Abstract
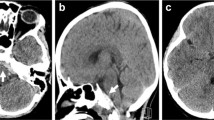
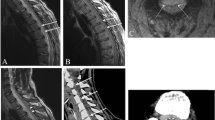
Vertebral artery injuries can be seen following trauma. Most traumatic vertebral artery injuries are limited to an intimal dissection. Rarely, transection of the vertebral artery can be seen with extravasation of hemorrhage into the surrounding soft tissues of the neck. Dural tears are rare in the setting of trauma. They are usually the result of penetrating trauma or severe blunt trauma. We present a case with both a vertebral artery transection and a dural tear. The combination of these lethal injuries resulted in extravasation of hemorrhage into the soft tissues of the neck, through the dural tear, and into the subarachnoid space of the cervical spine. The subarachnoid hemorrhage extended superiorly into the brain. The diagnosis was made by computed tomography (CT) and computed tomography angiography (CTA). The treatment of traumatic vertebral artery transections and dural tears are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atar E, Griton I, Bachar GN, Bartal G, et al. Embolization of transected vertebral arteries in unstable trauma patients. Emerg Radiol 2005;11:291–4.
Kobernick M, Carmody R. Vertebral artery transection from blunt trauma treated by embolization. J Trauma 1984;24:854–6.
Simionato F, Righi C, Silvani P, Torri G, Scotti G. Emergency endovascular treatment of a life-threatening hemorrhage from traumatic rupture of the left extracranial vertebral artery. Intensive Care Med 1999;25:1177–9.
Cohen JE, Rajz G, Itshayek E, Umansky F, Gomori J. Endovascular management of exsanguinating vertebral artery transection. Surg Neurol 2005;64:331–4.
Willis BK, Greiner F, Orrison WW, Benzel EC. The incidence of vertebral artery injury after midcervical spine fracture or subluxation. Neurosurgery 1994;3:435–42.
Porto DP, Adams GL, Foster C. Emergency management of carotid artery rupture. Am J Otolaryngol 1986;7: 199–209.
Demetriades D, Theodorou D, Asensio J, Golshani S, Belzberg H, Yellin A, Weaver F, Berne TV. Management options in vertebral artery injuries. Br J Surg 1996;83:83–6.
Ben-Menachem Y, Fields WS, Cadavid G, Gomez LS, Anderson EC, Fisher RG. Vertebral artery trauma: transcatheter embolization. Am J Neuroradiol 1987;8:501–7.
Hetz SP, Frykberg ER, Northup HM, West DL, Alexander RH. Penetrating injury of the vertebral artery: a unique management approach. South Med J 1989;82:1037–40.
Kluger Y, Sagie B, Soffer D, Hai N, Oron D. Combined approach in the management of penetrating injury of vertebral artery. Harefuah 2000;139:274–6.
Chaara M, Chapot R, Bernard C, Rossignol M, Mebazaa A. Successful endovascular embolization in the vertebral artery after failed surgery in a patient with severe hemorrhagic shock. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim 2001;20:853–6.
Ben-Menachem Y. Interventive and guidance procedures. In: Ben-Menachem (Ed.), Angiography in trauma: a work atlas. Saunders, Philedelphia 1981, pp 420–9.
Schonholz CJ, Uflacker R, De Gregorio MA, Parodi JC. Stent-graft treatment of trauma to the supra-aortic arteries. A review. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 2007;48:537–49.
Cox MW, Whittaker DR, Martinez C, Fox CJ, Feuerstein IM, Gillespie DL. Traumatic pseudoaneurysms of the head and neck: early endovascular intervention. J Vasc Surg 2007;46:1227–33.
Okuyama T, Niwa J, Shimizu K, Hirai H, Kubota T. Traumatic rupture of the vertebral artery associated with fracture of the cervical spine: a case report. No Shinkei Geka 1989;17:973–7.
Keenen TL, Antony J, Benson DR. Dural tears associated with lumbar burst fractures. J Orthop Trauma 1990;4:43–5.
Colachis SC 3rd, Rea GL. Dural tear following traumatic spinal cord injury. A delayed complication. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 1992;71:352–5.
Watters MR, Stears JC, Osborn AG, Turner GE, Burton BS, Lillehei K, Yuh WT. Transdural spinal cord herniation: imaging and clinical aspects. Am J Neuroradiol 1998;19:1337–44.
De Gelb D, Lenke L, Pond J. Dural tear associated with a flexion distraction subluxation to the cervical spine without neurologic injury. Acta Orthop Belg 1998;64:224–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baerlocher, M.O., Zakrison, T.L., Tien, H. et al. Traumatic Cervical Vertebral Artery Transection Associated with a Dural Tear Leading to Subarachnoid Extravasation. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 35, 67–70 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-008-7184-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-008-7184-z