Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of bardoxolone methyl (BM), a nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activator, on acute kidney injury in a rat model of crush syndrome model.
Methods
Sixty-four rats were separated equally into eight groups, sham (sterile saline ip), crush, crush + vehicle (DMSO ip), and crush + BM (10 mg/kg ip) (n = 8). All groups were also divided as 3 and 24 h after decompression. Crush injury was induced by 6 h of direct compression to both hind limbs of the rats with blocks weighing 3.6 kg on each side, followed by 3 and 24 h of decompression. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), tumor necrotizing factor-α (TNF-α), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) concentrations, tissue total oxidant status (TOS) and total antioxidant status (TAS) were measured in the kidneys. Serum creatine kinase (CK), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine concentrations were also measured. Glomerular and tubular structures were examined histopathologically. Bcl-2 was measured using immunohistochemistry. Apoptosis was assessed using the TUNEL method.
Results
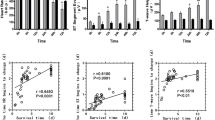
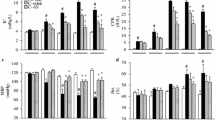
BM treatment reduced KIM-1, NGAL, TNF-α, TGF-β1, TOS concentrations, and increased TAS concentrations in the kidneys 3 and 24 h after decompression. Serum CK, BUN and creatinine concentrations were also reduced with BM. BM treatment decreased apoptosis in crush-related AKI. The Nrf2 activator BM reversed the crush-induced changes in the experimental rats.
Conclusion
BM treatment prevented the progression of crush-related AKI in rats possibly through its cytoprotective effects of being an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic agent.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sever MS, Vanholder R, Ashkenazi I, Becker G, Better O, Covic A, De Smet M, Eckardt KU, Eknoyan G, Gibney N, Hoste E, Kazancioglu R, Lameire N, Luyckx V, Portilla D, Tuglular S, Van Biesen W. Recommendation for the management of crush victims in mass disasters. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2012;27(Suppl 1):i1–67.
Sever MS, Kellum J, Hoste E, Vanholder R. Application of the RIFLE criteria in patients with crush-related acute kidney injury after mass disasters. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(2):515–24.
Murata I, Ooi K, Shoji S, Motohashi Y, Kan M, Ohtake K, Kimura S, Ueda H, Nakano G, Sonoda K, Inoue Y, Uchida H, Kanamoto I, Morimoto Y, Kobayashi J. Acute lethal crush-injured rats can be successfully rescued by a single injection of high-dose dexamethasone through a pathway involving PI3K-Akt-eNOS signaling. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;75:241–9.
Murata I, Nozaki R, Ooi K, Ohtake K, Kimura S, Ueda H, Nakano G, Sonoda K, Inoue Y, Uchida H, Kanamoto I, Morimoto Y, Kobayashi J. Nitrite reduces ischemia/reperfusion-induced muscle damage and improves survival rates in rat crush injury model. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(6):1548–54.
Sgarbi MW, Silva BA Jr, Peres CM, Alba TC, Curi R, Soriano FG, Ribeiro DA, Velasco IT. Leukocyte infiltration in lung, muscle, and liver after limb compression in rats. Pathophysiology. 2013;20(2):111–6.
Plotnikov EY, Chupyrkina AA, Pevzner IB, Isaev NK, Zorov DB. Myoglobin causes oxidative stress, increase of NO production and dysfunction of kidney's mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792(8):796–803.
Nishikata R, Kato N, Hiraiwa K. Oxidative stress may be involved in distant organ failure in tourniquet shock model mice. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2014;16(2):70–5.
Lambers Heerspink HJ, Chertow GM, Akizawa T, Audhya P. Baseline characteristics in the bardoxolone methyl evaluation in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: the occurrence of renal events (BEACON) trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28(11):2841–50.
Ahmad R, Raina D, Meyer C, Kharbanda S, Kufe D. Triterpenoid CDDO-Me blocks the NF-kB pathway by direct inhibition of IKKb on Cys-179. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(47):35764–9.
Lee JM, Li J, Johnson DA, Stein TD, Kraft AD, Calkins MJ, Jakel RJ, Johnson JA. Nrf2, a multi-organ protector? FASEB J. 2005;19:1061–6.
