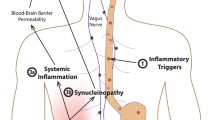
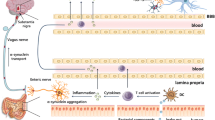
Abstract
Inflammation is the result of the loss of host’s resilience towards the surrounding world. At gross tissue level, inflammation coincides with fluid leakage from vessels, swelling, and blood stasis and extravasation of mononuclear/macrophage cells. Biochemically, these events lead to anoxia and dramatic changes: interruption of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, influx of the M1 macrophage subset, which live on anaerobic glycolysis. Fall of ATP then leads to energy shortage and debt. In their chronic forms, these phenomena are now known to mark a number of degenerative disorders that have invaded the Western World since the last century: Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s syndromes, rheumatic diseases, metabolic diseases. Intriguingly, these affections seem to derive from the gut, along two possible pathways. A sort of ascending loss of function caused by accumulation of (and hyperreactivity to) proteins released to restrain spread of enteric viruses: the alpha-synucleins, now increasingly spotted in relation to Parkinson’s pathogenesis. The second pathway would entail the intellectual decline perhaps brought about by large use of food containing the proteins of red processed meat. The bacterium Bilophila wadsworthia, thriving in this meat, can erode the mucus layer on colon surfaces, allowing further bacterial flora to approach lining cells, so upgrading the alarm state. We discuss two strategies to prevent such instability from ending up to full-blown inflammatory bowel disease: physical exercise and systematic switch to fibre-containing diets.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottazzi B, Garlanda C, Salvatori G, Jeannin P, Manfredi A, Mantovani A (2010) Pentraxins as a key component of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 18:10–15
Corliss BA, Azimi MS, Munson JM, Peirce SM, Murfee WL (2016) Macrophage: an inflammatory link between angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Microcirculation 23:95–121
Ryan GB, Majno G (1977) Acute inflammation: a review. Am J Pathol 86:183–276
Straub RH (2012) Evolutionary medicine and chronic inflammatory state—known and new concepts in pathophysiology. J Mol Med 90:523–534
Wilmore D (1991) Catabolic illness. New Engl J Med 325:695–702
Wilmore D (1976) Hormonal responses and their effects on metabolism. Surg Clin North Am 56:999–1018
Gajewski M, Gujski M, Księżopolska-Pietrzak K et al (1997) The influence of adrenergic and cholinergic agents on the respiratory burst of human neutrophils from peripheral blood and synovial fluid. J Physiol Pharmacol 48(suppl 2):72–79
Dinarello CA (1992) Interleukin-1. In: Thomson AW (ed) The cytokine handbook. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 47–82
Kopf M, Bachmann MF, Marsland BJ (2010) Averting inflammation by targeting the cytokine environment. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:703–718
Gajewski M, Rzodkiewicz P, Maśliński S (2017) The human body as an energetic hybrid? New perspectives for chronic disease treatment? Reumatologia 55:94–99
Maciver NJ, Jacobs SR, Wieman HL, Wofford JA, Coloff JL, Rathmell JC (2008) Glucose metabolism in lymphocytes is a regulated process with significant effects on immune cell function and survival. J Leukoc Biol 84:949–957
Fedrigo O, Pfefferle AD, Babbitt CC, Haygood R, Wall CE, Wray GA (2011) A potential role for glucose transporters in the evolution of human brain size. Brain Behav Evol 78:315–326
Seror P (2017) Neuralgic amyotrophic: an update. Joint Bone Spine 84:153–158
Vavricka SR, Greuter T, Scharl M, Mantzaris G, Shitrit AB, Filip R, Karmiris K, Thoeringer CK, Boldys H, Wewer AV, Yanai H, Flores C, Schmidt C, Kariv R, Rogler G, Rahier JF, investigators ECCOCONFER (2015) Cogan’s syndrome in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. A case series. J Crohn's Colitis 9:886–890
Kaur T, Uppoor A, Naik D (2016) Parkinson’s disease and periodontitis—the missing link? Gerodontology 33:434–438
Perry VH, Nicoll JA, Holmes C (2010) Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6:193–201
