Abstract
Background
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been reported to be crucial modulatory molecules in the etiology of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This study aimed to probe the precise role and mechanism of circRNA discs large MAGUK scaffold protein 1 (circDLG1) in the malignant progression of NSCLC.
Methods
The abundances of circDLG1, miR-630, and centromere protein F (CENPF) mRNAs were gauged by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Cell proliferation was tested in 3‑(4, 5‑dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5‑diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and 5‑ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU)-incorporation assay. Cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry. Cell migration and invasion were assessed by transwell assay. Western blot was exploited to examine the levels of all proteins. The interaction between miR-630 and circDLG1 or CENPF was verified by dual-luciferase reporter, RNA pull-down, and/or RNA immunoprecipitation assays. Tumor xenograft assay and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were executed for the role of circDLG1 in tumor growth in vivo.
Results
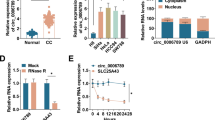
CircDLG1 and CENPF were highly expressed in NSCLC, while miR-630 was downregulated. CircDLG1 silencing repressed proliferation, migration, and invasion, and expedited apoptosis of NSCLC cells in vitro. Mechanistically, circDLG1 deficiency modulated NSCLC cell malignant development through interacting with miR-630. Furthermore, CENPF was targeted by miR-630, and circDLG1 could positively control CENPF expression through acting as an miR-630 sponge. Furthermore, CENPF overexpression reversed the repressive impacts of circDLG1 inhibition in the malignant behaviors of NSCLC cells. Besides, circDLG1 interference hindered tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion
CircDLG1 knockdown could impede NSCLC advancement through modulating the miR-630/CENPF axis, manifesting as a promising molecular target for NSCLC treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwartz AG, Cote ML (2016) Epidemiology of lung cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 893:21–41
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C (2018) The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553(7689):446–454
Nagano T, Tachihara M, Nishimura Y (2019) Molecular mechanisms and targeted therapies including immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 19(8):595–630
Imyanitov EN, Iyevleva AG, Levchenko EV (2021) Molecular testing and targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: current status and perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 157:103194
Qian L, Yu S, Chen Z, Meng Z, Huang S, Wang P (2018) The emerging role of circRNAs and their clinical significance in human cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1870(2):247–260
Chen LL, Yang L (2015) Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol 12(4):381–388
Cui C, Yang J, Li X, Liu D, Fu L, Wang X (2020) Functions and mechanisms of circular RNAs in cancer radiotherapy and chemotherapy resistance. Mol Cancer 19(1):58
He J, Xie Q, Xu H, Li J, Li Y (2017) Circular RNAs and cancer. Cancer Lett 396:138–144
Xu N, Chen S, Liu Y, Li W, Liu Z, Bian X, Ling C, Jiang M (2018) Profiles and bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed circrnas in taxol-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 48(5):2046–2060
Van Der Steen N, Lyu Y, Hitzler AK, Becker AC, Seiler J, Diederichs S (2020) The circular RNA landscape of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancers (Basel) 12(5):1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051091
Guan S, Li L, Chen WS, Jiang WY, Ding Y, Zhao LL, Shi YF, Wang J, Gui Q, Xu CC et al (2021) Circular RNA WHSC1 exerts oncogenic properties by regulating miR-7/TAB2 in lung cancer. J Cell Mol Med 25(20):9784–9795. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.16925
Hu X, Wang P, Qu C, Zhang H, Li L (2021) Circular RNA Circ_0000677 promotes cell proliferation by regulating microRNA-106b-5p/CCND1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Bioengineered 12(1):6229–6239
O’Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C (2018) Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:402
Lu TX, Rothenberg ME (2018) MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol 141(4):1202–1207
Mendell JT, Olson EN (2012) MicroRNAs in stress signaling and human disease. Cell 148(6):1172–1187
Peng Y, Croce CM (2016) The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 1:15004
Bhaskaran M, Mohan M (2014) MicroRNAs: history, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development and disease. Vet Pathol 51(4):759–774
Feng B, Zhang K, Wang R, Chen L (2015) Non-small-cell lung cancer and miRNAs: novel biomarkers and promising tools for treatment. Clin Sci (Lond) 128(10):619–634
Song YF, Hong JF, Liu DL, Lin QA, Lan XP, Lai GX (2015) miR-630 targets LMO3 to regulate cell growth and metastasis in lung cancer. Am J Transl Res 7(7):1271–1279
Li MX, Zhang MY, Dong HH, Li AJ, Teng HF, Liu AL, Xu N, Qu YQ (2021) Overexpression of CENPF is associated with progression and poor prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Med Sci 18(2):494–504
Hexiao T, Yuquan B, Lecai X, Yanhong W, Li S, Weidong H, Ming X, Xuefeng Z, Gaofeng P, Li Z et al (2021) Knockdown of CENPF inhibits the progression of lung adenocarcinoma mediated by ERbeta2/5 pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 13(2):2604–2625
