Abstract
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a recently recognised pathologic entity whose prevalence has risen significantly since first being described in 1993. Defined as a chronic, local immune-mediated disease with predominant eosinophil infiltration, it is nowadays the leading cause of dysphagia and food bolus impaction in children and young adults. Genetic and environmental risk factors, and especially food antigens, trigger the disease and are in the focus of investigation as avoidance can cure three quarters of patients. The most common antigen involved is milk, followed by egg and gluten. These patients frequently come undiagnosed to the otolaryngologist with complaints of dysphagia and recurrent non-sharp food impactions, although pharyngolaryngeal reflux symptoms and other airway complaints could also be a first sign. Delayed diagnosis and treatment can produce fibrostenosis of the esophagus that greatly impairs patients’ quality of life.
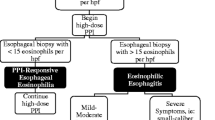
In-office transnasal esophagoscopy with esophageal biopsy offers a unique opportunity to promptly diagnose and follow-up these patients, without causing the morbidity of repeated sedations and reducing exploration overload in gastroenterology departments. The search for food-antigen triggers, response evaluation to swallowed steroids, or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) make multiple endoscopies and biopsies necessary every 6 to 8 weeks.
There are three first-line interchangeable treatments with the same recommendation: PPIs, dietary allergen elimination and topical swallowed steroids. The choice should be discussed with the patient on an individual basis.
The objective of this article is to raise awareness of this condition, update otolaryngologists with the new EoE consensus, and highlight the need for biopsy in patients with dysphagia to rule out EoE.
Zusammenfassung
Die eosinophile Ösophagitis (EÖ) ist ein kürzlich anerkanntes Krankheitsbild, dessen Prävalenz seit der Erstbeschreibung im Jahr 1993 deutlich gestiegen ist. Definiert als eine chronische, lokale immunvermittelte Erkrankung mit überwiegend eosinophilem Infiltrat ist die EÖ heute die Hauptursache von Dysphagie und Nahrungsbolusimpaktion bei Kindern und jungen Erwachsenen. Genetische und umweltbezogene Risikofaktoren, insbesondere Nahrungsmittelantigene, lösen die Erkrankung aus und stehen im Fokus der Forschung, da ihre Vermeidung bei drei von vier Patienten zur Heilung führt. Als Antigen am häufigsten involviert ist Milch, gefolgt von Ei und Gluten. Betroffene Patienten suchen nicht selten ohne Diagnose den Hals-Nasen-Ohren-Arzt auf und klagen über Dysphagie sowie wiederholte Impaktionen nichtspitzer Nahrungsmittel, auch wenn pharyngolaryngeale Refluxsymptome und andere Atemwegsbeschwerden ebenfalls ein erstes Erkrankungszeichen sein können. Eine verzögerte Diagnose und Behandlung können eine Fibrostenose des Ösophagus zur Folge haben, die die Lebensqualität der Patienten stark beeinträchtigt.
Die transnasale Ösophagoskopie mit Ösophagusbiopsie bietet in der HNO-Praxis die einmalige Möglichkeit, unverzüglich eine Diagnose zu stellen und die Patienten weiter zu beobachten. Dabei wird eine durch wiederholte Sedierungen bedingte gesundheitliche Beeinträchtigung vermieden und die diagnostische Überlastung gastroenterologischer Abteilungen reduziert. Die Suche nach Nahrungsmittelantigenen, die als Auslöser wirken, sowie die Beurteilung des Ansprechens auf oral eingenommene Steroide oder Protonenpumpenhemmer (PPI) erfordern regelmäßige Endoskopien und Biopsien alle 6 bis 8 Wochen.
Drei gleichwertige Erstlinientherapien mit derselben Empfehlung stehen zur Auswahl: die PPI-Gabe, die Beseitigung des Nahrungsmittelallergens und die topische Behandlung mit oral eingenommenen Steroiden. Der Patient sollte in die individuelle Therapieentscheidung einbezogen werden.
