Abstract
Introduction
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a severe disease associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The overall outcome has improved, but specific treatment(s) remains elusive. The challenge is the early identification and treatment of patients who will develop severe acute pancreatitis. Therefore, the aim of the present study is to investigate plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) in the initial phase of predicted severe acute pancreatitis.
Methods
Between June 2014 and January 2016, 64 patients with acute pancreatitis and 36 healthy individuals were included to study. Four blood samples, for serum TWEAK measurement, were taken from each individual in each group. The first measurement was taken from the admission blood sample. The subsequent three samples were taken at 12, 24, and 48 h after the hospital admission.
Results
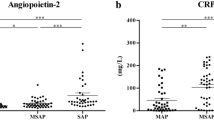
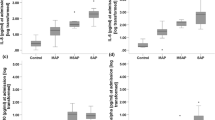
Serum TWEAK levels were significantly higher in patients with acute pancreatitis when compared with healthy controls. TWEAK plasma concentrations in severe pancreatitis patients were significantly higher than in mild pancreatitis patients.
Conclusion
Serum TWEAK levels increase progressively with the severity of acute pancreatitis and TWEAK might be a novel early marker of severity in acute pancreatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flint RS, Phillips AR, Farrant GJ, McKay D, Buchanan CM, Cooper GS, Windsor JA (2007) Probing the urinary proteome of severe acute pancreatitis. HPB (Oxford) 9(6):447–55.
Peng YS, Chen YC, Tian YC, Yang CW, Lien JM, Fang JT, Wu CS, Hung CF, Hwang TL, Tsai YH, Lee MS, Tsai MH.Serum levels of apolipoprotein A-I and high-density lipoprotein can predict organ failure in acute pancreatitis. Crit Care. 2015; 19:88.
Ferat-Osorio E, Wong-Baeza I, Esquivel-Callejas N, Figueroa-Figueroa S, Duarte-Rojo A, Guzmán-Valdivia-Gómez G, Rodea-Rosas H, Torres-González R, Sánchez-Fernández P, Arriaga-Pizano L, López-Macías C, Robles-Díaz G, Isibasi A. Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 expression on monocytes is associated with inflammation but not with infection in acute pancreatitis. Crit Care. 2009;13(3):R69.
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013;62(1):102–11.
Rahman SH, Menon KV, Holmfield JH, McMahon MJ, Guillou JP. Serum macrophage migration inhibitory factor is an early marker of pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 2007 Feb;245(2):282–9.
Chen T, Guo ZP, Li MM, Li JY, Jiao XY, Zhang YH, Liu HJ. Tumour necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK), an important mediator of endothelial inflammation, is associated with the pathogenesis of Henoch-Schonlein purpura. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 Oct;166(1):64–71.
Maymó-Masip E, Fernández-Veledo S, Garcia España A, Vázquez-Carballo A, Tinahones FJ, García-Fuentes E, Garrifo-Sanchez L, Rodriguez Mdel M, Vendrell J. Chacón MR.The rise of soluble TWEAK levels in severely obese subjects after bariatric surgery may affect adipocyte-cytokine production induced by TNFα. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Aug;98(8):E1323–33.
Balthazar EJ. Acute Pancreatitis: Assessment of Severity with Clinical and CT Evaluation. Radiology. 2002;223(3):603–13.
Schnúr A, Hegyi P, Rousseau S, Lukacs GL, Veit G. Epithelial Anion Transportas Modulator of Chemokine Signaling. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:7596531.
Bhatia M, Brady M, Shokuhi S, Christmas S, Neoptolemos JP, Slavin J. Inflammatory mediators in acute pancreatitis. J Pathol. 2000 Feb;190(2):117–25.
Bhatia M, Wong FL, Cao Y, Lau HY, Huang J, Puneet P, Chevali L. Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2005;5(2–3):132–44.
Bhatia M, Moochhala S. Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Pathol. 2004 Feb;202(2):145–56.
Burkly LC. Regulation of tissue responses: the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway and other TNF/TNFR superfamily members that activate non-canonical NFκB signaling. Front Immunol. 2015;6:92.
Cho JH, Kim TN, Chung HH, Kim KH. Comparison of scoring systems in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;Feb 28;21(8):2387–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zulfikaroglu, B., Isman, F.K., Bora, G. et al. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 45, 539–543 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-018-0938-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-018-0938-3