Abstract
Purpose
To report early toxicity and 5‑year clinical outcomes of adjuvant breast inversely planned intensity-modulated radiotherapy with simultaneously integrated boost (IMRT-SIB) after breast-conserving surgery for early stage breast cancer patients.
Patients and methods
In all, 467 patients including 406 invasive breast cancer and 61 ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) were enrolled in a single institutional phase II trial. All patients underwent IMRT-SIB treatment to irradiate the whole breast and the tumor bed. Doses to whole breast and surgical bed were 45 and 60 Gy, respectively, delivered in 25 fractions over 5 weeks. The grade of maximum acute skin toxicity during treatment was recorded. Lung toxicity was noted within 6 months and patient-reported cosmetic outcomes were recorded at the 12 month follow-up after the end of radiotherapy. Clinical outcomes were assessed during follow-up.
Results
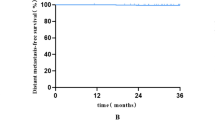
Median follow-up time was 5.46 years. Median age was 46 years old (range 22–70 years old). No patient with DCIS had a local recurrence or distant metastasis. Among 406 patients with invasive breast cancer, the unadjusted 5‑year actuarial rate of locoregional control was 98.7% (95% confidence interval [CI] 97.5–100), and distant metastasis-free survival 98.7% (95% CI 97.4–100), respectively. Acute skin toxicity was recorded at grade 0–1 in 76.5% of patients, and grade 2 in 23.5% of patients. None of these patients had grade 3 or more than grade 3 skin toxicity. Grade 1 pneumonitis was found in 25.3% of patients. Assessment of patient reported cosmetic outcomes at the 12 month follow-up showed good or excellent outcome in 86.5% of cases.
Conclusions
The use of inversely planned IMRT-SIB as part of breast-conserving therapy results in optimal 5‑year tumor control and minor early toxicities.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Madyan Y, Welzel G, Sperk E et al (2019) Single-center long-term results from the randomized phase‑3 TARGIT—a trial comparing intraoperative and whole-breast radiation therapy for early breast cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 195:640–647
Anonymous (1991) NIH consensus conference. Treatment of early-stage breast cancer. JAMA 265:391–395
Bantema-Joppe EJ, Schilstra C, De Bock GH et al (2012) Simultaneous integrated boost irradiation after breast-conserving surgery: physician-rated toxicity and cosmetic outcome at 30 months’ follow-up. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:e471–477
Bantema-Joppe EJ, Van Der Laan HP, De Bock GH et al (2011) Three-dimensional conformal hypofractionated simultaneous integrated boost in breast conserving therapy: results on local control and survival. Radiother Oncol 100:215–220
Bantema-Joppe EJ, Vredeveld EJ, De Bock GH et al (2013) Five year outcomes of hypofractionated simultaneous integrated boost irradiation in breast conserving therapy; patterns of recurrence. Radiother Oncol 108:269–272
Bartelink H, Maingon P, Poortmans P et al (2015) Whole-breast irradiation with or without a boost for patients treated with breast-conserving surgery for early breast cancer: 20-year follow-up of a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 16:47–56
Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S et al (2005) Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 366:2087–2106
Darby SC, Ewertz M, Mcgale P et al (2013) Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med 368:987–998
De Rose F, Fogliata A, Franceschini D et al (2016) Phase II trial of hypofractionated VMAT-based treatment for early stage breast cancer: 2‑year toxicity and clinical results. Radiat Oncol 11:120
Dewan A, Chufal KS, Dewan AK et al (2018) Simultaneous integrated boost by Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (SIB-IMRT) in patients undergoing breast conserving surgery—a clinical and dosimetric perspective. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst 30:165–171
Duma MN, Baumann R, Budach W et al (2019) Heart-sparing radiotherapy techniques in breast cancer patients: a recommendation of the breast cancer expert panel of the German society of radiation oncology (DEGRO). Strahlenther Onkol 195:861–871
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative G, Darby S, Mcgale P et al (2011) Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet 378:1707–1716
Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ et al (2014) Breast cancer in China. Lancet Oncol 15:e279–289
Fan L, Zheng Y, Yu KD et al (2009) Breast cancer in a transitional society over 18 years: trends and present status in Shanghai, China. Breast Cancer Res Treat 117:409–416
Fiorentino A, Mazzola R, Giaj Levra N et al (2018) Comorbidities and intensity-modulated radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost in elderly breast cancer patients. Aging Clin Exp Res 30:533–538
Hammer C, Maduro JH, Bantema-Joppe EJ et al (2017) Radiation-induced fibrosis in the boost area after three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy with a simultaneous integrated boost technique for early-stage breast cancer: a multivariable prediction model. Radiother Oncol 122:45–49
