(H) phosphates mediate tetramer assembly of human C-terminal binding protein (CtBP). J Biol Chem 296:100351
Jecrois AM, Dcona MM, Deng X, Bandyopadhyay D, Grossman SR, Schiffer CA et al (2021) Cryo-EM structure of CtBP2 confirms tetrameric architecture. Structure 29(4):310–319e5
Kornberg RD (2007) The molecular basis of eukaryotic transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(32):12955–12961
Lee TI, Young RA (2013) Transcriptional regulation and its misregulation in disease. Cell 152(6):1237–1251
Wang Z, Wang P, Li Y, Peng H, Zhu Y, Mohandas N et al (2021) Interplay between cofactors and transcription factors in hematopoiesis and hematological malignancies. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):24
Haberle V, Stark A (2018) Eukaryotic core promoters and the functional basis of transcription initiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19(10):621–637
Arnold PR, Wells AD, Li XC (2019) Diversity and emerging roles of enhancer RNA in regulation of gene expression and cell fate. Front Cell Dev Biol 7:377
Papadopoulou V, Postigo A, Sanchez-Tillo E, Porter AC, Wagner SD (2010) ZEB1 and CtBP form a repressive complex at a distal promoter element of the BCL6 locus. Biochem J 427(3):541–550
Wang H, Xiao Z, Zheng J, Wu J, Hu XL, Yang X et al (2019) ZEB1 Represses neural differentiation and cooperates with CTBP2 to dynamically regulate cell migration during neocortex development. Cell Rep 27(8):2335–2353e6
Chinnadurai G (2009) The transcriptional corepressor CtBP: a foe of multiple tumor suppressors. Cancer Res 69(3):731–734
Zhao LJ, Kuppuswamy M, Vijayalingam S, Chinnadurai G (2009) Interaction of ZEB and histone deacetylase with the PLDLS-binding cleft region of monomeric C-terminal binding protein 2. BMC Mol Biol 10:89
Bialkowska AB, Yang VW, Mallipattu SK (2017) Kruppel-like factors in mammalian stem cells and development. Development 144(5):737–754
Sue N, Jack BH, Eaton SA, Pearson RC, Funnell AP, Turner J et al (2008) Targeted disruption of the basic Kruppel-like factor gene (Klf3) reveals a role in adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 28(12):3967–3978
van Vliet J, Turner J, Crossley M (2000) Human Kruppel-like factor 8: a CACCC-box binding protein that associates with CtBP and represses transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 28(9):1955–1962
Pollak NM, Hoffman M, Goldberg IJ, Drosatos K (2018) Kruppel-like factors: crippling and un-crippling metabolic pathways. JACC Basic Transl Sci 3(1):132–156
Dewi V, Kwok A, Lee S, Lee MM, Tan YM, Nicholas HR et al (2015) Phosphorylation of Kruppel-like factor 3 (KLF3/BKLF) and C-terminal binding protein 2 (CtBP2) by homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2) modulates KLF3 DNA binding and activity. J Biol Chem 290(13):8591–8605
Quinlan KG, Verger A, Kwok A, Lee SH, Perdomo J, Nardini M et al (2006) Role of the C-terminal binding protein PXDLS motif binding cleft in protein interactions and transcriptional repression. Mol Cell Biol 26(21):8202–8213
Shi Y, Sawada J, Sui G, el Affar B, Whetstine JR, Lan F et al (2003) Coordinated histone modifications mediated by a CtBP co-repressor complex. Nature 422(6933):735–738
Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, Mulligan P, Whetstine JR, Cole PA et al (2004) Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell 119(7):941–953
Barroilhet L, Yang J, Hasselblatt K, Paranal RM, Ng SK, Rauh-Hain JA et al (2013) C-terminal binding protein-2 regulates response of epithelial ovarian cancer cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Oncogene 32(33):3896–3903
Kim JH, Cho EJ, Kim ST, Youn HD (2005) CtBP represses p300-mediated transcriptional activation by direct association with its bromodomain. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12(5):423–428
Zhao LJ, Subramanian T, Zhou Y, Chinnadurai G (2006) Acetylation by p300 regulates nuclear localization and function of the transcriptional corepressor CtBP2. J Biol Chem 281(7):4183–4189
Senyuk V, Sinha KK, Nucifora G (2005) Corepressor CtBP1 interacts with and specifically inhibits CBP activity. Arch Biochem Biophys 441(2):168–173
