Abstract
Purpose
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) has been firmly established as a treatment choice for patients with oligometastases, as it has demonstrated both safety and efficacy by consistently achieving high rates of local control. Moreover, it offers potential survival benefits for carefully selected patients in real-world clinical settings.
Methods
Between January 2008 and May 2020, a total of 149 patients (with 414 liver metastases) received treatment. The Active Breathing Coordinator device was used for 68 patients, while respiratory gating was used for 65 and abdominal compression was used for 16 patients. The most common histological finding was colorectal adenocarcinoma, with 37.6% of patients having three or more metastases, and 18% having two metastases. The prescribed dose ranged from 36 to 60 Gy, delivered in 3–5 fractions.
Results
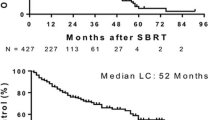
Local control rates at 2 and 3 years were 76.1% and 61.2%, respectively, with no instances of local recurrence after 3 years. Factors negatively impacting local control included colorectal histology, lower prescribed dose, and the occurrence of new liver metastases. The median overall survival from SBRT was 32 months, with the presence of metastases outside the liver and the development of new liver metastases after SBRT affecting survival. The median disease-free survival was 10 months. No substantial differences in both local control and survival were observed between the respiratory motion control techniques employed. Treatment tolerance was excellent, with only one patient experiencing acute grade IV thrombocytopenia and two patients suffering from ≥ grade II chronic toxicity.
Conclusion
For radical management of single or multiple liver metastases, SBRT is an effective and well-tolerated treatment option. Regardless of the technology employed, experienced physicians can achieve similarly positive outcomes. However, additional studies are required to elucidate prognostic factors that can facilitate improved patient selection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR (1995) Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol 13(1):8–10
Klement RJ, Abbasi-Senger N, Adebahr S, Alheid H, Allgaeuer M, Becker G et al (2019) The impact of local control on overall survival after stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver and lung metastases from colorectal cancer: A combined analysis of 388 patients with 500 metastases. BMC Cancer 19(1):173
Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, Gaede S, Louie AV, Haasbeek C et al (2019) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard of care palliative treatment in patients with oligometastatic cancers (SABR-COMET): a randomised, phase 2, open-label trial. Lancet 393(10185):2051–2058
Phillips R, Shi WY, Deek M, Radwan N, Lim SJ, Antonarakis ES et al (2020) Outcomes of observation vs stereotactic ablative radiation for oligometastatic prostate cancer: the ORIOLE phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 6(5):650–659
Gomez DR, Blumenschein GR, Lee JJ, Hernandez M, Ye R, Camidge DR et al (2016) Local consolidative therapy versus maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer without progression after first-line systemic therapy: a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 17(12):1672–1682
Benedict SH, Yenice KM, Followill D, Galvin JM, Hinson W, Kavanagh B et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy: the report of AAPM Task Group 101. Med Phys 37(8):4078–4101
Ingold JA, Reed GB, Kaplan HS, Bagshaw MA (1965) Radiation hepatitis. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 93:200–208
Dawson LA, Ten Haken RK (2005) Partial volume tolerance of the liver to radiation. Semin Radiat Oncol 15(4):279–283
Blomgren H, Lax I, Näslund I, Svanström R (1995) Stereotactic high dose fraction radiation therapy of extracranial tumors using an accelerator: clinical experience of the first thirty-one patients. Acta Oncol 34(6):861–870
Schefter TE, Rusthoven KE, Kavanagh BD, Cardenes H, Stieber VW, Burri SH et al (2009) Multi-institutional phase I/II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases. J Clin Oncol 27(10):1572–1578
