Abstract
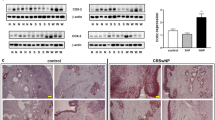
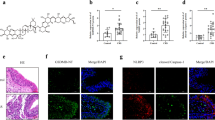
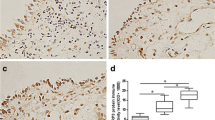
Numerous studies have shown that microbiomes play an important role in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). In addition to a known short pentraxin, C-reactive protein, long pentraxin 3 (PTX3) belongs to pentraxin family which detects conserved microbial pentraxin motifs and mobilizes early defense against foreign invaders, but its participation in CRS remains unclear. In the present study, through an intensive screening, peptidoglycan (PGN) was selected as a main material to investigate the action mechanism of a cell wall component on CRS without nasal polyps (CRSsNP) nasal mucosa-derived fibroblasts and the PTX3 expression in human nasal mucosa tissue and discharge. The PGN not only enhanced PTX3 mRNA and protein production in cells but also caused marked PTX3 secretion into extracellular space. The pharmacological interventions indicated that the PTX3 induction was mediated mainly through toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), phosphoinositide-phospholipase C (PI-PLC), protein kinase C (PKC), NF-κB, and cAMP response element binding protein (CREB), which was further confirmed by the observations that a direct PKC activator (phorbol ester) had a similar inductory effect on PTX3 expression/production and the siRNA interference knockdown of PKCμ/δ, NF-κB, and CREB compromised PTX3 production. Meanwhile, PTX3 was found to be overexpressed/produced in nasal mucosa and discharge/secretion of the CRSsNP patients. Collectively, we first demonstrated here that PGN enhances PTX3 expression and release in nasal fibroblasts through TLR2, PI-PLC, PKCμ/δ, NF-κB, and CREB signaling pathways. The PTX3 is overexpressed in nasal mucosa and discharge/secretion of CRSsNP patients, revealing its possible importance in CRSsNP development and progression.
Key messages
-
Long pentraxin 3 (PTX3) is highly expressed in nasal mucosa and discharge/secretion of patients of chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps (CRSsNP).
-
The bacteria cell wall component-peptidoglycan (PGN) causes PTX3 expression in CRSsNP nasal mucosa-derived fibroblasts, contributing to the PTX3 increase in tissues.
-
PGN induces PTX3 expression through a previously known IκB/NF-κB and a novel PKCμ/δ and CREB signaling pathway.
-
The PTX3 may be used as a biomarker for CRS.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CREB:
-
cAMP response element binding protein
- CRSsNP:
-
Chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps
- CRSwNP:
-
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
- PI-PLC:
-
Phosphoinositide-phospholipase C
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PTX3:
-
Pentraxin 3
- PGN:
-
Peptidoglycan
- TLR :
-
Toll-like receptor
- hNMDFs:
-
Human nasal mucosa-derived fibroblasts
References
Pleis JR, Ward BW, Lucas JW (2010) Summary health statistics for U.S. adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2009. Vital Health Stat 10:1–207
Hamilos DL (2011) Chronic rhinosinusitis: epidemiology and medical management. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128:693–707
Tomassen P, Van Zele T, Zhang N, Perez-Novo C, Van Bruaene N, Gevaert P, Bachert C (2011) Pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 8:115–120
Van Crombruggen K, Zhang N, Gevaert P, Tomassen P, Bachert C (2011) Pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis: inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128:728–732
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, Cohen N, Cervin A, Douglas R, Gevaert P et al (2012) European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. Rhinol Suppl 3 p preceding table of contents:1–298
Wood AJ, Douglas RG (2010) Pathogenesis and treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis. Postgrad Med J 86:359–364
Niederfuhr A, Kirsche H, Riechelmann H, Wellinghausen N (2009) The bacteriology of chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135:131–136
Wertheim HFL, Melles DC, Vos MC, van Leeuwen W, van Belkum A, Verbrugh HA, Nouwen JL (2005) The role of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infections. Lancet Infect Dis 5:751–762
Lee JT, Frank DN, Ramakrishnan V (2016) Microbiome of the paranasal sinuses: update and literature review. Am J Rhinol Allergy 30:3–16