Pelka P, Ablack JN, Torchia J, Turnell AS, Grand RJ, Mymryk JS (2009) Transcriptional control by adenovirus E1A conserved region 3 via p300/CBP. Nucleic Acids Res 37(4):1095–1106
Zhang CL, McKinsey TA, Lu JR, Olson EN (2001) Association of COOH-terminal-binding protein (CtBP) and MEF2-interacting transcription repressor (MITR) contributes to transcriptional repression of the MEF2 transcription factor. J Biol Chem 276(1):35–39
Kim SC, Kim YS, Jetten AM (2005) Kruppel-like zinc finger protein Gli-similar 2 (Glis2) represses transcription through interaction with C-terminal binding protein 1 (CtBP1). Nucleic Acids Res 33(21):6805–6815
Fernandes I, Bastien Y, Wai T, Nygard K, Lin R, Cormier O et al (2003) Ligand-dependent nuclear receptor corepressor LCoR functions by histone deacetylase-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Mol Cell 11(1):139–150
Quinlan KG, Nardini M, Verger A, Francescato P, Yaswen P, Corda D et al (2006) Specific recognition of ZNF217 and other zinc finger proteins at a surface groove of C-terminal binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol 26(21):8159–8172
Nardini M, Spano S, Cericola C, Pesce A, Massaro A, Millo E et al (2003) CtBP/BARS: a dual-function protein involved in transcription co-repression and Golgi membrane fission. EMBO J 22(12):3122–3130
Bruton RK, Pelka P, Mapp KL, Fonseca GJ, Torchia J, Turnell AS et al (2008) Identification of a second CtBP binding site in adenovirus type 5 E1A conserved region 3. J Virol 82:8476–8486
Hickabottom M, Parker GA, Freemont P, Crook T, Allday MJ (2002) Two nonconsensus sites in the Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein EBNA3A cooperate to bind the co-repressor carboxyl-terminal-binding protein (CtBP). J Biol Chem 277(49):47197–47204
Gocke CB, Yu H (2008) ZNF198 stabilizes the LSD1-CoREST-HDAC1 complex on chromatin through its MYM-type zinc fingers. PLoS One 3:e3255
Du K, Zhang X, Lou Z, Guo P, Zhang F, Wang B et al (2018) MicroRNA485-3p negatively regulates the transcriptional co-repressor CtBP1 to control the oncogenic process in osteosarcoma cells. Int J Biol Sci 14(11):1445–1456
Deng H, Liu J, Deng Y, Han G, Shellman YG, Robinson SE et al (2013) CtBP1 is expressed in melanoma and represses the transcription of p16INK4a and Brca1. J Invest Dermatol 133(5):1294–1301
Chawla AT, Chougoni KK, Joshi PJ, Cororaton AD, Memari P, Stansfield JC et al (2019) CtBP-a targetable dependency for tumor-initiating cell activity and metastasis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncogenesis 8:55
Paliwal S, Pande S, Kovi RC, Sharpless NE, Bardeesy N, Grossman SR (2006) Targeting of C-terminal binding protein (CtBP) by ARF results in p53-independent apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 26(6):2360–2372
Wang R, Asangani IA, Chakravarthi BV, Ateeq B, Lonigro RJ, Cao Q et al (2012) Role of transcriptional corepressor CtBP1 in prostate cancer progression. Neoplasia 14:905–914
Birts CN, Harding R, Soosaipillai G, Halder T, Azim-Araghi A, Darley M et al (2010) Expression of CtBP family protein isoforms in breast cancer and their role in chemoresistance. Biol Cell 103:1–19
Zhang Y, Kwok JS, Choi PW, Liu M, Yang J, Singh M et al (2016) Pinin interacts with C-terminal binding proteins for RNA alternative splicing and epithelial cell identity of human ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 7:11397–11411
Senyuk V, Chakraborty S, Mikhail FM, Zhao R, Chi Y, Nucifora G (2002) The leukemia-associated transcription repressor AML1/MDS1/EVI1 requires CtBP to induce abnormal growth and differentiation of murine hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 21:3232–3240
Wang P, Yu B, Wang C, Zhou S (2020) C-terminal of E1A binding protein 2 promotes the malignancy of osteosarcoma cells via JAK1/Stat3 signaling. J Cell Commun Signal 14:67–76
Straza MW, Paliwal S, Kovi RC, Rajeshkumar B, Trenh P, Parker D et al (2010) Therapeutic targeting of C-terminal binding protein in human cancer. Cell Cycle 9:3740–3750
Kovi RC, Paliwal S, Pande S, Grossman SR (2010) An ARF/CtBP2 complex regulates BH3-only gene expression and p53-independent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 17:513–521
