Background:
The so-called “supraclavicular” region bears the confluence of deep jugular, upper mediastinal and axillary lymph node groups and therefore it is often part of the target volume in common malignancies like lung cancer, breast cancer and head and neck cancer. For treating this area, several authors recommend an anterior portal with the dose prescribed to a tissue depth of 3 cm, which does not fit our institution's experience.
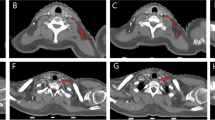
Patients and Methods: In 119 consecutive patients a computed tomography for planning purposes was performed. We used the subclavian blood vessels between clavicula and first rib as an estimate of the confluence of the mentioned lymph node regions and determined their tissue depth (which does not describe the deepest part of the lymph vessels).
Results: Mean and median of the tissue depth were 5 cm in a range from 2 to 9 cm. Only in less than 20% of the measurements we found the vessels located 3 cm or less under the surface which would correspond to a depth of the lymph node target volume 4 to 5 cm. Increasing body mass resulted in deeper location of the vessels. The position of the patient's arms influenced the tissue depth even more. Arms risen above the head resulted in 55% of the measurements in tissue depths of 6 cm or deeper compared to 6% in patients treated with arms beside the body.
Conclusion: Standardized treatment prescriptions do not cope adequately with individual anatomy. Treatment position especially of the arms influences location of the “supraclavicular” lymph node region in thoracic treatment. Target volume delineation by computed tomography seems the most accurate solution, although it is the most expensive one. Patient immobilization is crucial for accuracy of treatment delivery.
Hintergrund:
In der so genannten “Supraklavikularregion” findet sich der Zusammenfluss der tief zervikalen, oberen mediastinalen und zentral axillären Lymphwege; daher gehört sie oft zum Zielvolumen häufiger Tumorerkrankungen wie Bronchial-, Mamma- und Kopf-Hals-Karzinomen. Viele Empfehlungen zur Bestrahlung dieser Region verschreiben ein anteriores Stehfeld mit Dosierung auf 3 cm Gewebetiefe, was nicht den Erfahrungen unserer Institution entspricht.
Patienten und Methode: Bei 119 konsekutiven Patienten wurde eine Computertomographie zur Planung durchgeführt. Als Schätzung des Zusammenflusses der genannten Lymphknotenregionen dienten uns die Subklaviagefäße zwischen Klavikula und erster Rippe, deren Gewebetiefe bestimmt wurde (die damit nicht den oberflächenfernsten Teil des Lymphgefäßareals beschreibt, Abbildung 1).
Ergebnisse: Arithmetisches Mittel und Median der Gewebetiefe betrugen 5 cm bei einem gemessenen Wertebereich von 2 bis 9 cm. Nur weniger als 20% aller Messungen fanden eine Gefäßtiefe von 3 cm oder weniger, die zu einer Zielvolumentiefe von 4 bis 5 cm führen würde. Die Gefäßtiefe stieg mit zunehmender Körpermasse an. Noch deutlicher beeinflusste die Armhaltung die Gewebetiefe. Bei Armhaltung über dem Kopf resultierten 55% aller Messungen in einer Gewebetiefe von 6 cm oder mehr, verglichen mit 6% bei Armhaltung neben dem Körper (Abbildung 2).
Schlussfolgerung: Pauschale Empfehlungen zur Dosierungstiefe der genannten Lymphknoten werden der individuellen Anatomie nicht gerecht. Die Patientenlagerung, insbesondere der Arme, beeinflusst die Lage der Lymphknotenareale bei thorakaler Bestrahlung. Der beste, wenn auch aufwändigste Weg ist die individuelle Lagebestimmung der Lymphknotenregionen mittels CT-Planung. Eine Immobilisierung der Patienten ist entscheidend für die Genauigkeit der Behandlung.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Submitted: 14 Feb 2000 / Accepted: 8 May 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klages, H., Szafinski, F. & Makoski, HB. Variation in “Supraclavicular” Lymph Node Depth is Partly Determined by Treatment Position. Strahlenther Onkol 176, 315–318 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000660050013
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000660050013