Abstract
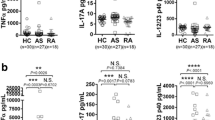
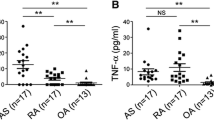
Spondyloarthritis (SpA) is characterized by inflammation and new bone formation and can be treated by inhibition of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-17A. IL-26 is considered a proinflammatory cytokine, predominantly related to Th17 cells. In the present study, we investigate IL-26 expression in SpA patients, and examine the in vitro production of IL-26 by synovial cells and the effects of IL-26 on human osteoblasts. IL-26 was measured by ELISA in plasma and synovial fluid (SF) of 15 SpA patients and in plasma samples from 12 healthy controls. Facet joints from axial SpA patients were stained for IL-26 and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Synovial fluid mononuclear cells, C-C motif chemokine receptor 6 memory Th17 cells, and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) were isolated, and supernatants were analyzed for IL-26 content by ELISA. FLSs were further stained for IL-26 production and the myofibroblast marker α-smooth-muscle-actin (αSMA) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Human osteoblasts were cultured in the presence of IL-26, and the degree of mineralization was quantified. We found that IL-26 levels in SF were increased compared with plasma (P < 0.0001). Moreover, IL-26 expression was found in facet joints of axial SpA patients within the bone marrow. IL-26 secretion was primarily found in αSMA+ myofibroblasts. In contrast, Th17 cells did not produce detectable amounts of IL-26. Human osteoblasts treated with IL-26 showed increased mineralization compared with untreated osteoblasts (P = 0.02). In conclusion, IL-26 seems to be produced by myofibroblasts in the inflamed synovium and could be a possible facilitator of bone mineralization in SpA.
Key messages
-
IL-26 levels are higher in synovial fluid compared to plasma in spondyloarthritis.
-
IL-26 was identified in axial facet joints of spondyloarthritis patients.
-
Myofibroblasts from the spondyloarthritis synovium produce large amounts of IL-26.
-
IL-26 induces bone mineralization in human osteoblasts.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dougados M, Baeten D (2011) Spondyloarthritis. Lancet 377:2127–2137
Claudepierre P, Voisin M-C (2005) The entheses: histology, pathology, and pathophysiology. Joint Bone Spine 72:32–37
Yang M, Yuan H, Miao M, Xu W (2015) Größeres osteogenes Potenzial von ligamentären Fibroblasten bei Patienten mit Spondylitis ankylosans als bei Patienten mit Arthrose. Z Rheumatol 74:340–345
Maksymowych WP, Morency N, Conner-Spady B, Lambert RG (2013) Suppression of inflammation and effects on new bone formation in ankylosing spondylitis: evidence for a window of opportunity in disease modification. Ann Rheum Dis 72:23–28
Lories RJU, Luyten FP, de Vlam K (2009) Progress in spondyloarthritis. Mechanisms of new bone formation in spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 11:221
Beyer C, Distler JHW (2012) Changing paradigms in spondyloarthritis: the myofibroblast signature. Arthritis & Rheum 65:24–27
Deodhar A, Dougados M, Baeten D, Wei C, Geusens P, Readie A, Richards H, Martin R, Porter B (2016) Effect of secukinumab on patient-reported outcomes in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis: a phase 3 randomized trial (MEASURE 1). Arthritis Rheumatol. doi:10.1002/art.39805
Baeten D, Sieper J, Braun J, Baraliakos X, Dougados M, Emery P, Deodhar A, Porter B, Martin R, Andersson M et al (2015) Secukinumab, an interleukin-17A inhibitor, in ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med 373:2534–2548
Blair HA, Dhillon S (2016) Secukinumab: a review in ankylosing spondylitis. Drugs 76:1023–1030
Raychaudhuri SK, Saxena A, Raychaudhuri SP (2015) Role of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34:1019–1023
Kirkham BW, Kavanaugh A, Reich K (2014) Interleukin-17A: a unique pathway in immune-mediated diseases: psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Immunology 141:133–142
LeBleu VS, Taduri G, O’Connell J, Teng Y, Cooke VG, Woda C, Sugimoto H, Kalluri R (2013) Origin and function of myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis. Nat Med 19:1047–1053
Yeremenko N, Noordenbos T, Cantaert T, van Tok M, van de Sande M, Cañete JD, Tak PP, Baeten D (2012) Disease-specific and inflammation-independent stromal alterations in spondylarthritis synovitis. Arthritis & Rheum 65:174–185
Wolk K, Kunz S, Asadullah K, Sabat R (2002) Cutting edge: immune cells as sources and targets of the IL-10 family members? J Immunol 168:5397–5402