Liu M, Grigoryev DN, Crow MT, Haas M, Yamamoto M, Reddy SP, Rabb H. Transcription factor NRF2 is protective during ischemic and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury in mice. Kidney Int. 2009;76:277–85.
Jiang T, Huang Z, Lin Y, Zhang Z, Fang D, Zhang DD. The protective role of NRF2 in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2010;59:850–60.
Pergola PE, Krauth M, Huff JW, Ferguson DA, Ruiz S, Meyer CJ, Warnock DG. Effect of bardoxolone methyl on kidney function in patients with T2D and stage 3b–4 CKD. Am J Nephrol. 2011;33:469–76.
de Zeeuw D, Akizawa T, Audhya P, Bakris GL, Chin M, Christ-Schmidt H, Goldsberry A, Houser M, Krauth M, Lambers Heerspink HJ, McMurray JJ, Meyer CJ, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Toto RD, Vaziri ND, Wanner C, Wittes J, Wrolstad D, Chertow GM, BEACON Trial Investigators. Bardoxolone methyl in type 2 diabetes and stage 4 chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:2492–503.
Chin MP, Bakris GL, Block GA, Chertow GM, Goldsberry A, Inker LA, Heerspink HJL, O'Grady M, Pergola PE, Wanner C, Warnock DG, Meyer CJ. Bardoxolone methyl improves kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 4 and type 2 diabetes: post-hoc analyses from bardoxolone methyl evaluation in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes study. Am J Nephrol. 2018;47(1):40–7.
Wu QQ, Wang Y, Senitko M, Meyer C, Wigley WC, Ferguson DA, Grossman E, Chen J, Zhou XJ, Hartono J, Winterberg P, Chen B, Agarwal A, Lu CY. Bardoxolone methyl (BARD) ameliorates ischemic AKI and increases expression of protective genes Nrf2, PPARγ, and HO-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011;300:F1180–F1192192.
Aminzadeh MA, Reisman SA, Vaziri ND, Khazaeli M, Yuan J, Meyer CJ. The synthetic triterpenoid RTAdh404 (CDDO-dhTFEA) restores Nrf2 activity and attenuates oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in rats with chronic renal failure. Xenobiotica. 2014;44:570–8.
Takikawa M, Nakamura S, Ishihara M, Takabayashi Y, Fujita M, Hattori H, Kushibiki T, Ishihara M. Improved angiogenesis and healing in crush syndrome by fibroblast growth factor-2-containing low-molecular-weight heparin (Fragmin)/protamine nanoparticles. J Surg Res. 2015;196(2):247–57.
Yates MS, Tauchi M, Katsuoka F, Flanders KC, Liby KT, Honda T, Gribble GW, Johnson DA, Johnson JA, Burton NC, Guilarte TR, Yamamoto M, Sporn MB, Kensler TW. Pharmacodynamic characterization of chemopreventive triterpenoids as exceptionally potent inducers of Nrf2-regulatedgenes. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:154–62.
Bubb KJ, Kok C, Tang O, Rasko NB, Birgisdottir AB, Hansen T, Ritchie R, Bhindi R, Reisman SA, Meyer C, Ward K, Karimi Galougahi K, Figtree GA. The NRF2 activator DH404 attenuates adverse ventricular remodeling post-myocardial infarction by modifying redox signalling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;108:585–94.
Erel O. A novel automated method to measure total antioxidant response against potent free radical reactions. Clin Biochem. 2004;37:112–9.
Erel O. A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin Biochem. 2005;38:1103–11.
Jablonski P, Howden BO, Rae DA, Birrell CS, Marshall VC, Tange J. An experimental model for assessment of renal recovery from warm ischemia. Transplantation. 1983;35:198–204.
Gobé G, Zhang XJ, Willgoss DA, Schoch E, Hogg NA, Endre ZH. Relationship between expression of Bcl-2 genes and growth factors in ischemic acute renal failure in the rat. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000;11(3):454–67.
El Mouedden M, Laurent G, Mingeot-Leclercq MP, Tulkens PM. Gentamicin-induced apoptosis in renal cell lines and embryonic rat fibroblasts. Toxicol Sci. 2000;56(1):229–39.
Rysz J, Gluba-Brzózka A, Franczyk B, Jabłonowski Z, Ciałkowska-Rysz A. Novel biomarkers in the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease and the prediction of its outcome. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(8):E1702.
