Abstract
Background
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is characterized by a high risk of brain metastasis and poor survival. This study aims to assess the prognostic role of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in limited-stage small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC) treated with thoracic radiotherapy (TRT) and prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI).
Methods
This study retrospectively evaluated 197 consecutive patients who underwent TRT and PCI for LS-SCLC between November 2005 and October 2017. Both pretreatment and maximal serum LDH levels (mLDH) during treatment were checked, and an increased LDH level was defined as more than 240 IU/ml. Clinical factors were tested for associations with intracranial progression-free survival (IPFS) and overall survival (OS) after PCI. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to calculate survival rates, and multivariate Cox regression analyses were carried out to identify variables associated with survival.
Results
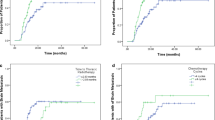
Of the total patients, 28 had higher pretreatment LDH levels and mLDH levels were increased in 95 patients during treatment. In patients in the normal and elevated mLDH groups, the 1‑, 2‑, and 5‑year IPFS rates were 96.7% vs. 90.1%, 91.7% vs. 73.8%, and 87.8% vs. 61.0% (P < 0.01), respectively. Compared to those with normal LDH levels, patients with increased mLDH levels had a higher cumulative risk of intracranial metastasis (hazard ratio [HR] 3.87; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.73–8.63; P < 0.01) and worse overall survival (HR 2.59; 95% CI 1.67–4.04; P < 0.01). The factors LDH level at baseline or changes between pretreatment level and maximum level during treatment failed to predict brain metastases or OS with statistical significance. In the multivariate analyses, both mLDH during treatment (HR 3.53; 95% CI 1.57–7.92; P = 0.002) and patient age ≥ 60 (HR 2.46; 95% CI 1.22–4.94; P = 0.012) were independently associated with worse IPFS. Factors significantly associated with worse OS included mLDH during treatment (HR 2.45; 95% CI 1.56–3.86; P < 0.001), IIIB stage (HR 1.75; 95% CI 1.06–2.88; P = 0.029), and conventional radiotherapy applied in TRT (HR 1.66; 95% CI 1.04–2.65; P = 0.034).
Conclusion
The mLDH level during treatment predicts brain metastasis and survival in LS-SCLC patients treated with TRT and PCI, which may provide valuable information for identifying patients with poor survival outcomes and possible candidates for treatment intensification.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine-triphosphate
- BED:
-
Biologically effective dose
- BM:
-
Brain metastasis
- CCRT:
-
Concurrent chemoradiotherapy
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CR:
-
Complete response
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- ECOG-PS:
-
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status
- ECPFS:
-
Extracranial progression-free survival
- ECT:
-
Emission computed tomography
- ED:
-
Extensive disease
- EP:
-
Etoposide and platinum
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- IMRT:
-
Intensity-modulated radiotherapy
- IPFS:
-
Intracranial progression-free survival
- LD:
-
Limited disease
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- LS-SCLC:
-
Limited-stage small cell lung cancer
- mLDH:
-
Maximal serum LDH levels
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NCCN:
-
National Comprehensive Cancer Network
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- NSE:
-
Neuron-specific enolase
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PCI:
-
Prophylactic cranial irradiation
- PET:
-
Positron-emission tomography
- PR:
-
Partial response
- Pro-GRP:
-
Prosoma gastric secretin release peptide
- PS:
-
Performance status
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SCLC:
-
Small cell lung cancer
- SCRT:
-
Sequential chemotherapy and radiotherapy
- SD:
-
Standard dose
- TRT:
-
Thoracic radiotherapy
- ULN:
-
Upper limit of normal value
- WBRT:
-
Whole-brain radiation therapy
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70(1):7–30
Van Meerbeeck JP, Fennell DA, De Ruysscher DK (2011) Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 378:1741–1755
Jett JR, Schild SE, Kesler KA et al (2013) Treatment of small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 143:e400S–e419S
Wang L, Cao L, Jiang R, Huang D (2020) Prognostic significance of combined bomarkers in small cell lung cancer. Clin Lab. https://doi.org/10.7754/Clin.Lab.2020.191002
