Abstract
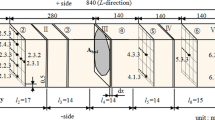
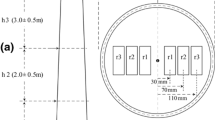
This study was performed to investigate a radial distribution of moistures and tangential strains within a 30 mm thick log cross section of larch by a circumferential slicing-method during radio-frequency/vacuum (RF/V) drying. Before the RF/V drying, the moisture contents (MC) at the heartwood zone remained nearly constant in the range of about 42 percent MC to 53 percent MC, while from around 0.80 diameters away from the pith toward bark they abruptly raised to maximum 149.4 percent MC and then decreased slightly. From 79 hours of the drying times to end of the drying the moisture distribution along the radial direction remained almost uniform. When the log cross section fell below fiber saturation point at 79 hours of drying, most of the slices represented the maximum tensile strains, and from that time the tangential strains in tension steadily increased toward the bark side, and reached the maximum value at the border zone between heartwood and sapwood. Most of log cross sections of larch could be dried without formation of checks and V-shaped cracks during the RF/V drying process.
Zusammenfassung
Diese Studie wurde durchgeführt, um die radiale Verteilung von Feuchte und tangentieller Belastung innerhalb eines 30 cm dicken Rundholzquerschnitts von Lärchenholz mittels einer speziellen Aufschnitt-Methode während RF/V-Trocknung zu untersuchen. Dünne Ringproben werden aus dem Rundholz geschnitten. Vor der RF/V-Trocknung zeigt die Feuchte in der Kernholzzone beinahe konstant eine Feuchte im Bereich von ca. 42% bis 53% an, während bei ungefähr 0,80 Durchmesser entfernt vom Mark zur Rinde hin sich die Feuchte auf 149,4% erhöhte und dann leicht absank. In 79 Stunden Trocknungszeit bis zum Trocknungsende blieb die Feuchteverteilung entlang der radialen Richtung beinahe einheitlich. Wenn der Rundholzquerschnitt unter den Fasersättigungspunkt bei 79 Stunden Trocknungszeit fiel, zeigten die meisten Ringproben die maximale Zugbelastung und von dieser Zeit an nahm die Zugbelastung zur Rindenseite hin ständig zu und erreichte die höchsten Werte an der Grenze zwischen Kern- und Splintholz. Die meisten Balkenquerschnitte von Lärchenholz konnten ohne das Auftreten von Rissen und V-förmigen Brüchen während des RF/V-Trocknungsprozesses getrocknet werden.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jung et al. (1999) Development of vacuum-press drying technology for structural softwood lumbers and woods for special goods. Report of Korean Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, Korea, pp 149–173 (in Korean)
Kanagawa Y, Hayashi K, Yasuzima M (1992) Improvement of dryability by local steam explosion for Japanese cedar. Proceedings of 3rd IUFRO International Wood Drying Conference, Vienna, Austria, pp 269–276
Kubler H (1974) Drying tree disks simply and without defects. Forest Prod J 24(7):33–34
Kubler H (1975) Study on drying of tree cross sections. Wood Science 7(3):173–181
Kubler H, Chen TH (1975) Prevention of crosscut and heating heart checks in log ends. Wood Sci Technol 9:15–24
Lee NH, Hayashi K, Jung HS (1998) Effect of radio-frequency/vacuum drying and mechanical press-drying on shrinkage and checking of walnut log cross sections. Forest Prod J 48(5):73–79
Lee NH, Hayashi K (2000) Effect of end-covering and low pressure steam explosion treatment on drying rate and checking during radio-frequency/vacuum drying of Japanese cedar log cross sections. Forest Prod J 50(2):73–79
Lee NH et al. (1997) Development of the specification technology for international competitive power of the wooden crafts manufacturing companies around Chri-Mountain area. Report of Korean Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, Korea, pp 33–86 (in Korean)
Liu F, Avramidis S, Zwick RL (1994) Drying thick western hemlock in a laboratory radio-frequency/vacuum dryer with constant and variable electrode voltage. Forest Prod J 44(6):71–75
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grant of Post-Doc. Program, Chonbuk National University in Korea (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, W., Lee, NH. & Choi, JH. A radial distribution of moistures and tangential strains within a larch log cross section during radio-frequency/vacuum drying. Holz Roh Werkst 62, 59–63 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-003-0432-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-003-0432-3