Holli K, Pitkanen M, Jarvenpaa R et al (2002) Early skin and lung reactions in breast cancer patients after radiotherapy: prospective study. Radiother Oncol 64:163–169
Kahan Z, Csenki M, Varga Z et al (2007) The risk of early and late lung sequelae after conformal radiotherapy in breast cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:673–681
Kestin LL, Sharpe MB, Frazier RC et al (2000) Intensity modulation to improve dose uniformity with tangential breast radiotherapy: initial clinical experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48:1559–1568
Kindts I, Laenen A, Christiaens M et al (2019) Comparison of brachytherapy and external beam radiotherapy boost in breast-conserving therapy: patient-reported outcome measures and aesthetic outcome. Strahlenther Onkol 195:21–31
Lin Y, Wang B (2015) Dosimetric absorption of intensity-modulated radiotherapy compared with conventional radiotherapy in breast-conserving surgery. Oncol Lett 9:9–14
Lind PA, Wennberg B, Gagliardi G et al (2001) Pulmonary complications following different radiotherapy techniques for breast cancer, and the association to irradiated lung volume and dose. Breast Cancer Res Treat 68:199–210
Mcdonald MW, Godette KD, Whitaker DJ et al (2010) Three-year outcomes of breast intensity-modulated radiation therapy with simultaneous integrated boost. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:523–530
Morganti AG, Cilla S, Valentini V et al (2009) Phase I–II studies on accelerated IMRT in breast carcinoma: technical comparison and acute toxicity in 332 patients. Radiother Oncol 90:86–92
Pez M, Keller A, Welzel G et al (2020) Long-term outcome after intraoperative radiotherapy as a boost in breast cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 196(4):349–355
Pignol JP, Olivotto I, Rakovitch E et al (2008) A multicenter randomized trial of breast intensity-modulated radiation therapy to reduce acute radiation dermatitis. J Clin Oncol 26:2085–2092
Piroth MD, Baumann R, Budach W et al (2019) Heart toxicity from breast cancer radiotherapy: current findings, assessment, and prevention. Strahlenther Onkol 195:1–12
Romestaing P, Lehingue Y, Carrie C et al (1997) Role of a 10-Gy boost in the conservative treatment of early breast cancer: results of a randomized clinical trial in Lyon, France. J Clin Oncol 15:963–968
Sedlmayer F, Sautter-Bihl ML, Budach W et al (2013) Is the simultaneously integrated boost (SIB) technique for early breast cancer ready to be adopted for routine adjuvant radiotherapy? Statement of the German and the Austrian Societies of Radiooncology (DEGRO/OGRO). Strahlenther Onkol 189:193–196
Song QK, Li J, Huang R et al (2014) Age of diagnosis of breast cancer in china: almost 10 years earlier than in the United States and the European union. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:10021–10025
Speers C, Pierce LJ (2016) Postoperative radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery for early-stage breast cancer: a review. JAMA Oncol 2:1075–1082
Teoh M, Clark CH, Wood K et al (2011) Volumetric modulated arc therapy: a review of current literature and clinical use in practice. Br J Radiol 84:967–996
Van Den Bogaard VA, Ta BD, Van Der Schaaf A et al (2017) Validation and modification of a prediction model for acute cardiac events in patients with breast cancer treated with radiotherapy based on three-dimensional dose distributions to cardiac substructures. J Clin Oncol 35:1171–1178
Van Der Laan HP, Dolsma WV, Maduro JH et al (2007) Three-dimensional conformal simultaneously integrated boost technique for breast-conserving radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:1018–1023
Van Der Laan HP, Dolsma WV, Schilstra C et al (2010) Limited benefit of inversely optimised intensity modulation in breast conserving radiotherapy with simultaneously integrated boost. Radiother Oncol 94:307–312
Wang J, Hu W, Yang Z et al (2017) Is it possible for knowledge-based planning to improve intensity modulated radiation therapy plan quality for planners with different planning experiences in left-sided breast cancer patients? Radiat Oncol 12:85
Yang Z, Chen J, Xie J et al (2013) Simultaneous integrated boost in breast conserving radiotherapy: is replanning necessary following tumor bed change? Technol Cancer Res Treat 12:115–122
Yang Z, Zhang L, Chen X et al (2015) Multibeam inverse intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) for whole breast irradiation: a single center experience in China. Oncotarget 6:35063–35072
Funding
This study was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(81703025,81972846,81872457) and Shanghai Municipal Population and Family Planning Commission (20174Y0107).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
J. Meng, W. Huang, X. Mei, X. Yu, Z. Pan, J. Ma, X. Ma, J. Chen, X. Guo and Z. Yang declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, J., Huang, W., Mei, X. et al. Adjuvant breast inversely planned intensity-modulated radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost for early stage breast cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 196, 764–770 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-020-01611-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-020-01611-1