Abstract
Purpose
Osthole possesses anti-tumor activities. However, whether osthole can have a radiosensitization effect on hepatic cancer remains unclear. Here, an HCC-LM3 cells-inoculated subcutaneous transplanted tumor was adopted to explore the effect of osthole.
Methods
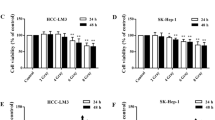
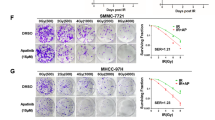
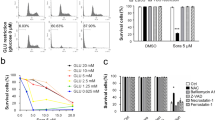
The tumor-bearing mice were treated with 100 mg/kg osthole for 12 days, 4 Gy irradiation twice, or their combination. The tumor volume and weight, lactic acid content, glycolytic enzyme activities, and protein expression of glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β), p‑GSK-3β, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), p‑mTOR, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), p‑AMPK, glucose transporter 1/3, and pyruvate kinase M2 were determined. The GSK-3β-overexpressed HCC-LM3 or SK-Hep‑1 cell models were also adopted to verify the effects of osthole on expression of these proteins.
Results
The tumor volume and weight, lactic acid content, and glycolytic enzyme activities in tumor tissues were lower in the osthole + radiation group than in the radiation group. Moreover, osthole could reverse the radiation-induced increments of p‑GSK-3β/GSK-3β and p‑mTOR/mTOR protein ratios and the expression of glucose transporter 1/3 and pyruvate kinase M2 proteins in tumor tissues, and increase the protein ratio of p‑AMPK/AMPK. The effects of osthole on these glycolysis-related proteins were also observed in GSK-3β-overexpressed HCC-LM3 or SK-Hep‑1 cell models.
Conclusion
Osthole has a radiosensitizing effect on subcutaneous transplanted hepatocellular carcinoma, and its mechanism may be related to inhibition of GSK-3β/AMPK/mTOR pathway-controlled glycolysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang L, Li J, Di LJ (2022) Glycogen synthesis and beyond, a comprehensive review of GSK3 as a key regulator of metabolic pathways and a therapeutic target for treating metabolic diseases. Med Res Rev 42:946–982
Emma MR, Augello G, Cusimano A, Azzolina A, Montalto G, McCubrey JA, Cervello M (2020) GSK‑3 in liver diseases: friend or foe? Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1867:118743
Zhang N, Liu XJ, Liu L, Deng ZS, Zeng QX, Pang WQ, Liu Y, Song DQ, Deng HB (2018) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition promotes lysosome-dependent degradation of c‑FLIPL in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 9:230
Fang GX, Zhang PL, Liu JF, Zhang X, Zhu XJ, Li R, Wang HY (2019) Inhibition of GSK-3β activity suppresses HCC malignant phenotype by inhibiting glycolysis via activating AMPK/mTOR signaling. Cancer Lett 463:11–26
Tang L, Wei F, Wu YF, He Y, Shi L, Xiong F, Gong ZJ, Guo C, Li XY, Deng H, Cao K, Zhou M, Xiang B, Li XL, Li Y, Li GY, Xiong W, Zeng ZY (2018) Role of metabolism in cancer cell radioresistance and radiosensitization methods. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:87
Vogel A, Cervantes A, Chau I, Daniele B, Llovet JM, Meyer T, Nault JC, Neumann U, Ricke J, Sangro B, Schirmacher P, Verslype C, Zech CJ, Arnold D, Martinelli E (2018) Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 29(iv238):iv255
Shokoohinia Y, Jafari F, Mohammadi Z, Bazvandi L, Hosseinzadeh L, Chow N, Bhattacharyya P, Farzaei MH, Farooqi AA, Nabavi SM, Yerer MB, Bishayee A (2018) Potential anticancer properties of osthol: a comprehensive mechanistic review. Nutrients 10:36
Ashrafizadeh M, Mohammadinejad R, Samarghandian S, Yaribeygi H, Johnston TP, Sahebkar A (2020) Anti-tumor effects of osthole on different malignant tissues: A review of molecular mechanisms. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 20:918–931
Chen YQ, Song HY, Zhou ZY, Ma J, Luo ZY, Zhou Y, Wang JY, Liu S, Han XH (2022) Osthole inhibits the migration and invasion of highly metastatic breast cancer cells by suppressing ITGα3/ITGβ5 signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin 43:1544–1555