Grooteclaes M, Deveraux Q, Hildebrand J, Zhang Q, Goodman RH, Frisch SM (2003) C-terminal-binding protein corepresses epithelial and proapoptotic gene expression programs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:4568–4573
Li C, Xiao XQ, Qian YH, Zhou ZY (2019) The CtBP1-p300-FOXO3a transcriptional complex represses the expression of the apoptotic regulators Bax and Bim in human osteosarcoma cells. J Cell Physiol 234:22365–22377
Duan N, Zhang W, Li Z, Sun L, Song T, Yu Z et al (2021) Overexpression of HIPK2 removes the transrepression of proapoptotic genes mediated by the CtBP1-p300-FOXO3a complex and increases the chemosensitivity in osteosarcoma cells. J Cancer 12:1826–1837
Ding B, Yuan F, Damle PK, Litovchick L, Drapkin R, Grossman SR (2020) CtBP determines ovarian cancer cell fate through repression of death receptors. Cell Death Dis 11:286
Paliwal S, Kovi RC, Nath B, Chen YW, Lewis BC, Grossman SR (2007) The alternative reading frame tumor suppressor antagonizes hypoxia-induced cancer cell migration via interaction with the COOH-terminal binding protein corepressor. Cancer Res 67:9322–9329
Yu Y, Chen L, Zhao G, Li H, Guo Q, Zhu S et al (2020) RBBP8/CtIP suppresses P21 expression by interacting with CtBP and BRCA1 in gastric cancer. Oncogene 39:1273–1289
Mroz EA, Baird AH, Michaud WA, Rocco JW (2008) COOH-terminal binding protein regulates expression of the p16INK4A tumor suppressor and senescence in primary human cells. Cancer Res 68:6049–6053
Di Cristofano A, Pandolfi PP (2000) The multiple roles of PTEN in tumor suppression. Cell 100:387–390
Lee YR, Chen M, Pandolfi PP (2018) The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor: new modes and prospects. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19:547–562
Sansal I, Sellers WR (2004) The biology and clinical relevance of the PTEN tumor suppressor pathway. J Clin Oncol 22:2954–2963
Patel S, Alam A, Pant R, Chattopadhyay S (2019) Wnt signaling and its significance within the tumor microenvironment: novel therapeutic insights. Front Immunol 10:2872
Jung YS, Park JI (2020) Wnt signaling in cancer: therapeutic targeting of Wnt signaling beyond beta-catenin and the destruction complex. Exp Mol Med 52:183–191
Pai SG, Carneiro BA, Mota JM, Costa R, Leite CA, Barroso-Sousa R et al (2017) Wnt/beta-catenin pathway: modulating anticancer immune response. J Hematol Oncol 10:101
Hamada F, Bienz M (2004) The APC tumor suppressor binds to C-terminal binding protein to divert nuclear beta-catenin from TCF. Dev Cell 7:677–685
Yu Y, Hann SS (2019) Novel tumor suppressor lncRNA growth arrest-specific 5 (GAS5) in human cancer. Onco Targets Ther 12:8421–8436
Ma C, Shi X, Zhu Q, Li Q, Liu Y, Yao Y et al (2016) The growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5): a pivotal tumor suppressor long noncoding RNA in human cancers. Tumour Biol 37:1437–1444
Yang J, Hao T, Sun J, Wei P, Zhang H (2019) Long noncoding RNA GAS5 modulates alpha-Solanine-induced radiosensitivity by negatively regulating miR-18a in human prostate cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother 112:108656
Zhang X, Du K, Lou Z, Ding K, Zhang F, Zhu J et al (2019) The CtBP1-HDAC1/2-IRF1 transcriptional complex represses the expression of the long noncoding RNA GAS5 in human osteosarcoma cells. Int J Biol Sci 15:1460–1471
Yeung KT, Yang J (2017) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Mol Oncol 11:28–39
Ribatti D, Tamma R, Annese T (2020) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: a historical overview. Transl Oncol 13:100773
Aghdassi A, Sendler M, Guenther A, Mayerle J, Behn CO, Heidecke CD et al (2012) Recruitment of histone deacetylases HDAC1 and HDAC2 by the transcriptional repressor ZEB1 downregulates E-cadherin expression in pancreatic cancer. Gut 61:439–448
Postigo AA, Dean DC (1999) ZEB represses transcription through interaction with the corepressor CtBP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:6683–6688
Pena C, Garcia JM, Garcia V, Silva J, Dominguez G, Rodriguez R et al (2006) The expression levels of the transcriptional regulators p300 and CtBP modulate the correlations between SNAIL, ZEB1, E-cadherin and vitamin D receptor in human colon carcinomas. Int J Cancer 119:2098–2104