Su W, Jiang Y (2015) Bacterial culture analysis for patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with or without polyps. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 40:1253–1257
Lee CW, Chung SW, Bae MJ, Song S, Kim SP, Kim K (2015) Peptidoglycan up-regulates CXCL8 expression via multiple pathways in monocytes/macrophages. Biomol Ther 23:564–570
Lee SA, Kim SM, Son YH, Lee CW, Chung SW, Eo SK, Rhim BY, Kim K (2011) Peptidoglycan enhances secretion of monocyte chemoattractants via multiple signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 408:132–138
Yamamoto K, Kawamura I, Ito J, Mitsuyama M (2006) Modification of allergic inflammation in murine model of rhinitis by different bacterial ligands: involvement of mast cells and dendritic cells. Clin Exp Allergy 36:760–769
Tsai Y-J, Chi JC-Y, Hao C-Y, Wu W-B (2018) Peptidoglycan induces bradykinin receptor 1 expression through toll-like receptor 2 and NF-κB signaling pathway in human nasal mucosa-derived fibroblasts of chronic rhinosinusitis patients. J Cell Physiol 233:7226–7238
Mantovani A, Valentino S, Gentile S, Inforzato A, Bottazzi B, Garlanda C (2013) The long pentraxin PTX3: a paradigm for humoral pattern recognition molecules. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1285:1–14
Daigo K, Mantovani A, Bottazzi B (2014) The yin-yang of long pentraxin PTX3 in inflammation and immunity. Immunol Lett 161:38–43
Doni A, Musso T, Morone D, Bastone A, Zambelli V, Sironi M, Castagnoli C, Cambieri I, Stravalaci M, Pasqualini F, Laface I, Valentino S, Tartari S, Ponzetta A, Maina V, Barbieri SS, Tremoli E, Catapano AL, Norata GD, Bottazzi B, Garlanda C, Mantovani A (2015) An acidic microenvironment sets the humoral pattern recognition molecule PTX3 in a tissue repair mode. J Exp Med 212:905–925
Rua R, McGavern DB (2015) Pentraxin 3 innately preps damaged tissue for wound healing. J Exp Med 212:829–829
Bonavita E, Gentile S, Rubino M, Maina V, Papait R, Kunderfranco P, Greco C, Feruglio F, Molgora M, Laface I, Tartari S, Doni A, Pasqualini F, Barbati E, Basso G, Galdiero MR, Nebuloni M, Roncalli M, Colombo P, Laghi L, Lambris JD, Jaillon S, Garlanda C, Mantovani A (2015) PTX3 is an extrinsic oncosuppressor regulating complement-dependent inflammation in cancer. Cell 160:700–714
Maina V, Cotena A, Doni A, Nebuloni M, Pasqualini F, Milner CM, Day AJ, Mantovani A, Garlanda C (2009) Coregulation in human leukocytes of the long pentraxin PTX3 and TSG-6. J Leukoc Biol 86:123–132
Inforzato A, Baldock C, Jowitt TA, Holmes DF, Lindstedt R, Marcellini M, Rivieccio V, Briggs DC, Kadler KE, Verdoliva A, Bottazzi B, Mantovani A, Salvatori G, Day AJ (2010) The angiogenic inhibitor long pentraxin PTX3 forms an asymmetric octamer with two binding sites for FGF2. J Biol Chem 285:17681–17692
He X, Han B, Liu M (2007) Long pentraxin 3 in pulmonary infection and acute lung injury. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 292:L1039–L1049
Yildirim YS, Apuhan T, Kocoglu E, Simsek T, Kazaz H (2011) High sensitivity C-reactive protein levels in chronic rhinosinusitis and allergic rhinitis. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 21:266–269
Kim HS, Won S, Lee EK, Chun YH, Yoon J-S, Kim HH, Kim JT (2016) Pentraxin 3 as a clinical marker in children with lower respiratory tract infection. Pediatr Pulmonol 51:42–48
Tsai YJ, Hao SP, Chen CL, Lin BJ, Wu WB (2015) Involvement of B2 receptor in bradykinin-induced proliferation and proinflammatory effects in human nasal mucosa-derived fibroblasts isolated from chronic rhinosinusitis patients. PLoS One 10:e0126853
Lai T-H, Shieh J-M, Tsou C-J, Wu W-B (2015) Gold nanoparticles induce heme oxygenase-1 expression through Nrf2 activation and Bach1 export in human vascular endothelial cells. Int J Nanomedicine 10:5925–5939
Zhang S, Zhu Y-T, Chen S-Y, He H, Tseng SCG (2014) Constitutive expression of pentraxin 3 (PTX3) protein by human amniotic membrane cells leads to formation of the heavy chain (HC)-hyaluronan (HA)-PTX3 complex. J Biol Chem 289:13531–13542
Hsu J, Peters AT (2011) Pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp. Am J Rhinol Allergy 25:285–290
Morrison DC, Jacobs DM (1976) Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry 13:813–818
Murthy KS, Makhlouf GM (1995) Agonist-mediated activation of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C and D in intestinal smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol 48:293–304