Motawi TK, Shehata NI, ElNokeety MM, El-Emady YF. Potential serum biomarkers for early detection of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;136:150–8.
Murata I, Ooi K, Sasaki H, Kimura S, Ohtake K, Ueda H, Uchida H, Yasui N, Tsutsui Y, Yoshizawa N, Hirotsu I, Morimoto Y, Kobayashi J. Characterization of systemic and histologic injury after crush syndrome and intervals of reperfusion in a small animal model. J Trauma. 2011;70(6):1453–63.
Akcay A, Nguyen Q, Edelstein CL. Mediators of inflammation in acute kidney injury. Mediat Inflamm. 2009;2009:1370–2.
Wang Z, Huang W, Li H, Tang L, Sun H, Liu Q, Zhang L. Synergistic action of inflammation and lipid dysmetabolism on kidney damage in rats. Ren Fail. 2018;40(1):175–82.
Yoshimura A, Wakabayashi Y, Mori T. Cellular and molecular basis for the regulation of inflammation by TGF-β. J Biochem. 2010;147(6):781–92.
Sgarbi MW, Silva Júnior BA, Peres CM, Loureiro TC, Curi R, Soriano FG, Ribeiro DA, Velasco IT. Plasma cytokine expression after lower-limb compression in rats. Rev Bras Ortop. 2014;50:105–9.
Shin DH, Park HM, Jung KA, Choi HG, Kim JA, Kim DD, Kim SG, Kang KW, Ku SK, Kensler TW, Kwak MK. The NRF2-heme oxygenase-1 system modulates cyclosporine a-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;48:1051–63.
Ding Y, Stidham RD, Bumeister R, Trevino I, Winters A, Sprouse M, Ding M, Ferguson DA, Meyer CJ, Wigley WC, Ma R. The synthetic triterpenoid, RTA 405, increases the glomerular filtration rate and reduces angiotensin II-induced contraction of glomerular mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 2013;83(5):845–54.
Hisamichi M, Kamijo-Ikemori A, Sugaya T, Hoshino S, Kimura K, Shibagaki Y. Role of bardoxolone methyl, a nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 activator, in aldosterone- and salt-induced renal injury. Hypertens Res. 2018;41(1):8–17.
Rath PC, Aggarwal BB. TNF-induced signaling in apoptosis. J Clin Immunol. 1999;19:350–64.
Huang Y, Li W, Su ZY, Kong AN. The complexity of the Nrf2 pathway: beyond the antioxidant response. Nutr Biochem. 2015;26(12):1401–13.
Thimmulappa RK, Fuchs RJ, Malhotra D, Scollick C, Traore K, Bream JH, Trush MA, Liby KT, Sporn MB, Kensler TW, et al. Preclinical evaluation of targeting the Nrf2 pathway by triterpenoids (CDDO-Im and CDDO-Me) for protection from LPS-induced inflammatory response and reactive oxygen species in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and neutrophils. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007;9:1963–70.
Noel S, Zheng L, Navas-Acien A, Fuchs RJ. The effect of ex vivo CDDO-Me activation on nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 pathway in white blood cells from patients with septic shock. Shock. 2014;42(5):392–9.
Zoja C, Corna D, Nava V, Locatelli M, Abbate M, Gaspari F, Carrara F, Sangalli F, Remuzzi G, Benigni A. Analogs of bardoxolone methyl worsen diabetic nephropathy in rats with additional adverse effects. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013;304(6):F808–F819819.
Vaziri ND, Liu S, Farzaneh SH, Nazertehrani S, Khazaeli M, Zhao YY. Dose-dependent deleterious and salutary actions of the Nrf2 inducer dh404 in chronic kidney disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;86:374–81.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Dumlupınar University Scientific Research Projects Unit, Kütahya, Turkey (Project no. 2016-16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study design: EK and YT. Animal studies and ELISA measurements: FEK and YT. Histopathologic examinations: CK. Biochemical measurement and interpretation: FEK. Manuscript writing and preparation of figures: YT and EK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The experimental protocol was approved by the animal ethical committee of Dumlupınar University (Approval no. 2015.11.02).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadıoğlu, E., Tekşen, Y., Koçak, C. et al. Beneficial effects of bardoxolone methyl, an Nrf2 activator, on crush-related acute kidney injury in rats. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 47, 241–250 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-019-01216-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-019-01216-z