Ichikawa K, Kubota Y, Nakamura T, Weng JS, Tomida T, Saito H et al (2015) MCRIP1, an ERK substrate, mediates ERK-induced gene silencing during epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating the co-repressor CtBP. Mol Cell 58:35–46
Di LJ, Fernandez AG, De Siervi A, Longo DL, Gardner K (2010) Transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 expression by a metabolic switch. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1406–1413
Tripathi MK, Misra S, Khedkar SV, Hamilton N, Irvin-Wilson C, Sharan C et al (2005) Regulation of BRCA2 gene expression by the SLUG repressor protein in human breast cells. J Biol Chem 280:17163–17171
Minard ME, Ellis LM, Gallick GE (2006) Tiam1 regulates cell adhesion, migration and apoptosis in colon tumor cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 23:301–313
Izumi D, Toden S, Ureta E, Ishimoto T, Baba H, Goel A (2019) TIAM1 promotes chemoresistance and tumor invasiveness in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis 10:267
Paliwal S, Ho N, Parker D, Grossman SR (2012) CtBP2 promotes human cancer cell migration by transcriptional activation of Tiam1. Genes Cancer 3:481–490
Patel J, Baranwal S, Love IM, Patel NJ, Grossman SR, Patel BB (2014) Inhibition of C-terminal binding protein attenuates transcription factor 4 signaling to selectively target colon cancer stem cells. Cell Cycle 13:3506–3518
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Davudian S, Shirjang S, Baradaran B (2017) The different mechanisms of cancer drug resistance: a brief review. Adv Pharm Bull 7:339–348
Jin W, Scotto KW, Hait WN, Yang JM (2007) Involvement of CtBP1 in the transcriptional activation of the MDR1 gene in human multidrug resistant cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 74:851–859
Chen X, Zhang Q, Dang X, Song T, Wang Y, Yu Z et al (2021) Targeting the CtBP1-FOXM1 transcriptional complex with small molecules to overcome MDR1-mediated chemoresistance in osteosarcoma cancer stem cells. J Cancer 12:482–497
Chen Z, Dong WH, Chen Q, Li QG, Qiu ZM (2019) Downregulation of miR-199a-3p mediated by the CtBP2-HDAC1-FOXP3 transcriptional complex contributes to acute lung injury by targeting NLRP1. Int J Biol Sci 15:2627–2640
Chen Z, Dong WH, Qiu ZM, Li QG (2020) The monocyte-derived exosomal CLMAT3 activates the CtBP2-p300-NF-kappaB transcriptional complex to induce proinflammatory cytokines in ALI. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 21:1100–1110
Zhou P, Wan X, Zou Y, Chen Z, Zhong A (2020) Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) is activated by the CtBP2-p300-AP1 transcriptional complex in chronic renal failure. Int J Biol Sci 16:204–215
Li H, Zhang C, Yang C, Blevins M, Norris D, Zhao R et al (2020) C-terminal binding proteins 1 and 2 in traumatic brain injury-induced inflammation and their inhibition as an approach for anti-inflammatory treatment. Int J Biol Sci 16:1107–1120
Sun X, Xiao L, Chen J, Chen X, Chen X, Yao S et al (2020) DNA methylation is involved in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis by regulating CtBP expression and CtBP-mediated signaling. Int J Biol Sci 16:994–1009
Zhang W, Duan N, Zhang Q, Song T, Li Z, Chen X et al (2018) The intracellular NADH level regulates atrophic nonunion pathogenesis through the CtBP2-p300-Runx2 transcriptional complex. Int J Biol Sci 14:2023–2236
Johnson ER, Matthay MA (2010) Acute lung injury: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 23:243–252
Goodman RB, Pugin J, Lee JS, Matthay MA (2003) Cytokine-mediated inflammation in acute lung injury. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14:523–535
Sureshbabu A, Muhsin SA, Choi ME (2016) TGF-beta signaling in the kidney: profibrotic and protective effects. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 310:F596–F606
Meng XM, Tang PM, Li J, Lan HY (2015) TGF-beta/Smad signaling in renal fibrosis. Front Physiol 6:82
Zhao Z, Hao D, Wang L, Li J, Meng Y, Li P et al (2019) CtBP promotes metastasis of breast cancer through repressing cholesterol and activating TGF-beta signaling. Oncogene 38:2076–2091
