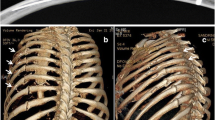
Abstract
Objectives
In this study, we assessed the bending strength of two surgical repairs of rib fracture using RibLoc® U Plus system made by Acute Innovations and the anterior plate by Synthes.
Methods
After a rib fracture was created in seven pairs of cadaveric rib specimens, one side was repaired with the anterior plate and the other side repaired with the RibLoc U Plus® plate. Each of the rib is loaded using a custom device over 360,000 bending cycles to simulate in vivo fatiguing related to respiration. Upon completion of the cyclic loading, the specimens were compressively loaded to failure and the failure bending moment was determined.
Results
The ribs repaired with the RibLoc U Plus® system showed 79% higher failure bending moment than that of the anterior plate, with a p value of 0.033. The ribs repaired with RibLoc U Plus® showed a trend of less stiffness reduction over the 360,000 loading cycles.
Conclusion
The biomechanical study showed that the RibLoc U Plus® system is stronger in the bending moment loading of repaired ribs, possibly due to the U-shape structure supporting both the inner and outer cortices of a repaired rib.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peek J, Ochen Y, Saillant N, Groenwold RHH, Leenen LPH, Uribe-Leitz T, et al. Traumatic rib fractures: a marker of severe injury. A nationwide study using the national trauma data bank. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2020;5:e000441. https://doi.org/10.1136/tsaco-2020-000441.
Dehghan N. Challenges in plate fixation of chest wall injuries. Injury. 2018;49:S39-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1383(18)30301-2.
Lichte P, Kalverkamp S, Spillner J, Hildebrand F, Kobbe P. Thoraxtrauma aus chirurgischer Sicht. Unfallchirurg. 2018;121:403–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00113-018-0494-7.
Majercik S, Pieracci FM. Chest wall trauma. Thorac Surg Clin. 2017;27:113–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thorsurg.2017.01.004.
Fleishman N, Richardson T, Attard T. The clinical characteristics of fractures in pediatric patients exposed to proton pump inhibitors. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2020;70:815–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000002690.
Mello M, Weideman RA, Little BB, Weideman MW, Cryer B, Brown GR. Proton pump inhibitors increase the incidence of bone fractures in hepatitis c patients. Dig Dis Sci. 2012;57:2416–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2185-5.
Cooper A, Barlow B, DiScala C, String D. Mortality and truncal injury: the pediatric perspective. J Pediatr Surg. 1994;29:33–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3468(94)90518-5.
Singh R, Taylor DM, D’Souza D, Gorelik A, Page P, Phal P. Injuries significantly associated with thoracic spine fractures: a case-control study. Emerg Med Australas. 2009;21:419–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-6723.2009.01209.x.
Brasel KJ, Guse CE, Layde P, Weigelt JA. Rib fractures: relationship with pneumonia and mortality*. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:1642–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000217926.40975.4B.
Bearn P, Patel J, O’Flynn WR. Cervical ribs: a cause of distal and cerebral embolism. Postgrad Med J. 1993;69:65–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/pgmj.69.807.65.
Wijffels MME, Prins JTH, Polinder S, Blokhuis TJ, De Loos ER, Den Boer RH, et al. Early fixation versus conservative therapy of multiple, simple rib fractures (FixCon): protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial. World J Emerg Surg. 2019;14:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13017-019-0258-x.
Fokin AA, Hus N, Wycech J, Rodriguez E, Puente I. Surgical stabilization of rib fractures: indications, techniques, and pitfalls. JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2020;10:e0032–e0032. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.ST.19.00032.
Daegling DJ, Warren MW, Hotzman JL, Self CJ. Structural analysis of human rib fracture and implications for forensic interpretation*. J Forensic Sci. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2008.00876.x.
Talbot BS, Gange CP, Chaturvedi A, Klionsky N, Hobbs SK, Chaturvedi A. Traumatic rib injury: patterns, imaging pitfalls, complications, and treatment—erratum. Radiographics. 2017;37:1004–1004. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2017174003.
Lin HC, Chou CS, Hsu TC. Stress fractures of the ribs in amateur golf players. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi Chin Med J Free China Ed. 1994;54:33–7.
Love JC, Symes SA. Understanding rib fracture patterns: incomplete and buckle fractures. J Forensic Sci. 2004;49:1153–8.
Yang K, Lynch M, O’Donnell C. “Buckle” rib fracture: an artifact following cardio-pulmonary resuscitation detected on postmortem CT. Leg Med. 2011;13:233–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.legalmed.2011.05.004.
Blackburne WB, Waddell JN, Swain MV, de Alves Sousa RJ, Kieser JA. Biomechanical investigation of impact induced rib fractures of a porcine infant surrogate model. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;62:588–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2016.05.025.