Mit dem vorliegenden Beitrag soll das Bewusstsein für die EÖ geschärft werden. Zudem werden die aktuellen Konsensusempfehlungen vorgestellt. Unterstrichen werden soll die Notwendigkeit der Biopsie zum Ausschluss einer EÖ bei Patienten mit Dysphagie.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landres RT, Kuster GG, Strum WB (1978) Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology 74(6):1298–1301
Attwood SE, Smyrk TC, Demeester TR, Jones JB (1993) Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. A distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 38(1):109–116
Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, Gupta SK, Justinich C, Putnam PE et al (2007) Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology 133(4):1342–1363
Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, Atkins D, Attwood SE, Bonis PA et al (2011) Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol 128(1):3–20e6 (quiz 21-2)
Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Katzka DA et al (2013) ACG clinical guideline: evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am J Gastroenterol 108(5):679–692 (quiz 693)
Lucendo AJ, Molina-Infante J, Arias Á, von Arnim U, Bredenoord AJ, Bussmann C et al (2017) Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United European Gastroenterol J 5(3):335–358. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050640616689525
Kelly EA, Linn D, Keppel KL, Noel RJ, Chun RH (2015) Otolaryngologic surgeries are frequent in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 124(5):355–360
Smith LP, Chewaproug L, Spergel JM, Zur KB (2009) Otolaryngologists may not be doing enough to diagnose pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73(11):1554–1557
Padia R, Curtin K, Peterson K, Orlandi RR, Alt J (2016) Eosinophilic esophagitis strongly linked to chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 126(6):1279–1283
Kubik M, Thottam P, Shaffer A, Choi S (2017) The role of the otolaryngologist in the evaluation and diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis. Laryngoscope 127(6):1459–1464
Benninger MS, Strohl M, Holy CE, Hanick AL, Bryson PC (2017) Prevalence of atopic disease in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 7(8):757–762
Schoepfer AM, Safroneeva E, Bussmann C, Kuchen T, Portmann S, Simon H‑U et al (2013) Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 145(6):1230–1236.e1-2
Molina-Infante J, Bredenoord AJ, Cheng E, Dellon ES, Furuta GT, Gupta SK et al (2016) Proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia: an entity challenging current diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic oesophagitis. Gut 65(3):524–531
Ronkainen J, Talley NJ, Aro P, Storskrubb T, Johansson S‑E, Lind T et al (2007) Prevalence of oesophageal eosinophils and eosinophilic oesophagitis in adults: the population-based Kalixanda study. Gut 56(5):615–620
Lucendo AJ, Arias Á, Molina-Infante J, Rodríguez-Sánchez J, Rodrigo L, Nantes Ó et al (2013) Diagnostic and therapeutic management of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults: results from a Spanish registry of clinical practice. Dig Liver Dis 45(7):562–568
Sperry SL, Woosley JT, Shaheen NJ, Dellon ES (2012) Influence of race and gender on the presentation of eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol 107(2):215–221
Assa’ad A (2008) Eosinophilic esophagitis: association with allergic disorders. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 18(1):119–132
McKenzie C, Tan J, Macia L, Mackay CR (2017) The nutrition-gut microbiome-physiology axis and allergic diseases. Immunol Rev 278(1):277–295
von Arnim U, Wex T, Link A, Messerschmidt M, Venerito M, Miehlke S et al (2016) Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with a reduced risk of developing eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 43(7):825–830
Rajan J, Newbury RO, Anilkumar A, Dohil R, Broide DH, Aceves SS (2016) Long-term assessment of esophageal remodeling in patients with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis treated with topical corticosteroids. J Allergy Clin Immunol 137(1):147–156.e8
Lucendo AJ, De Rezende L (2007) Endoscopic dilation in eosinophilic esophagitis: a treatment strategy associated with a high risk of perforation. Endoscopy 39(4):376 (author reply 377)
Otteson TD, Mantle BA, Casselbrant ML, Goyal A (2012) The otolaryngologic manifestations in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76(1):116–119
Yawn RJ, Acra S, Goudy SL, Flores R, Wootten CT (2015) Eosinophilic laryngitis in children with aerodigestive dysfunction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 153(1):124–129. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599815577568