Du J, Li Y, Wang L, Zhou Y, Shen Y, Xu F, Chen Y (2020) Selective application of neuroendocrine markers in the diagnosis and treatment of small cell lung cancer. Clin Chim Acta 509:295–303
Bremnes RM, Sundstrom S, Aasebø U, Kaasa S, Hatlevoll R, Aamdal S, Norweigian Lung Cancer Study Group (2003) The value of prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer: results from a randomised multicenter study with minimum 5 year follow-up. Lung Cancer 39(3):303–313
Nugent JL, Bunn PA Jr, Matthews MJ et al (1979) CNS metastases in small cell bronchogenic carcinoma: increasing frequency and changing pattern with lengthening survival. Cancer 44:1885–1893
Hardy J, Smith I, Cherryman G et al (1990) The value of computed tomographic (CT) scan surveillance in the detection and management of brain metastases in patients with small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 62:684–686
Kalemkerian GP et al (2018) NCCN guidelines insights: small cell lung cancer, version 2.2018. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 16:1171–1182
Auperin A et al (1999) Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. Prophylactic cranial irradiation overview collaborative group. N Engl J Med 341:476–484
Pezzi TA, Fang P, Gjyshi O, Feng L, Liu S, Komaki R, Lin SH (2020) Rates of overall survival and intracranial control in the magnetic resonance imaging era for patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer with and without prophylactic cranial irradiation. JAMA Netw Open 3(4):e201929
Held MK, Hansen O, Schytte T, Hansen KH, Bahij R, Nielsen M, Nielsen TB, Jeppesen SS (2021) Outcomes of prophylactic cranial irradiation in patients with small cell lung cancer in the modern era of baseline magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Acta Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2021.1974553
Laplanche A, Monnet I, Santos-Miranda JA, Bardet E, Le Péchoux C, Tarayre M, Arriagada R (1998) Controlled clinical trial of prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. Lung Cancer 21(3):193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-5002(98)00056-7
Gregor A, Cull A, Stephens RJ, Kirkpatrick JA, Yarnold JR, Girling DJ, Macbeth FR, Stout R, Machin D (1997) Prophylactic cranial irradiation is indicated following complete response to induction therapy in small cell lung cancer: results of a multicentre randomised trial. United Kingdom Coordinating Committee for Cancer Research (UKCCCR) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Eur J Cancer 33(11):1752–1758
Forkasiewicz A, Dorociak M, Stach K, Szelachowski P, Tabola R, Augoff K (2020) The usefulness of lactate dehydrogenase measurements in current oncological practice. Cell Mol Biol Lett 25:35
Anami S, Doi H, Nakamatsu K, Uehara T, Wada Y, Fukuda K, Inada M, Ishikawa K, Kanamori S, Nishimura Y (2019) Serum lactate dehydrogenase predicts survival in small-cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases that were treated with whole-brain radiotherapy. J Radiat Res 60(2):257–263
Mishra D, Banerjee D (2019) Lactate Dehydrogenases as metabolic links between tumor and stroma in the tumor microenvironment. Cancers (Basel) 11(6):750–729. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060750 (Erratum in: Cancers (Basel) 2020 12(4))
Wen Q, Meng X, Xie P, Wang S, Sun X, Yu J (2017) Evaluation of factors associated with platinum-sensitivity status and survival in limited-stage small cell lung cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy. Oncotarget 8(46):81405–81418
Hermes A, Gatzemeier U, Waschki B, Reck M (2010) Lactate dehydrogenase as prognostic factor in limited and extensive disease stage small cell lung cancer—a retrospective single institution analysis. Respir Med 104(12):1937–1942
Tas F, Aydiner A, Demir C, Topuz E (2001) Serum lactate dehydrogenase levels at presentation predict outcome of patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 24(4):376–378
Sagman U, Feld R, Evans WK, Warr D, Shepherd FA, Payne D, Pringle J, Yeoh J, DeBoer G, Malkin A et al (1991) The prognostic significance of pretreatment serum lactate dehydrogenase in patients with small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 9(6):954–961
He M, Chi X, Shi X, Sun Y, Yang X, Wang L, Wang B, Li H (2021) Value of pretreatment serum lactate dehydrogenase as a prognostic and predictive factor for small-cell lung cancer patients treated with first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy. Thorac Cancer 12(23):3101–3109