LaHue SC, Comella CL, Tanner CM (2016) The best medicine? The influence of physical activity and inactivity on Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 31:1444–1454
Cusso ME, Donald KJ, Khoo TK (2016) The impact of physical activity on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review. Front Med 3:35
Del Tredici K, Braak H (2016) Review: Sporadic Parkinson’s disease: development and distribution of alpha-synuclein pathology. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 42:33–50
Jang H, Boltz D, Sturm-Ramirez K, Shepherd KR, Jiao Y, Webster R, Smeyne RJ (2009) Highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus can enter the central nervous system and induce neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:14063–14068
Rao M, Gershon MD (2016) The bowel and beyond: the enteric nervous system in neurological disorders. Nat Rev Gastro Hepatol 13:517–528
Selgrad M, De Giorgio R, Fini L, Cogliandro RF, Williams S, Stanghellini V, Barbara G, Tonini M, Corinaldesi R, Genta RM, Domiati-Saad R, Meyer R, Goel A, Boland CR, Ricciardiello L (2009) JC virus infects the enteric glia of patients with chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. GUT 58:25–32
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Peuralinna T, Dutra A, Nussbaum R, Lincoln S, Crawley A, Hanson M, Maraganore D, Adler C, Cookson MR, Muenter M, Baptista M, Miller D, Blancato J, Hardy J, Gwinn-Hardy K (2003) Alpha-synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:841
Liu B, Fang F, Pedersen NL, Tillander A, Ludvigsson JF, Ekbom A, Svenningsson P, Chen H, Wirdefeldt K (2017) Vagotomy and Parkinson’s disease: a Swedish register-based matched-cohort study. Neurology 88:1996–2002
Phillips RJ, Walter GC, Ringer BE, Higgs KM, Powley TL (2009) Alpha-synuclein immunopositive aggregates in the myenteric plexus of the ageing Fischer 344 rat. Exp Neurol 220:109–119
Stolzenberg E, Berry D, Yang LEY, Kroemer A, Kaufman S, Wong GCL, Oppenheim JJ, Sen S, Fishbein T, Bax A, Harris B, Barbut D, Zasloff MA (2017) A role for neuronal alpha-synuclein in gastrointestinal immunity. J Innate Immun 9:456–463
Titova N, Padmakumar C, Lewis SJG, Chaudhuri KR (2017) Parkinson’s: a syndrome rather than disease? J Neural Transm 124:907–914
Actis GC, Rosina F (2013) IBD: an archetype disorder of outer environment sensor systems. W J Gastroent Pharmacol Ther 4:41–46
Pedersen BK, Saltin B (2015) Exercise as medicine—evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 chronic diseases. Scand J Med Sci Sports 25:1–72
Dethfelsen C, Pedersen KS, Hojman P (2017) Every exercise bout matters: linking systemic exercise responses to breast cancer control. Breast Cancer Res Treat 162:399–408
Dimitrov S, Hulteng E, Hong S (2017) Inflammation and exercise: inhibition of monocytic intracellular TNF production by acute exercise via beta-2 adrenergic activation. Brain Behav Immun 61:60–68
Kyu HH, Bachman FV, Alexander LT, Mumford JE, Afshin A, Estep K, Veerman JL, Delwiche K, Iannarone ML, Moyer ML, Cercy K, Vos T, Murray CJ, Forouzanfar MH (2016) Physical activity and risk of breast cancer, colon cancer, diabetes, ischemic heart disease, and ischemic strokeevents; systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. BMJ 354:i3857
Kruzel ML, Zimecki M, Actor JK (2017) Lactoferrin in context of inflammation induced pathology. Front Immunol 8:1438
Okazaki Y, Kono I, Kuriki T, Funahashi S, Fushimi S, Iqbal M, Okada S, Toyokuni S (2012) Bovine lactoferrin ameliorates ferric nitriloacetate-induced renal oxidative damage in rats. J Clin Biochem Nutr 51:84–90
Legrand D, Mazurier J (2010) A critical review of the role of host lactoferrin in immunity. Biometals 23:365–376
Curran CS, Demick KP, Mansfield JM (2006) Lactoferrin activates macrophages via TLR-4 dependent and independent signalling pathways. Cell Immunol 242:23–30
Drago-Serrano ME, de la Garza-Amaya M, Luna JS, Campos-Rodríguez R (2012) Lactoferrin-lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding as key to antibacterial and antiendotoxic effects. Int Immunopharmacol 12:1–9
Zimecki M, Miedrybrodzki R, Mazurier J, Spik G (1999) Regulatory effects of lactoferrin and LPS on LFA-1 expression on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 47:257–264