Hirano I, Moy N, Heckman MG, Thomas CS, Gonsalves N, Achem SR (2013) Endoscopic assessment of the oesophageal features of eosinophilic oesophagitis: validation of a novel classification and grading system. Gut 62(4):489–495
Kim HP, Vance RB, Shaheen NJ, Dellon ES (2012) The prevalence and diagnostic utility of endoscopic features of eosinophilic esophagitis: a meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 10(9):988–996.e5
van Rhijn BD, Verheij J, Smout AJPM, Bredenoord AJ (2016) The Endoscopic Reference Score shows modest accuracy to predict histologic remission in adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 28(11):1714–1722
Friedlander JA, DeBoer EM, Soden JS, Furuta GT, Menard-Katcher CD, Atkins D et al (2016) Unsedated transnasal esophagoscopy for monitoring therapy in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc 83(2):299–306.e1
Salek J, Clayton F, Vinson L, Saffari H, Pease LF, Boynton K et al (2015) Endoscopic appearance and location dictate diagnostic yield of biopsies in eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 41(12):1288–1295
Furuta GT, Kagalwalla AF, Lee JJ, Alumkal P, Maybruck BT, Fillon S et al (2013) The oesophageal string test: a novel, minimally invasive method measures mucosal inflammation in eosinophilic oesophagitis. Gut 62(10):1395–1405
Katzka DA, Geno DM, Ravi A, Smyrk TC, Lao-Sirieix P, Miramedi A et al (2015) Accuracy, safety, and tolerability of tissue collection by Cytosponge vs endoscopy for evaluation of eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 13(1):77–83.e2
Nicodème F, Hirano I, Chen J, Robinson K, Lin Z, Xiao Y et al (2013) Esophageal distensibility as a measure of disease severity in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(9):1101–1107.e1
Dellon ES, Irani A‑M, Hill MR, Hirano I (2013) Development and field testing of a novel patient-reported outcome measure of dysphagia in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 38(6):634–642
Safroneeva E, Straumann A, Coslovsky M, Zwahlen M, Kuehni CE, Panczak R et al (2016) Symptoms have modest accuracy in detecting endoscopic and Histologic remission in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 150(3):581–590.e4
Cheng E, Souza RF, Spechler SJ (2014) Eosinophilic esophagitis: interactions with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 43(2):243–256
Tobey NA, Hosseini SS, Argote CM, Dobrucali AM, Awayda MS, Orlando RC (2004) Dilated intercellular spaces and shunt permeability in nonerosive acid-damaged esophageal epithelium. Am J Gastroenterol 99(1):13–22
Gómez-Torrijos E, García-Rodríguez R, Castro-Jiménez A, Rodríguez-Sanchez J, Méndez Díaz Y, Molina-Infante J (2016) The efficacy of step-down therapy in adult patients with proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 43(4):534–540
Murali AR, Gupta A, Attar BM, Ravi V, Koduru P (2016) Topical steroids in eosinophilic esophagitis: systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized clinical trials. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 31(6):1111–1119
Dellon ES, Sheikh A, Speck O, Woodward K, Whitlow AB, Hores JM et al (2012) Viscous topical is more effective than nebulized steroid therapy for patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 143(2):321–324.e1
Kagalwalla AF, Shah A, Li BUK, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, Manuel-Rubio M et al (2011) Identification of specific foods responsible for inflammation in children with eosinophilic esophagitis successfully treated with empiric elimination diet. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 53(2):145–149
Gonsalves N, Yang G‑Y, Doerfler B, Ritz S, Ditto AM, Hirano I (2012) Elimination diet effectively treats eosinophilic esophagitis in adults; food reintroduction identifies causative factors. Gastroenterology 142(7):1451–1459.e1 (quiz e14-5)
Górriz-Gil C, Villarreal IM, Álvarez-Montero Ó, Rodríguez-Valiente A, Magaz M, García-Berrocal JR (2016) Eosinophilic esophagitis: a relevant entity for the otolaryngologist. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 67(3):167–178
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
C. Górriz Gil, V. Matallana Royo, Ó. Álvarez Montero, A. Rodríguez Valiente, C. Fernández Manzano, B. Conde García and J. R. García-Berrocal declare that they have no competing interests.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Caption Electronic Supplementary Material
Video: Patient with eosinophilic esophagitis seen by transnasal esophagoscopy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Górriz Gil, C., Matallana Royo, V., Álvarez Montero, Ó. et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: an underdiagnosed cause of dysphagia and food impaction to be recognized by otolaryngologists. HNO 66, 534–542 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00106-018-0516-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00106-018-0516-3