Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate feasibility and efficacy of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for unresectable liver metastasis in oligometastatic patients.
Methods
Oligometastatic patients with up to three liver metastases of a maximum diameter of 6 cm were treated with SBRT. Total dose was 75 Gy in three consecutive fractions. Study endpoints were efficacy of this fractionation in terms of local control (LC), overall survival (OS), toxicity, and prognostic factors affecting OS and LC.
Results
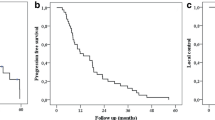
Between February 2010 and December 2016, we enrolled 202 patients, with a total of 268 unresectable liver metastases. Median follow-up time from SBRT was 33 months (5–87 months). One-, 3‑, and 5‑year LC rates were 92%, 84%, and 84%, respectively. In univariate analysis, the primary histology and previous local ablative therapies were significant. Median OS was 21 months and the survival rates were 79%, 27%, and 15% at 1, 3, and 5 years after SBRT, respectively. At univariate analysis, sex, primary disease histology, intra-, and extra-hepatic progression were significant prognostic factors. This analysis confirmed the absence of late toxicity >G3.
Conclusion
This study confirms the efficacy and safety of SBRT for unresectable liver metastases. Selection of cases may improve survival and LC.
Zusammenfassung
Zielsetzung
Bewertung von Durchführbarkeit und Wirksamkeit von SBRT („stereotactic body radiation therapy“), für nichtresezierbare Lebermetastasen bei oligometastatischen Patienten.
Methoden
Oligometastatische Patienten mit bis zu 3 Lebermetastasen mit einem maximalen Durchmesser von 6 cm wurden mit SBRT behandelt. Gesamtdosis war 75 Gy in 3 Fraktionen hintereinander. Endpunkt der Untersuchung war die Wirksamkeit der Fraktionierung bezüglich lokaler Kontrolle (LC), Gesamtüberleben (OS), Toxizität und prognostischer Faktoren mit Einfluss auf OS und LC.
Ergebnisse
Zwischen Februar 2010 und Dezember 2016 wurden 202 aus 268 Patienten mit nichtresezierbaren Lebermetastasen ausgewählt. Mediane Nachbeobachtungszeit nach SBRT war 33 Monate (Spanne 5–87 Monate). Die 1‑, 3‑ und 5‑Jahres-LC-Raten lagen jeweils bei 92%, 84% und 84%. In der univariaten Analyse waren die Primärhistologie und die früheren ablativen lokalen Therapien signifikant. Das mediane OS lag bei 21 Monaten und die Überlebensraten waren 1, 3 und 5 Jahre nach SBRT jeweils bei 79%, 27% und 15%. In der univariaten Analyse waren Geschlecht, primäre Krankheitshistologie, intra- und extrahepatische Progression signifikante prognostische Faktoren. Diese Analyse bestätigte die Abwesenheit von Spättoxizität >G3.
Schlussfolgerung
Diese Untersuchung bestätigt die Wirksamkeit und die Sicherheit von SBRT für nichtresezierbare Lebermetastasen. Eine Fallauswahl kann die Überlebensrate und die LC verbessern.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weichselbaum RR, Hellman S (2011) Oligometastases revisited. Nat Rev Clinoncol 8:378–382
Alongi F, Arcangeli S, Filippi AR, Ricardi U, Scorsetti M (2012) Review and uses of stereotactic body radiation therapy for oligometastases. Oncologist 17:1100–1117
Yoon SS, Tanabe KK (1999) Surgical treatment and other regional treatments for colorectal cancer liver metastases. Oncologist 4:197–208
Scheele J, Stangl R, Altendorf-Hofmann A (1990) Hepatic metastases from colorectal carcinoma: Impact of surgical resection on the natural history. Br J Surg 77:1241–1246
Bengmark S, Hafstrom L (1969) The natural history of primary and secondary malignant tumors of the liver. I. The prognosis for patients with hepatic metastases from colonic and rectal carcinoma by laparotomy. Cancer 23:198–202
Cummings LC, Payes JD, Cooper GS (2007) Survival after hepatic resection in metastatic colorectal cancer: A population-based study. Cancer 109:718–726