Méndez Romero A, Wunderink W, Hussain SM, De Pooter JA, Heijmen BJ et al (2006) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary and metastatic liver tumors: A single institution phase i–ii study. Acta Oncol 45(7):831–837
Hoyer M, Roed H, Hansen AT, Ohlhuis L, Petersen J, Nellemann H et al (2006) Phase II study on stereotactic body radiotherapy of colorectal metastases. Acta Oncol 45(7):823–830
Herfarth KK, Debus J, Lohr F, Bahner ML, Wannenmacher M (2001) Stereotactic irradiation of liver metastases. Radiologe 41(1):64–68
Wulf J, Guckenberger M, Haedinger U, Oppitz U, Mueller G, Baier K et al (2006) Stereotactic radiotherapy of primary liver cancer and hepatic metastases. Acta Oncol 45(7):838–847
Katz AW, Carey-Sampson M, Muhs AG, Milano MT, Schell MC, Okunieff P (2007) Hypofractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for limited hepatic metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67(3):793–798
Chang DT, Swaminath A, Kozak M, Weintraub J, Koong AC, Kim J et al (2011) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for colorectal liver metastases: a pooled analysis. Cancer 117(17):4060–4069
Vautravers-Dewas C, Dewas S, Bonodeau F, Adenis A, Lacornerie T, Penel N et al (2011) Image-guided robotic stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases: Is there a dose response relationship? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(3):e39–e47
Lanciano R, Lamond J, Yang J, Feng J, Arrigo S, Good M et al (2012) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for patients with heavily pretreated liver metastases and liver tumors. Front Oncol 2:23
Habermehl D, Herfarth KK, Bermejo JL, Hof H, Rieken S, Kuhn S et al (2013) Single-dose radiosurgical treatment for hepatic metastases—therapeutic outcome of 138 treated lesions from a single institution. Radiat Oncol 8:175
Lee MT, Kim JJ, Dinniwell R, Brierley J, Lockwood G, Wong R et al (2009) Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy of liver metastases. J Clin Oncol 27(10):1585–1591
Feng M, Suresh K, Schipper MJ, Bazzi L, Ben-Josef E, Matuszak MM et al (2018) Individualized adaptive stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver tumors in patients at high risk for liver damage a phase 2 clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 4(1):40–47
Scorsetti M, Comito T, Clerici E, Franzese C, Tozzi A, Iftode C et al (2018) Phase II trial on SBRT for unresectable liver metastases: long-term outcome and prognostic factors of survival after 5 years of follow-up. Radiat Oncol 13(1):234
Goodman KA, Wiegner EA, Maturen KE, Zhang Z, Mo Q, Yang G et al (2010) Dose-escalation study of single-fraction stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(2):486–493
McPartlin A, Swaminath A, Wang R, Pintilie M, Brierley J, Kim J et al (2017) Long-term outcomes of phase 1 and 2 studies of SBRT for hepatic colorectal metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99(2):388–395
Folkert MR, Meyer JJ, Aguilera TA, Yokoo T, Sanford NN, Rule WG et al (2021) Long-term results of a phase 1 dose-escalation trial and subsequent institutional experience of single-fraction stereotactic ablative radiation therapy for liver metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 109(5):1387–1395
Méndez Romero A, Schillemans W, van Os R, Koppe F, Haasbeek CJ, Hendriksen EM et al (2021) The Dutch-Belgian registry of Stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases: clinical outcomes of 515 patients and 668 metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 109(5):1377
Palma DA, Salama JK, Lo SS, Senan S, Treasure T, Govindan R et al (2014) The oligometastatic state-separating truth from wishful thinking. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 11(9):549–557
Hernando-Requejo O, Sánchez E, Fernández P, Zucca D, Pérez JM, García-Aranda M et al (2011) Institutional experience on the treatment of lung and liver lesions with stereotactic body radiotherapy and Novalis Exactrac Adaptive Gating technique. J Radiosurg SBRT 1(3):231–236
Eccles C, Brock KK, Bissonnette JP, Hawkins M, Dawson LA (2006) Reproducibility of liver position using active breathing coordinator for liver cancer radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64(3):751–759
Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Adam R, Sobrero A, Van Krieken JH, Aderka D et al (2016) ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 27(8):1386–1422