Griffard J, Daley B, Campbell M, Martins D, Beam Z, Rowe S, et al. Plate of ribs: single institution’s matched comparison of patients managed operatively and non-operatively for rib fractures. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2020;5:e000519. https://doi.org/10.1136/tsaco-2020-000519.
Pouzac M, Blanchard N, Canarelli JP. Traumatismes thoraciques de l’enfant. Arch. Pediatrie. 2000;7:67s–72s. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0929-693X(00)88823-5.
Pieracci FM, Leasia K, Bauman Z, Eriksson EA, Lottenberg L, Majercik S, et al. A multicenter, prospective, controlled clinical trial of surgical stabilization of rib fractures in patients with severe, nonflail fracture patterns (chest wall injury society Nonflail). J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020;88:249–57. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0000000000002559.
de Jong MB, Kokke MC, Hietbrink F, Leenen LPH. Surgical management of rib fractures: strategies and literature review. Scand J Surg. 2014;103:120–5. https://doi.org/10.1177/1457496914531928.
Saritas A, Guneren G, UzunSaritas P, Kizilkaya SA, Ugis C. The decrease of the duration of stay in the icu with rib fixation in a case of multiple rib fracture. Turk J Anesth Reanim. 2014;42:277–9. https://doi.org/10.5152/TJAR.2014.67044.
DeFreest L, Tafen M, Bhakta A, Ata A, Martone S, Glotzer O, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of rib fractures in polytrauma patients with flail chest. Am J Surg. 2016;211:761–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2015.11.014.
Marasco SF, Šutalo ID, Bui AV. Mode of failure of rib fixation with absorbable plates: a clinical and numerical modeling study. J Trauma Inj Infect Crit Care. 2010;68:1225–33. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3181d27cab.
de Moya M, Nirula R, Biffl W. Rib fixation: Who, What, When? Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2017;2:e000059. https://doi.org/10.1136/tsaco-2016-000059.
Imajima Y, Kitano M, Ueda T. Intramedullary fixation using Kirschner wires in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr Orthop. 2015;35:431–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000285.
Zhang Q, Song L, Ning S, Xie H, Li N, Wang Y. Recent advances in rib fracture fixation. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11:S1070–7. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2019.04.99.
Bottlang M, Walleser S, Noll M, Honold S, Madey SM, Fitzpatrick D, et al. Biomechanical rationale and evaluation of an implant system for rib fracture fixation. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2010;36:417–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-010-0047-4.
Reber PU, Kniemeyer HW, Ris HB. Reconstruction plates for internal fixation of flail chest. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998;66:2158.
Bulger EM, Arneson MA, Mock CN, Jurkovich GJ. Rib fractures in the elderly. J Trauma. 2000;48:1040–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005373-200006000-00007 (discussion 1046-1047).
Rehm KE, Rehm KE. Die osteosynthese der thoraxwandinstabilitäten: mit 44 tabellen. Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo: Springer; 1986.
Helzel I, Long W, Fitzpatrick D, Madey S, Bottlang M. Evaluation of intramedullary rib splints for less-invasive stabilisation of rib fractures. Injury. 2009;40:1104–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2009.06.004.
Ypma TJ. Historical development of the Newton-Raphson method. SIAM Rev. 1995;37:531–51. https://doi.org/10.1137/1037125.
Yoganandan N, Pintar FA. Biomechanics of human thoracic ribs. J Biomech Eng. 1998;120:100–4. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2834288.
Lodhia JV, Konstantinidis K, Papagiannopoulos K. Surgical management of multiple rib fractures/flail chest. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11:1668–75. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2019.03.54.
Marasco S, Quayle M, Summerhayes R, Šutalo ID, Liovic P. An assessment of outcomes with intramedullary fixation of fractured ribs. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016;11:126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13019-016-0510-3.
Marasco S, Saxena P. Surgical rib fixation—technical aspects. Injury. 2015;46:929–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2014.12.021.
Sarani B, Schulte L, Diaz JJ. Pitfalls associated with open reduction and internal fixation of fractured ribs. Injury. 2015;46:2335–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2015.10.022.
Sarani B, Allen R, Pieracci FM, Doben AR, Eriksson E, Bauman ZM, et al. Characteristics of hardware failure in patients undergoing surgical stabilization of rib fractures: a chest wall injury society multicenter study. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2019;87:1277–81. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0000000000002373.
Funding
National Institute of Health, ACUTE innovations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Giovanni Oppizzi, Dali Xu, Tirth Patel, Jose Diaz and Li-Qun Zhang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclosure
The study was support in part by Acumed and the National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Oppizzi, G., Xu, D., Patel, T. et al. Open reduction internal fixation of rib fractures: a biomechanical comparison between the RibLoc U Plus® system and anterior plate in rib implants. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 49, 383–391 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-022-02075-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-022-02075-x