Wei AC, Greig PD, Grant D, Taylor B, Langer B, Gallinger S (2006) Survival after hepatic resection for colorectal metastases: A 10-year experience. Ann Surgoncol 13:668–676
Fong Y, Fortner J, Sun RL, Brennan MF, Blumgart LH (1999) Clinical score for predicting recurrence after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: Analysis of 1001 consecutive cases. Ann Surg 230:309–318
Leonard GD, Brenner B, Kemeny NE (2005) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy before liver resection for patients with unresectable liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. J Clinoncol 23:2038–2048
Berney T, Mentha G, Roth AD, Morel P (1998) Results of surgical resection of liver metastases from non-colorectal primaries. Br J Surg 85:1423–1427
Lindell G, Ohlsson B, Saarela A, Andersson R, Tranberg KG (1998) Liver resection of noncolorectalsecondaries. J Surgoncol 69:66–70
Benevento A, Boni L, Frediani L, Ferrari A, Dionigi R (2000) Result of liver resection as treatment for metastases from noncolorectal cancer. J Surgoncol 74:24–29
van Ruth S, Mutsaerts E, Zoetmulder FA, van Coevorden F (2001) Metastasectomy for liver metastases of non-colorectal primaries. Eur J Surgoncol 27:662–667
Adam R, Chiche L, Aloia T, Elias D, Salmon R, Rivoire M et al (2006) Association Française de Chirurgie. Hepatic resection for noncolorectalnonendocrine liver metastases: analysis of 1,452 patients and development of a prognostic model. Ann Surg 244:524–535
Nosher JL, Ahmed I, Patel AN, Gendel V, Murillo PG, Moss R et al (2015) Non-operative therapies for colorectal liver metastases. J Gastrointestoncol 6:224–240
Gillams A et al (2013) Thermal ablation of colorectal liver metastases: a position paper by an international panel of ablation experts, the interventional oncology sans frontières meeting. Eur Radiol 2015(25):3438–3454
Hoyer M, Roed H, Traberg Hansen A, Ohlhuis L, Petersen J, Nellemann H et al (2006) Phase II study on stereotactic body radiotherapy of colorectal metastases. ActaOncol 45:823–830
van der Pool AE, Méndez Romero A, Wunderink W, Heijmen BJ, Levendag PC, Verhoef C et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for colorectal liver metastases. Br J Surg 97:377–382
Lee MT, Kim JJ, Dinniwell R, Brierley J, Lockwood G, Wong R et al (2009) Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy of liver metastases. J Clinoncol 27:1585–1591
Rusthoven KE, Kavanagh BD, Cardenes H, Stieber VW, Burri SH, Feigenberg SJ et al (2009) Multi-institutional phase I/II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases. J Clinoncol 27:1572–1578
Scorsetti M, Arcangeli S, Tozzi A, Comito T, Alongi F, Navarria P et al (2013) Is stereotactic body radiation therapy an attractive option for unresectable liver metastases? A preliminary report from a phase 2 trial. Int J Radiatoncolbiolphys 86:336–342
Goodman KA, Wiegner EA, Maturen KE, Zhang Z, Mo Q, Yang G et al (2010) Dose escalation study of single-fraction stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver malignancies. Int J Radiatoncolbiolphys 78:486–493
Ambrosino G, Polistina F, Costantin G, Francescon P, Guglielmi R, Zanco P et al (2009) Image guided robotic stereotactic radiosurgery for unresectable liver metastases: Preliminary results. Anticancer Res 29:3381–3384
Schefter TE, Kavanagh BD (2011) Radiation therapy for liver metastases. SeminRadiatOncol 21:264–270
Penna C, Nordlinger B (2002) Colorectal metastasis (liver and lung). Surgclin North Am 82:1075–1090 (Review)
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumors: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
McCammon R, Schefter TE, Gaspar LE, Zaemisch R, Gravdahl D, Kavanagh B (2009) Observation of a dose control relationship for lung and liver tumors after stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiatoncolbiolphys 73:112–118
McPartlin A, Swaminath A, Wang R, Pintilie M, Brierley J, Kim J et al (2017) Long-Term Outcomes of Phase 1 and 2 Studies of SBRT for Hepatic Colorectal Metastases. Int J Radiatoncolbiolphys 99:388–395