Zimecki M, Wlaszczyk A, Zagulski T, Kübler A (1998) Lactoferrin lowers serum interleukin 6 and TNF alpha levels in mice subjected to surgery. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 46:97–104
Baveye S, Elass E, Mazurier J, Spik G, Legrand D (1999) Lactoferrin: a multifunctional glycoprotein involved in the modulation of the inflammatory process. Clin Chem Lab Med 37:281–286
Legrand D (2016) Overview of lactoferrin as a natural immune modulator. J Pediatr 173(Suppl):S10–S15
Cutone A, Rosa L, Lepanto MS, Scotti MJ, Berlutti F, Bonaccorsi di Patti MC, Musci G, Valenti P (2017) Lactoferrin efficiently counteracts the inflammation-induced changes of the iron homeostasis system of the macrophages. Front Immunol 8:705
Poli G, Schaur RJ (2000) 4-Hydroxynonenal in the pathomechanisms of oxidative stress. IUBMB Life 50:315–321
Saïd-Sadier N, Ojcius DM (2012) Alarmins, inflammasomes and immunity. Biom J 35:437–449
Oda H, Wakabayashi H, Yamauchi K, Abe F (2014) Lactoferrin and bifidobacteria. Biometals 27:915–922
Bertuccini L, Costanzo M, Iosi F, Tinari A, Terruzzi F, Stronati L, Aloi M, Cucchiara S, Superti F (2014) Lactoferrin prevents invasion and inflammatory response following E. coli strain LF82 infection in experimental model of Crohn’s disease. Dig Liver Dis 46:496–504
Innis SM (2014) Impact of maternal diet on human milk composition and neurological development of infants. Am J Clin Nutr 99:34S–41S
Wang J, Freire D, Knable L, Zhao W, Gong B, Mazzola P, Ho L, Levine S, Pasinetti GM (2015) Childhood and adolescent obesity and long-term cognitive consequences during aging. J Comp Neurol 523:757–768
Abrams ET, Miller EM (2011) The roles of the immune system in women’s reproduction: evolutionary constraints and life history trade-offs. Am J Phys Anthropol 146:134–154
Pedersen BK (2011) Muscles and their myokines. J Exp Biol 214:337–346
Pruimboom L, Raison CL, Muskiet FA (2015) Physical activity protects the human brain against metabolic stress induced by a postprandial and chronic inflammation. Behav Neurol 2015:569869
Andersen V, Hansen-Kornerup A, Heitmann BL (2017) Potential impact of diet on treatment effect from anti TNF drugs in IBD. Nutrients 9:286
Ozawa M, Shipley M, Kivimaki M, Singh-Manoux A, Brunner EJ (2017) Dietary pattern, inflammation, and cognitive decline: the Whitehall II prospective cohort study. Clin Nutr 36:506–512
Dror E, Dalmas E, Meier DT, Wueest S, Thévenet J, Thienel C, Timper K, Nordmann TM, Traub S, Schulze F, Item F, Vallois D, Pattou F, Kerr-Conte J, Lavallard V, Berney T, Thorens B, Konrad D, Böni-Schnetzler M, Donath MY (2017) Post prandial macrophage-derived IL-1 stimulates insulin, and both synergistically promote glucose disposal and inflammation. Nat Immunol 18:283–292
Shen ZH, Zhu CX, Quan YS, Yang ZY, Wu S, Luo WW, Tan B, Wang XY (2018) Relationship between intestinal microbiota and ulcerative colitis: mechanisms and clinical application of probiotics and fecal microbiota transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 24:5–14
Buffie CG, Pamer EG (2013) Microbiota-mediated colonization resistance against intestinal pathogens. Nat Rev Immunol 13:790–801
Marchesi JR, Adams DH, Fava F, Hermes GD, Hirschfield GM, Hold G, Quraishi MN, Kinross J, Smidt H, Tuohy KM, Thomas LV, Zoetendal EG, Hart A (2016) The gut microbiota and host health: a new clinical frontier. Gut 65:330–339
Round JL, Mazmanian SK (2009) The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9:313–323
Kostic AD, Xavier RJ, Gevers D (2014) The microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease: current status and the future ahead. Gastroenterology 146:1489–1499
Albenberg L, Esipova TV, Judge CP. Bittinger K, Chen J, Laughlin A, Grunberg S, Baldassano RN, Lewis JD, Li H, Thom SR, Bushman FD, Vinogradov SA, Wu GD (2014) Correlation between intraluminal oxygen gradient and radial partitioning of intestinal microbiota. Gastroenterology 147:e1058
Kruis W, Fric P, Pokrotnieks J, Lukás M, Fixa B, Kascák M, Kamm MA, Weismueller J, Beglinger C, Stolte M, Wolff C, Schulze J (2004) Maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis with the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is as effective as with standard mesalazine. Gut 53:1617–1623