Dai XX, Yin CT, Zhang Y, Guo GL, Zhao CG, Wang OC, Xiang YQ, Zhang XH, Liang G (2018) Osthole inhibits triple negative breast cancer cells by suppressing STAT3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:322
Mo Y, Wu Y, Li X, Rao H, Tian XX, Wu DN, Qiu ZP, Zheng GH, Hu JJ (2020) Osthole delays hepatocarcinogenesis in mice by suppressing AKT/FASN axis and ERK phosphorylation. Eur J Pharmacol 867:172788
Lin ZK, Liu J, Jiang GQ, Tan G, Gong P, Luo HF, Li HM, Du J, Ning Z, Xin Y, Wang ZY (2017) Osthole inhibits the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 37:1611–1618
Fan K, Huang H, Zhao Y, Xie T, Zhu ZY, Xie ML (2022) Osthole increases the sensitivity of liver cancer to sorafenib by inhibiting cholesterol metabolism. Nutr Cancer 74:3640–3650
Huang H, Xue J, Xie T, Xie ML (2023) Osthole increases the radiosensitivity of hepatoma cells by inhibiting GSK-3β/AMPK/mTOR pathway-controlled glycolysis. N‑S Arch. Pharmacol, vol 396, pp 683–692
Qi ZG, Zhao X, Zhong W, Xie ML (2016) Osthole improves glucose and lipid metabolism via modulation of PPARα/γ-mediated target gene expression in liver, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle in fatty liver rats. Pharm Biol 54:882–888
Liu JC, Zhou L, Wang F, Cheng ZQ, Chen R (2018) Osthole decreases collagen I/III contents and their ratio in TGF-beta 1‑overexpressed mouse cardiac fibroblasts through regulating the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Chin J Nat Med 16:321–329
Jia CH, Zhao Y, Huang H, Fan K, Xie T, Xie ML (2022) Apigenin sensitizes radiotherapy of mouse subcutaneous glioma through attenuations of cell stemness and DNA damage repair by inhibiting NF-κB/HIF-1α-mediated glycolysis. J Nutr Biochem 107:109038
Yu L, Sun YF, Li JJ, Wang Y, Zhu YX, Shi Y, Fan XJ, Zhou JD, Bao Y, Xiao J, Cao K, Cao PG (2017) Silencing the Girdin gene enhances radio-sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma via suppression of glycolytic metabolism. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:110
Feng J, Li JJ, Wu LW, Yu Q, Ji J, Wu JY, Dai WQ, Guo CY (2020) Emerging roles and the regulation of aerobic glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39:126
Feng J, Dai WQ, Mao YQ, Wu LW, Li JJ, Chen K, Yu Q, Kong R, Li SN, Zhang J, Ji J, Wu JY, Mo WH, Xu XF, Guo CY (2020) Simvastatin re-sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib by inhibiting HIF-1α/PPAR-γ/PKM2-mediated glycolysis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39:24
Lin YZ, Zhai H, Ouyang Y, Lu ZY, Chu CB, He QT, Cao XP (2019) Knockdown of PKM2 enhances radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int 19:129
Liu KX, Everdell E, Pal S, Haas-Kogan DA, Milligan MG (2021) Harnessing lactate metabolism for radiosensitization. Front Oncol 11:672339
Beurel E, Blivet-Van Eggelpoel MJ, Kornprobst M, Moritz S, Delelo R, Paye F, Housset C, Desbois-Mouthon C (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors augment TRAIL-induced apoptotic death in human hepatoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 77:54–65
Mamaghani S, Simpson CD, Cao PM, Cheung M, Chow S, Bandarchi B, Schimmer AD, Hedley DW (2012) Glycogen synthase kinase‑3 inhibition sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Plos One 7:e41102
Pal K, Cao Y, Gaisina IN, Bhattacharya S, Dutta SK, Wang EF, Gunosewoyo H, Kozikowski AP, Billadeau DD, Mukhopadhyay D (2014) Inhibition of GSK‑3 induces differentiation and impaired glucose metabolism in renal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 13:285–296
Lin JT, Song T, Li C, Mao WF (2020) GSK-3β in DNA repair, apoptosis, and resistance of chemotherapy, radiotherapy of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1867:118659