Li HJ, Ray SK, Pan N, Haigh J, Fritzsch B, Leiter AB (2019) Intestinal Neurod1 expression impairs paneth cell differentiation and promotes enteroendocrine lineage specification. Sci Rep 9:19489
Ray SK, Li HJ, Metzger E, Schule R, Leiter AB (2014) CtBP and associated LSD1 are required for transcriptional activation by NeuroD1 in gastrointestinal endocrine cells. Mol Cell Biol 34:2308–2317
Lee B, Villarreal-Ponce A, Fallahi M, Ovadia J, Sun P, Yu QC et al (2014) Transcriptional mechanisms link epithelial plasticity to adhesion and differentiation of epidermal progenitor cells. Dev Cell 29:47–58
Boxer LD, Barajas B, Tao S, Zhang J, Khavari PA (2014) ZNF750 interacts with KLF4 and RCOR1, KDM1A, and CTBP1/2 chromatin regulators to repress epidermal progenitor genes and induce differentiation genes. Genes Dev 28:2013–2026
Achouri Y, Noel G, Van Schaftingen E (2007) 2-Keto-4-methylthiobutyrate, an intermediate in the methionine salvage pathway, is a good substrate for CtBP1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:903–906
Korwar S, Morris BL, Parikh HI, Coover RA, Doughty TW, Love IM et al (2016) Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of substrate-competitive inhibitors of C-terminal binding protein (CtBP). Bioorg Med Chem 24:2707–2715
May T, Yang J, Shoni M, Liu S, He H, Gali R et al (2013) BRCA1 expression is epigenetically repressed in sporadic ovarian cancer cells by overexpression of C-terminal binding protein 2. Neoplasia 15:600–608
Hilbert BJ, Morris BL, Ellis KC, Paulsen JL, Schiffer CA, Grossman SR et al (2015) Structure-guided design of a high affinity inhibitor to human CtBP. ACS Chem Biol 10:1118–1127
Sumner ET, Chawla AT, Cororaton AD, Koblinski JE, Kovi RC, Love IM et al (2017) Transforming activity and therapeutic targeting of C-terminal-binding protein 2 in Apc-mutated neoplasia. Oncogene 36:4810–4816
Dcona MM, Damle PK, Zarate-Perez F, Morris BL, Nawaz Z, Dennis MJ et al (2019) Active-site tryptophan, the target of antineoplastic C-terminal binding protein inhibitors, mediates inhibitor disruption of CtBP oligomerization and transcription coregulatory activities. Mol Pharmacol 96:99–108
Birts CN, Nijjar SK, Mardle CA, Hoakwie F, Duriez PJ, Blaydes JP et al (2013) A cyclic peptide inhibitor of C-terminal binding protein dimerization links metabolism with mitotic fidelity in breast cancer cells. Chem Sci 4:3046–3057
Blevins MA, Kouznetsova J, Krueger AB, King R, Griner LM, Hu X et al (2015) Small molecule, NSC95397, inhibits the CtBP1-protein partner interaction and CtBP1-mediated transcriptional repression. J Biomol Screen 20:663–672
Dubey NK, Peng BY, Lin CM, Wang PD, Wang JR, Chan CH et al (2018) NSC 95397 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells through MKP-1 and the ERK1/2 pathway. Int J Mol Sci 19(6):1625
Larsson DE, Wickstrom M, Hassan S, Oberg K, Granberg D (2010) The cytotoxic agents NSC-95397, brefeldin A, bortezomib and sanguinarine induce apoptosis in neuroendocrine tumors in vitro. Anticancer Res 30(1):149–156
Jemaa M, Mischitelli M, Fezai M, Almasry M, Faggio C, Lang F (2016) stimulation of suicidal erythrocyte death by the CDC25 inhibitor NSC-95397. Cell Physiol Biochem 40(3–4):597–607
Berg MG, Wan L, Younis I, Diem MD, Soo M, Wang C et al (2012) A quantitative high-throughput in vitro splicing assay identifies inhibitors of spliceosome catalysis. Mol Cell Biol 32(7):1271–1283
Chen X, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Song T, Yu Z, Li Z et al (2020) NSM00158 specifically disrupts the CtBP2-p300 interaction to reverse CtBP2-mediated transrepression and prevent the occurrence of nonunion. Mol Cells 43(6):517–529
Funding
This study was supported by the Key Research and Development Project of Jiangxi Province (Social Development Field, No. 20202BBGL73059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z. The transrepression and transactivation roles of CtBPs in the pathogenesis of different diseases. J Mol Med 99, 1335–1347 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-021-02107-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-021-02107-w