Abstract
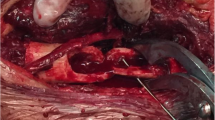
We describe a case of osteomyelitis due to Mycobacterium fortuitum after open tibial fracture. Extensive wound debridement, removal of the intramedullary nail and antibiotic therapy consisting of ofloxacin, roxythromycin and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole cured the infection. Moreover, the literature describing infections by atypical mycobacteria is reviewed, and common clinical characteristics as well as treatment options are displayed. Immunocompromised individuals are particularly threatened by wound infections due to atypical mycobacteria. Periprosthetic infections caused by atypical mycobacteria gain importance in postoperative care after trauma surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: November 13, 2000; revision accepted: February 6, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carl, HD., Schaller, P. & Freiheit, T. Osteomyelitis due to Mycobacterium fortuitum after Open Tibial fracture Case Report and a Summary of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Aspects. Eur J Trauma 27, 92–95 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-001-1090-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-001-1090-y