Kitano A, Shimasaki T, Chikano Y, Nakada M, Hirose M, Higashi T, Ishigaki Y, Endo Y, Takino T, Sato H, Sai Y, Miyamoto K, Motoo Y, Kawakami K, Minamoto T (2013) Aberrant glycogen synthase kinase 3beta is involved in pancreatic cancer cell invasion and resistance to therapy. Plos One 8:e55289
Abrams SL, Akula SM, Meher AK, Steelman LS, Gizak A, Duda P, Rakus D, Martelli AM, Ratti S, Cocco L, Montalto G, Cervello M, Ruvolo P, Libra M, Falzone L, Candido S, McCubrey JA (2021) GSK-3β can regulate the sensitivity of MIA-PaCa‑2 pancreatic and MCF‑7 breast cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs, targeted therapeutics and nutraceuticals. Cells 10:816
Park W, Park S, Song G, Lim W (2019) Inhibitory effects of osthole on human breast cancer cell progression via induction of cell cycle arrest, mitochondrial dysfunction, and ER stress. Nutrients 11:2777
Liu B, Jin JB, Zhang ZY, Zuo L, Jiang MX, Xie CF (2019) Shikonin exerts antitumor activity by causing mitochondrial dysfunction in hepatocellular carcinoma through PKM2-AMPK-PGC1 alpha signaling pathway. Biochm. Cell Biol 97:397–405
Zhang JH, Zhang YH, Mo F, Patel G, Butterworth K, Shao CL, Prise KM (2021) The roles of HIF‑1 alpha in radiosensitivity and radiation-induced bystander effects under hypoxia. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:637454
Meng W, Xie BH, Yang Q, Jia CC, Tang H, Zhang XM, Zhang Y, Zhang JW, Li HP, Fu BS (2019) Minichromosome maintenance 3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma radioresistance by activating the NF‑B pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:263
Liu WL, Gao M, Tzen KY, Tsai CL, Hsu FM, Cheng AL, Cheng JCH (2014) Targeting phosphatidylinositide 3‑kinase/Akt pathway by BKM120 for radiosensitization in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 5:3662–3672
Che YL, Li J, Li ZJ, Li J, Wang S, Yan Y, Zou K, Zou LJ (2018) Osthole enhances antitumor activity and irradiation sensitivity of cervical cancer cells by suppressing ATM/NF-κB signaling. Oncol Rep 40:737–747
Peng KY, Chou TC (2022) Osthole exerts inhibitory effects on hypoxic colon cancer cells via EIF2 alpha phosphorylation-mediated apoptosis and regulation of HIF‑1 alpha. Am J Chinese Med 50:621–637
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Fund of Nanjing Medical University (NMUB2020254), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HH and JX performed the animal and cell experiments. HH collected and analyzed the results and wrote the draft of the manuscript. JX revised and edited the manuscript. MLX and TX designed the experiments and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
H. Huang, J. Xue, M.-L. Xie and T. Xie declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
The animal study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines for the use and care of experimental animals of Soochow University and approved by the University Animal Ethics Committee (certificate no. 202103A0994; approval date 8 April 2021).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Hui Huang and Jie Xue contributed equally to this study.
Data availability
Data will be made available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Supplementary Information
Fig. S1
The results of full-length sequencing of GSK-3β
Fig. S2
GSK-3β protein expression in pcDNA3.1(+)-GSK-3β plasmid-transfected HCC-LM3 cells (A) or SK-Hep-1 cells (B). Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three different independent experiments. **P < 0.01 vs. the pcDNA3.1(+)-NC group. There was no obvious difference between the control group and the pcDNA3.1(+)-NC group
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Xue, J., Xie, ML. et al. Osthole inhibits GSK-3β/AMPK/mTOR pathway-controlled glycolysis and increases radiosensitivity of subcutaneous transplanted hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice. Strahlenther Onkol 200, 444–452 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-023-02173-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-023-02173-8