Abstract
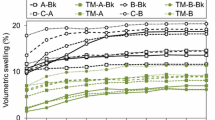
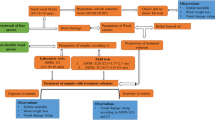
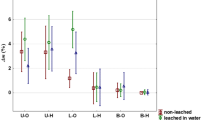
Various oils can be used to lower the equilibrium moisture content and increase the service life of Scots pine wood products. The aim of this study was to investigate effects of the lateral wood zone on the brown rot resistance of untreated and linseed oil-impregnated Scots pine wood in a laboratory test (EN 113). Significant differences were found in the mean mass losses of treated and untreated specimens taken from three lateral heartwood zones, but not between specimens taken from sapwood. The treatment had no significant effect on sapwood, although it seems to have some positive effect on the durability of heartwood, apparently due to interactive effects with the high extractives contents of heartwood.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
EN 84 (1997) Wood preservatives—accelerated ageing tests of treated wood prior to biological testing—leaching procedure. European Committee for Standardization (CEN), Brussels, Belgium
EN 113 (1996) Wood preservatives—test method for determining the protective effectiveness against wood destroying Basidiomycetes—determination of toxic values. European Committee for Standardization (CEN), Brussels, Belgium
Grønli MG, Varhegyi G, DiBlasi C (2002) Thermogravimetric analysis and devolatilization kinetics of wood. Ind Eng Chem Res 41:4201–4208
Harju AM, Venäläinen M (2002) Genetic parameters regarding the resistance of Pinus sylvestris heartwood to decay caused by Coniophora puteana. Scand J For Res 17:199–205
Hill C (2011) An introduction to sustainable resource use. Earthscan, London, 225 pp
Venäläinen M, Harju AM, Kainulainen P, Viitanen H, Nikulainen H (2002) Variation in the decay resistance and its relationship with other wood characteristics in old Scots pines. Ann For Sci 60:409–417
Ulvcrona T, Bergsten U (2007) Possibilities for compositional tailoring of Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst.) wood using a hydrophobic oil impregnation process. Holz Roh- Werkst 65:167–169
Ulvcrona T, Lindberg H, Bergsten U (2006) Impregnation of Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst.) wood by hydrophobic oil and dispersion patterns in different tissues. Forestry 79(1):123–134
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank Sveaskog AB and The Research Council of Norway for financial support, Gunnar Karlsson at SLU for valuable help with preparation of stakes and samples, and Sigrun Kolstad and Eva Grodås at the Norwegian Forest and Landscape Institute for valuable help with lab trials and TGA. Thanks also to SEES-EDITING for professional editorial service.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulvcrona, T., Flæte, P.O. & Alfredsen, G. Effects of lateral wood zone on brown rot resistance of untreated and linseed oil-impregnated Scots pine wood. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 70, 771–773 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-012-0604-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-012-0604-0