Che KF, Tengvall S, Levänen B, Silverpil E, Smith ME, Awad M, Vikström M, Palmberg L, Qvarfordt I, Sköld M et al (2014) Interleukin-26 in antibacterial host defense of human lungs - effects on neutrophil mobilization. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 190:1022–1031
Corvaisier M, Delneste Y, Jeanvoine H, Preisser L, Blanchard S, Garo E, Hoppe E, Barré B, Audran M, Bouvard B et al (2012) IL-26 is overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis and induces proinflammatory cytokine production and Th17 cell generation. PLoS Biol 10:e1001395–e1001315
Sheikh F, Baurin VV, Lewis-Antes A, Shah NK, Smirnov SV, Anantha S, Dickensheets H, Dumoutier L, Renauld J-C, Zdanov A et al (2004) Cutting edge: IL-26 signals through a novel receptor complex composed of IL-20 receptor 1 and IL-10 receptor 2. J Immunol 172:2006–2010
Hor S, Pirzer H, Dumoutier L, Bauer F, Wittmann S, Sticht H, Renauld JC, de Waal MR, Fickenscher H (2004) The T-cell lymphokine interleukin-26 targets epithelial cells through the interleukin-20 receptor 1 and interleukin-10 receptor 2 chains. J Biol Chem 279:33343–33351
Tengvall S, Che KF, Lindén A (2015) Interleukin-26: an emerging player in host defense and inflammation. J Innate Immun 0:1–8. doi: 10.1159/000434646
Blumberg H, Conklin D, Xu W, Grossmann A, Brender T, Carollo S, Eagan M, Foster D, Haldeman BA, Hammond A et al (2001) Interleukin 20: discovery, receptor identification, and role in epidermal function. Cell 104:9–19
Hsu Y-H, Chiu Y-S, Chen W-Y, Huang K-Y, Jou I-M, Wu P-T, Wu C-H, Chang M-S (2016) Anti-IL-20 monoclonal antibody promotes bone fracture healing through regulating IL-20-mediated osteoblastogenesis. Sci Rep 1–13. doi: 10.1038/srep24339
Kragstrup TW, Vorup-Jensen T, Deleuran B, Hvid M (2013) A simple set of validation steps identifies and removes false results in a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay caused by anti-animal IgG antibodies in plasma from arthritis patients. Spring 2:263
Appel H, Maier R, Wu P, Scheer R, Hempfing A, Kayser R, Thiel A, Radbruch A, Loddenkemper C, Sieper J (2011) Analysis of IL-17+ cells in facet joints of patients with spondyloarthritis suggests that the innate immune pathway might be of greater relevance than the Th17-mediated adaptive immune response. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R95
Kragstrup TW, Jalilian B, Hvid M, Kjærgaard A, Østgård R, Schiøttz-Christensen B, Jurik AG, Robinson WH, Vorup-Jensen T, Deleuran B (2014) Decreased plasma levels of soluble CD18 link leukocyte infiltration with disease activity in spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 16:R42–R15
Stebulis JA, Rossetti RG, Atez FJ, Zurier RB (2005) Fibroblast-like synovial cells derived from synovial fluid. J Rheumatol 32:301–306
Andersen MN, Al-Karradi SNH, Kragstrup TW, Hokland M (2016) Elimination of erroneous results in flow cytometry caused by antibody binding to Fc receptors on human monocytes and macrophages. Cytometry A 89:1001–1009
Maxwell LJ, Zochling J, Boonen A, Singh JA, Veras MMS, Tanjong Ghogomu E, Benkhalti Jandu M, Tugwell P, Wells GA (2015) TNF-alpha inhibitors for ankylosing spondylitis. Cochrane Db Syst Rev CD005468. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005468.pub2
Voulgari PV (2010) Golimumab: a new anti-TNF-alpha agent for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 6:721–733
Milia AF, Ibba-Manneschi L, Manetti M, Benelli G, Generini S, Messerini L, Matucci-Cerinic M (2011) Evidence for the prevention of enthesitis in HLA-B27/hβ(2)m transgenic rats treated with a monoclonal antibody against TNF-α. J Cell Mol Med 15:270–279
Shah R, Perry L, Deodhar A (2015) The role of secukinumab in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Immunotherapy 7:1241–1247
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by unrestricted grants from The Novo Nordisk Foundation and The Danish Rheumatism Association. Flow cytometry and cell sorting were performed at the FACS Core Facility, Aarhus University, Denmark.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All patient samples were obtained after written consent and the collection of samples were approved by the Central Denmark Region Committee on Biomedical and Research Ethics (project number 20121329), the Danish Data Protection Agency, and the Good Clinical Practice unit at Aarhus University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heftdal, L.D., Andersen, T., Jæhger, D. et al. Synovial cell production of IL-26 induces bone mineralization in spondyloarthritis. J Mol Med 95, 779–787 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1528-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1528-2