Wu-Zhang AX, Newton AC (2013) Protein kinase C pharmacology: refining the toolbox. Biochem J 452:195–209
Ho J, Hamizan AW, Alvarado R, Rimmer J, Sewell WA, Harvey RJ (2018) Systemic predictors of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 32:252–257
Vetter SW (2015) Chapter Five - Glycated serum albumin and AGE receptors. In: Makowski GS (ed) Advances in clinical chemistry. Elsevier, pp 205–275
Kouzaki H, Seno S, Fukui J, Owaki S, Shimizu T (2009) Role of platelet-derived growth factor in airway remodeling in rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 23:273–280
Sansoni ER, Sautter NB, Mace JC, Smith TL, Yawn JR, Lawrence LA, Schlosser RJ, Soler ZM, Mulligan JK (2015) Vitamin D3 as a novel regulator of basic fibroblast growth factor in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 5:191–196
Li Y, Li L, Wang T, Zang H, An Y, Li L, Zhang J, Wang F, Zheng Y (2014) Analysis of epidermal growth factor signaling in nasal mucosa epithelial cell proliferation involved in chronic rhinosinusitis. Chin Med J 127:3449–3453
Giorgi C, Agnoletto C, Baldini C, Bononi A, Bonora M, Marchi S, Missiroli S, Patergnani S, Poletti F, Rimessi A, Zavan B, Pinton P (2010) Redox control of protein kinase C: cell- and disease-specific aspects. Antioxid Redox Signal 13:1051–1085
Rhee SG, Kang SW, Jeong W, Chang TS, Yang KS, Woo HA (2005) Intracellular messenger function of hydrogen peroxide and its regulation by peroxiredoxins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:183–189
Tzeng J-I, Chen B-C, Chang H-M, Wang J-J, Sureshbabu M, Chien M-H, Hsu M-J, Bien M-Y, Chiu W-T, Hong C-Y, Lin CH (2010) Involvement of phosphatidylcholine-phospholipase C and protein kinase C in peptidoglycan-induced nuclear factor-κB activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Pharmacol Res 61:162–166
Lane AP, Truong-Tran QA, Myers A, Bickel C, Schleimer RP (2006) Serum amyloid A, properdin, complement 3, and toll-like receptors are expressed locally in human sinonasal tissue. Am J Rhinol 20:117–123
Sun Y, Zhou B, Wang C, Huang Q, Zhang Q, Han Y, Dai W, Fan E, Li Y (2012) Biofilm formation and toll-like receptor 2, toll-like receptor 4, and NF-kappaB expression in sinus tissues of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy 26:104–109
Chiu YC, Lin CY, Chen CP, Huang KC, Tong KM, Tzeng CY, Lee TS, Hsu HC, Tang CH (2009) Peptidoglycan enhances IL-6 production in human synovial fibroblasts via TLR2 receptor, focal adhesion kinase, Akt, and AP-1- dependent pathway. J Immunol 183:2785–2792
Lin HY, Tang CH, Chen JH, Chuang JY, Huang SM, Tan TW, Lai CH, Lu DY (2011) Peptidoglycan induces interleukin-6 expression through the TLR2 receptor, JNK, c-Jun, and AP-1 pathways in microglia. J Cell Physiol 226:1573–1582
Chen B-C, Chang H-M, Hsu M-J, Shih C-M, Chiu Y-H, Chiu W-T, Lin C-H (2009) Peptidoglycan induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages by activating the neutral sphingomyelinase-ceramide pathway. J Biol Chem 284:20562–20573
Chen B-C, Kang J-C, Lu Y-T, Hsu M-J, Liao C-C, Chiu W-T, Yeh F-L, Lin C-H (2009) Rac1 regulates peptidoglycan-induced nuclear factor-κB activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Mol Immunol 46:1179–1188
Proud D, Togias A, Naclerio RM, Crush SA, Norman PS, Lichtenstein LM (1983) Kinins are generated in vivo following nasal airway challenge of allergic individuals with allergen. J Clin Invest 72:1678–1685
Eddleston J, Christiansen SC, Jenkins GR, Koziol JA, Zuraw BL (2003) Bradykinin increases the in vivo expression of the CXC chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2 in patients with allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 111:106–112
Du Clos TW (2013) Pentraxins: structure, function, and role in inflammation. ISRN Inflamm 2013:379040–379040
Funding
This work was supported by the grant from Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan (MOST 105-2320-B-030-005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan, and conducted with the written informed consent of the patients.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 174 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, YJ., Hao, CY., Chen, CL. et al. Expression of long pentraxin 3 in human nasal mucosa fibroblasts, tissues, and secretions of chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps. J Mol Med 98, 673–689 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-01899-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-01899-7