Wang C, Tan S, Liu WR, Lei Q, Qiao W, Wu Y, Liu X, Cheng W, Wei YQ, Peng Y et al (2019) RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNA in human lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer 18(1):134
Arnaiz E, Sole C, Manterola L, Iparraguirre L, Otaegui D, Lawrie CH (2019) CircRNAs and cancer: biomarkers and master regulators. Semin Cancer Biol 58:90–99
Huang X, Zhang W, Shao Z (2019) Prognostic and diagnostic significance of circRNAs expression in lung cancer. J Cell Physiol 234(10):18459–18465
Di X, Jin X, Li R, Zhao M, Wang K (2019) CircRNAs and lung cancer: biomarkers and master regulators. Life Sci 220:177–185
Li S, Liu Y, Qiu G, Luo Y, Li X, Meng F, Li N, Xu T, Wang Y, Qin B et al (2021) Emerging roles of circular RNAs in nonsmall cell lung cancer (review). Oncol Rep 45(4):17
Sun Q, Li X, Xu M, Zhang L, Zuo H, Xin Y, Zhang L, Gong P (2020) Differential expression and bioinformatics analysis of circRNA in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Genet 11:586814
Xi J, Xi Y, Zhang Z, Hao Y, Wu F, Bian B, Hao G, Li W, Zhang S (2021) Hsa_circ_0060937 accelerates non-small cell lung cancer progression via modulating miR-195-5p/HMGB3 pathway. Cell Cycle 20(19):2040–2052. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2021.1969203
Song HM, Meng D, Wang JP, Zhang XY (2021) circRNA hsa_circ_0005909 predicts poor prognosis and promotes the growth, metastasis, and drug resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer via the miRNA-338-3p/SOX4 pathway. Dis Markers 2021:8388512
Zhang H, Shen Y, Li Z, Ruan Y, Li T, Xiao B, Sun W (2020) The biogenesis and biological functions of circular RNAs and their molecular diagnostic values in cancers. J Clin Lab Anal 34(1):e23049
Rong J, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Zhu D, Sun H, Tang W, Wang R, Shi W, Cao XF (2018) Circ-DLG1 promotes the proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 11:6723–6730
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer M (2013) Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495(7441):333–338
Panda AC (2018) Circular RNAs Act as miRNA sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:67–79
Liu DY, Li Z, Zhang K, Jiao N, Lu DG, Zhou DW, Meng YB, Sun L (2021) Circular RNA CircMTO1 suppressed proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma through miR-630/KLF6 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 25(1):86–93
Liu X, Wu W, Zhang S, Tan W, Qiu Y, Liao K, Yang K (2021) Effect of miR-630 expression on esophageal cancer cell invasion and migration. J Clin Lab Anal 35(6):e23815
Gong XF, Yu AL, Tang J, Wang CL, He JR, Chen GQ, Zhao Q, He M, Zhou CX (2018) MicroRNA-630 inhibits breast cancer progression by directly targeting BMI1. Exp Cell Res 362(2):378–385
Li YH, Xu CL, He CJ, Pu HH, Liu JL, Wang Y (2020) circMTDH.4/miR-630/AEG‑1 axis participates in the regulation of proliferation, migration, invasion, chemoresistance, and radioresistance of NSCLC. Mol Carcinog 59(2):141–153
Jin X, Yuan L, Liu B, Kuang Y, Li H, Li L, Zhao X, Li F, Bing Z, Chen W et al (2020) Integrated analysis of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network reveals potential prognostic biomarkers for radiotherapies with X‑rays and carbon ions in non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Transl Med 8(21):1373
Ying H, Zhao R, Yu Q, Zhang K, Deng Q (2022) CircATL2 enhances paclitaxel resistance of ovarian cancer via impacting miR-506-3p/NFIB axis. Drug Dev Res 83(2):512–524. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21882
Li F, Zhou X, Chen M, Fan W (2020) Regulatory effect of LncRNA DRAIC/miR-149-5p/NFIB molecular network on autophagy of esophageal cancer cells and its biological behavior. Exp Mol Pathol 116:104491
Yang H, Wu Z, Liu X, Chen M, Zhang X, Jiang Y (2021) NFIB promotes the progression of gastric cancer by upregulating circMAP7D1 to stabilize HER2 mRNA. Mol Med Rep 23(4):269
Li R, Wang X, Zhao X, Zhang X, Chen H, Ma Y, Liu Y (2020) Centromere protein F and forkhead box M1 correlation with prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett 19(2):1368–1374
Alagia A, Eritja R (2016) siRNA and RNAi optimization. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 7(3):316–329
Zhang MM, Bahal R, Rasmussen TP, Manautou JE, Zhong XB (2021) The growth of siRNA-based therapeutics: updated clinical studies. Biochem Pharmacol 189:114432
Funding
There was no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Yingying Chen. Data curation: Yingying Chen. Formal analysis: Yingying Chen, Ying Zhang. Methodology: Yingying Chen, Ying Zhang. Resource: Ying Zhang. Software: Yingying Chen, Ying Zhang. Writing original draft: Yingying Chen.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Y. Chen and Y. Zhang declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
The research has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University. Written informed consent was signed by every participant. The animal protocols were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University in accordance the ARRIVE guidelines and the Basel Declaration. Consent for Publication: not applicable.
Additional information
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors without undue reservation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zhang, Y. CircDLG1 promotes malignant development of non-small cell lung cancer through regulation of the miR-630/CENPF axis. Strahlenther Onkol 199, 169–181 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-022-01965-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-022-01965-8