Jackson WC, Tao Y, Mendiratta-Lala M, Bazzi L, Wahl DR, Schipper MJ et al (2018) Comparison of stereotactic body radiation therapy and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of Intrahepatic metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 100(4):950–958
Loi M, Desideri I, Dominici L, Francolini G, Garlatti P, Ciccone LP et al (2020) Thermal ablation versus SBRT in liver tumours: pros and cons. Med Oncol 37(6):52
Esposito M, Maggi G, Marino C, Bottalico L, Cagni E, Carbonini C et al (2016) Multicentre treatment planning inter-comparison in a national context: the liver stereotactic ablative radiotherapy case. Phys Med 32(1):277–283
Andratschke N, Alheid H, Allgäuer M, Becker G, Blanck O, Boda-Heggemann J et al (2018) The SBRT database initiative of the German Society for Radiation Oncology (DEGRO): patterns of care and outcome analysis of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for liver oligometastases in 474 patients with 623 metastases. BMC Cancer 18(1):283
Van Den Begin R, Engels B, Gevaert T, Duchateau M, Tournel K, Verellen D et al (2014) Impact of inadequate respiratory motion management in SBRT for oligometastatic colorectal cancer. Radiother Oncol 113(2):235
Berber B, Ibarra R, Snyder L, Yao M, Fabien J, Milano MT et al (2013) Multicentre results of stereotactic body radiotherapy for secondary liver tumours. HPB 15(11):851–857
Méndez Romero A, Keskin-Cambay F, van Os RM, Nuyttens JJ, Heijmen BJM et al (2017) Institutional experience in the treatment of colorectal liver metastases with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Oncol Radiother 22(2):126–131
Joo JH, Park JH, Kim JC, Yu CS, Lim SB et al (2017) Local control outcomes using stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99(4):876–883
Goodman BD, Mannina EM, Althouse SK, Maluccio MA, Cárdenes HR (2016) Long-term safety and efficacy of stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatic oligometastases. Pract Radiat Oncol 6(2):86–95
Fode MM, Høyer M (2015) Survival and prognostic factors in 321 patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligo-metastases. Radiother Oncol 114(2):155–160
Clerici E, Comito T, Franzese C, Di Brina L, Tozzi A et al (2020) Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy in the treatment of liver metastases: clinical results and prognostic factors. Strahlenther Onkol 196(4):325–333
Rubio C, Hernando-Requejo O, Zucca Aparicio D, ALlona Krauel M, López Gonzalez M, Pérez JM et al (2017) Image guided SBRT for multiple liver metastases with ExacTrac® Adaptive Gating. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 22(2):150–157
Comen E, Norton L, Massagué J (2011) Clinical implications of cancer self-seeding. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8(6):369–377
Kim MY, Oskarsson T, Acharyya S, Nguyen DX, Zhang XHF, Norton L et al (2009) Tumor self-seeding by circulating cancer cells. Cell 139(7):1315–1326
Aguirre-Ghiso JA (2010) On the theory of tumor self-seeding: Implications for metastasis progression in humans. Breast Cancer Res 12(2):304
Méndez Romero A, Wunderink W, van Os RM, Nowak PJCM, Heijmen BJM, Nuyttens JJ et al (2008) Quality of life after stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary and metastatic liver tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70(5):1447–1452
Acknowledgements
We thank Daniel García de Quinto, for reviewing, revising, and editing this manuscript for English language grammar and syntax.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
O. Hernando-Requejo, X. Chen, M. López, E. Sánchez, J. García, P. García, R. Alonso, A. Montero, R. Ciervide, B. Álvarez, D. Zucca, M. García Aranda, J. Valero, P. Fernández Letón and C. Rubio declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants or on human tissue were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1975 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hernando-Requejo, O., Chen, X., López, M. et al. Real-world effectiveness and safety of stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver metastases with different respiratory motion management techniques. Strahlenther Onkol 199, 1000–1010 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-023-02147-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-023-02147-w