Zhang X, Guo M, Fan J, Lv Z, Huang Q, Han J, Wu F, Hu G, Xu J, Jin Y (2016) Prognostic significance of serum LDH in small cell lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Cancer Biomark 16(3):415–423
Fischer GM, Jalali A, Kircher DA, Lee WC, McQuade JL, Haydu LE, Joon AY, Reuben A, de Macedo MP, Carapeto FCL, Yang C, Srivastava A, Ambati CR, Sreekumar A, Hudgens CW, Knighton B, Deng W, Ferguson SD, Tawbi HA, Glitza IC, Gershenwald JE, Vashisht Gopal YN, Hwu P, Huse JT, Wargo JA, Futreal PA, Putluri N, Lazar AJ, DeBerardinis RJ, Marszalek JR, Zhang J, Holmen SL, Tetzlaff MT, Davies MA (2019) Molecular profiling reveals unique immune and metabolic features of melanoma brain metastases. Cancer Discov 9(5):628–645
Yang J, Ren B, Yang G, Wang H, Chen G, You L, Zhang T, Zhao Y (2020) The enhancement of glycolysis regulates pancreatic cancer metastasis. Cell Mol Life Sci 77(2):305–321
Yang Y, Su D, Zhao L, Zhang D, Xu J, Wan J, Fan S, Chen M (2014) Different effects of LDH‑A inhibition by oxamate in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 5(23):11886–11896
Yang Y, Chong Y, Chen M, Dai W, Zhou X, Ji Y, Qiu G, Du X (2021) Targeting lactate dehydrogenase a improves radiotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer: from bedside to bench. J Transl Med 19(1):170
Yang Y, Zhang D, Zhou X, Bao W, Ji Y, Sheng L, Cheng L, Chen Y, Du X, Qiu G (2018) Prophylactic cranial irradiation in resected small cell lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Cancer 9(2):433–439
Suzuki R, Wei X, Allen PK, Welsh JW, Komaki R, Lin SH (2018) Hematologic variables associated with brain failure in patients with small-cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol 128(3):505–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2018.05.026
Kamran SC, Coroller T, Milani N, Agrawal V, Baldini EH, Chen AB, Johnson BE, Kozono D, Franco I, Chopra N, Zeleznik R, Aerts HJWL, Mak R (2020) The impact of quantitative CT-based tumor volumetric features on the outcomes of patients with limited stage small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol 15(1):14
Aupérin A, Arriagada R, Pignon JP, Le Péchoux C, Gregor A, Stephens RJ, Kristjansen PE, Johnson BE, Ueoka H, Wagner H, Aisner J (1999) Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Overview Collaborative Group. N Engl J Med 341(7):476–484
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of the Department of Thoracic Radiation Oncology.
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (no. LY20H160006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jianjiang Liu and Dongping Wu are responsible for data collation and paper writing, Yang Yang is responsible for paper guidance and revision, and the remaining authors are responsible for paper revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
J. Liu, D. Wu, B. Shen, M. Chen, X. Zhou, P. Zhang, G. Qiu, Y. Ji, X. Du, and Y. Yang declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
This study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of the Zhejiang Cancer Hospital. For this article no studies with human participants or animals were performed by any of the authors. All studies mentioned were in accordance with the ethical standards indicated in each case. Consent for publication: All authors agree to publish.
Additional information
The authors Jianjiang Liu and Dongping Wu contributed equally to the manuscript.
Availability of supporting data
The data of this study have been recorded in the Science and Education Department of Zhejiang Cancer Hospital in Excel format.
Supplementary Information
66_2022_1977_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary figures (A, B, and C). Kaplan–Meier curves of groups of higher and normal LDH levels for extracranial progression-free survival (ECPFS). (A): Kaplan–Meier survival curve of ECPFS of higher mLDH and normal groups during treatment; (B): Kaplan–Meier survival curve of ECPFS of higher pretreatment LDH and normal groups; (C): Kaplan–Meier survival curve of ECPFS of elevated and deceased groups after comparison between pretreatment and maximum LDH level during treatment
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Wu, D., Shen, B. et al. Serum lactate dehydrogenase predicts brain metastasis and survival in limited-stage small cell lung cancer patients treated with thoracic radiotherapy and prophylactic cranial irradiation. Strahlenther Onkol 198, 1094–1104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-022-01977-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-022-01977-4