Ahmed KA, Caudell JJ, El-Haddad G, Berglund AE, Welsh EA, Yue B et al (2016) Radiosensitivity Differences Between Liver Metastases Based on Primary Histology Suggest Implications for Clinical Outcomes After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Int J Radiatoncolbiolphys 95:1399–1404
Oishi N, Yamashita T, Kaneko S (2014) Molecular biology of liver cancer stem cells. Liver Cancer 3:71–84
Takemura N, Saiura A (2017) Role of surgical resection for non-colorectal non-neuroendocrine liver metastases. World J Hepatol 9:242–251
Adam R, Aloia T, Krissat J, Bralet MP, Paule B, Giacchetti S et al (2006) Is liver resection justified for patients with hepatic metastases from breast cancer? Ann Surg 244:897–907
Groeschl RT, Nachmany I, Steel JL, Reddy SK, Glazer ES, de Jong MC et al (2012) Hepatectomy for non colorectal non neuroendocrine metastatic cancer: a multi-institutional analysis. J Am Collsurg 214:769–777
Hoffmann K, Bulut S, Tekbas A,Hinz U, Büchler MW, Schemmer P (2015) Is Hepatic Resection for Non-colorectal, Non-neuroendocrine Liver Metastases Justified? Ann Surg Oncol 22(Suppl. 3):1083–1092
Pocard M, Pouillart P, Asselain B, Salmon R (2000) Hepatic resection in metastatic breast cancer: results and prognostic factors. Eurj Surgoncol 26:155–159
Elias D, Maisonnette F, Druet-Cabanac M, Ouellet JF, Guinebretiere JM, Spielmann M et al (2003) An attempt to clarify indications for hepatectomy for liver metastases from breast cancer. Am J Surg 185:158–164
Hoffmann K, Franz C, Hinz U, Schirmacher P, Herfarth C, Eichbaum M et al (2010) Liver resection for multimodal treatment of breast cancer metastases: identification of prognostic factors. Ann Surgoncol 17:1546–1554
Abbott DE, Brouquet A, MittendorfEA,Andreou A, Meric-Bernstam F, Valero V et al (2012) Resection of liver metastases from breast cancer: estrogen receptor status and response to chemotherapy before metastasectomy define outcome. Surgery 151:710–716
Sadot E, Lee SY, Sofocleous CT, Solomon SB, Gönen M, Kingham TP et al (2016) Hepatic Resection or Ablation for Isolated Breast Cancer Liver Metastasis: A Case-control Study With Comparison to Medically Treated Patients. Ann Surg 264:147–154
Scorsetti M, Franceschini D, De Rose F, Comito T, Villa E, Iftode C et al (2016) Stereotactic body radiation therapy: A promising chance for oligometastatic breast cancer. Breast 26:11–17
Iftode C, D’Agostino GR, Tozzi A, Comito T, Franzese C, De Rose F et al (2018) Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Oligometastatic Ovarian Cancer: A Promising Therapeutic Approach. Int J Gynecol Cancer 28(8):1507–1513 (Oct)
Andratschke N, Alheid H, Allgäuer M, Becker G, Blanck O, Boda-Heggemann J et al (2018) The SBRT database initiative of the German Society for Radiation Oncology (DEGRO): patterns of care and outcome analysis of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for liver oligometastases in 474 patients with 623 metastases. Bmc Cancer 13;18(1):283 (Mar)
Klement RJ, Abbasi-Senger N, Adebahr S, Alheid H, Allgaeuer M, Becker G et al (2019) The impact of local control on overall survival after stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver and lung metastases from colorectal cancer: a combined analysis of 388 patients with 500 metastases. Bmc Cancer 26;19(1):173 (Feb)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
E. Clerici, T. Comito, C. Franzese, L. Di Brina, A. Tozzi, C. Iftode, P. Navarria, P. Mancosu, G. Reggiori, S. Tomatis, and M. Scorsetti declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clerici, E., Comito, T., Franzese, C. et al. Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy in the treatment of liver metastases: clinical results and prognostic factors. Strahlenther Onkol 196, 325–333 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-019-01524-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-019-01524-8