Abstract
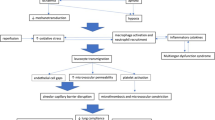
Background: Neutrophil recruitment into microvascular circuits is known to be initiated by selectin-mediated endothelial adherence. The effect of fucoidin (a natural sulfated polymer of L-fucose and this potent selectin ligand) on the selectin-dependent neutrophil migration within pulmonary and hepatic capillaries was studied in a two-hit trauma model in mice.
Methods and Results: Infrarenal ischemia (4 h) followed by reperfusion (4 h) and subsequent cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) resulted in pulmonary capillary leakage at 48 h as evidenced by an increased alveolar/plasma protein ratio (0.21 vs. 0.03 in control; p < 0.05) and also led to pulmonary neutrophil accumulation as assessed by the myeloperoxidase (MPO) content in homogenized lung tissue (0.29 U/min vs. 0.21 U/min in control; p > 0.05). A significant (p < 0.05) increase in interleukin-(IL-)6 (30.1 pg/ml) and IL-10 (44.9 pg/ml) was noted in the two-hit model. Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury alone resulted in the same pattern of injury but to a lesser extent, whereas CLP alone did only lead to a significant increase in IL-6 and IL-10. The effect of fucoidin was diverse and depended on the type of injury. In the two-hit model, fucoidin, infused at a dosage of 2.5 mg/kg at the time of reperfusion, significantly reduced pulmonary leakage but seemed to deteriorate neutrophil accumulation as reflected by a slight MPO increase (p > 0.05). Also both cytokines, IL-6 (318.8 pg/ml) and IL-10 (106.1 pg/ml), significantly (p < 0.05) increased under these circumstances. In the protocol of each single injury (I/R or CLP), fucoidin significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the protein ratio, diminished IL-6 and IL-10 serum levels (p < 0.05 only for IL-6 in the I/R protocol), but again slightly raised (p > 0.05) lung and liver MPO. In all histological sections of either experimental protocol, fucoidin revealed less neutrophil accumulation and less interstitial edema formation.
Conclusion: Based on our data, we would conclude that fucoidin attenuates selectin-mediated neutrophil adherence leading to capillary leakage, although neutrophil recruitment seems not to be influenced. For clinical perspectives, it could be relevant that the selectin-dependent pathway of neutrophil adherence can be blocked by sulfated L-fucose.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: June 5, 2001; revision accepted: November 6, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seekamp, A., van Griensven, M., Breyhan, K. et al. The Effect of Fucoidin on the Remote Pulmonary Injury in a Two-Hit Trauma Model in Mice. Eur J Trauma 27, 317–326 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-001-1145-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-001-1145-0