Sood A, Midha V, Makharia GK, Ahuja V, Singal D, Goswami P, Tandon RK (2009) The probiotic preparation, VSL#3 induces remission in patients with mild-to-moderately active ulcerative colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:1202–1209
Holleran G, Lopetuso LR, Ianito G, Pecere S, Pizzoferrato M, Petito V, Graziani C, McNAMARA D, Gasbarrini A, Scaldaferri F (2017) Gut microbiota and inflammatory bowel disease: so far so gut! Minerva Gatroenterol Dietol 63:373–384
Simondi D, Mengozzi G, Betteto S, Bonardi R, Ghignone RP, Fagoonee S, Pellicano R, Sguazzini C, Pagni R, Rizzetto M, Astegiano M (2008) Antiglycan antibodies as serological markers in the differential diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 14:645–651
Graham LM, Tsoni SV, Willment JA, Williams DL, Taylor PR, Gordon S, Dennehy K, Brown GD (2006) Soluble Dectin-1 as a tool to detect β-glucans. J Immunol Methods 314:164–169
Plato A, Hardison SE, Brown GD (2015) Pattern recognition receptors in antifungal immunity. Semin Immunopathol 37:97–106
Lepage P, Colombet J, Marteau P, Sime-Ngando T, Dore J, Leclerc M (2008) Dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease: a role for bacteriophages? 57:424–425
Zhang F, Luo W, Shi Y, Fan Z, Ji G (2012) Should we standardize the 1,700-year-old fecal microbiota transplantation? Am J Gastroenterol 107:1755
Actis GC (2014) The gut microbiome. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 13:217–223
Actis GC (2016) The gut immune system, inflammatory bowel diseases, and the body immune homeostasis: modern treatment strategies. Progr Health Sci 6:165–174
Negroni A, Pierdomenico M, Cucchiara S, Stronati L (2018) NOD2 and inflammation: current insights. J Inflamm Res 11:49–60
Imai H, Chen A, Wyatt RJ, Rifai A (1988) Lack of C’ activation by human IgA immune complexes. Clin Exp Immunol 73:479–483
Lan RY, MacKay IR, Gershwin ME (2007) Regulatory T-cells in the prevention of mucosal inflammatory diseases: patrolling the border. J Autoimmunity 29:272–280
Broussard JL, Devkota S (2016) The changing microbial landscape of Western society: diet, dwellings, and discordance. Molecular Metab 5:737–742
Batra A, Zeitz M, Siegmund B (2009) Adipokine signaling in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15:1897–1905
Abraham C, Cho JH (2009) Inflammatory bowel disease. New Engl J Med 361:2066–2078
Actis GC, Rosina F, MacKay IR (2011) Inflammatory bowel disease: beyond the boundaries of the bowel. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:401–410
Actis GC, Pellicano R (2016) The pathologic galaxy modulating the genotype and phenotype of inflammatory bowel disease: comorbidity, contiguity, and genetic, and epi-genetic factors. Minerva Med 107:401–412
Malekzadeh MM, Vahedi H, Gohari K, Mehdipour P, Sepanlou SG, Ebrahimi Daryani N, Zali MR, Mansour-Ghanaei F, Safaripour A, Aghazadeh R, Vossoughinia H, Fakheri H, Somi MH, Maleki I, Hoseini V, Ghadir MR, Daghaghzadeh H, Adibi P, Tavakoli H, Taghavi A, Zahedi MJ, Amiriani T, Tabib M, Alipour Z, Nobakht H, Yazdanbod A, Sadreddini M, Bakhshipour A, Khosravi A, Khosravi P, Nasseri-Moghaddam S, Merat S, Sotoudehmanesh R, Barazandeh F, Arab P, Baniasadi N, Pournaghi SJ, Parsaeian M, Farzadfar F, Malekzadeh R (2016) Emerging epidemic of inflammatory bowel disease in a middle income country: a nation-wide study from Iran. Arch Iran Med 19:2–15
Zuo T, Kamm MA, Colombel JF, Ng SC (2018) Urbanization and the gut microbiota in health and inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:440–452
Aller MA, Arias N, Fuentes-Julian S, Blazquez-Martinez A, Argudo S, Miguel MP, Arias JL, Arias J (2012) Coupling inflammation with evo-devo. Med Hypotheses 78:721–731
Aller MA, Arias JI, Arias J (2010) Pathological axes of wound repair: gastrulation revisited. Theor Biol Med Model 7:37
Muller GB (2007) Evo-devo: extending the evolutionary synthesis. Nat Rev Genet 8:943–949
Buford TW (2017) (Dis)Trust your gut: the gut microbiome in age-related inflammation, health, and disease. Microbiome 5:80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribaldone, D.G., Pellicano, R. & Actis, G.C. Inflammation: a highly conserved, Janus-like phenomenon—a gastroenterologist’ perspective. J Mol Med 96, 861–871 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1668-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1668-z