Abstract
Purpose
Pediatric radiotherapy (RT) is a highly specialized field, requiring great experience to delineate correctly tumor targets and organs at risk. To reduce treatment failures related to planning inaccuracies and to obtain robust clinical results despite the limited numbers of enrolled pediatric patients, the SIOP PNET5MB clinical trial on medulloblastoma requires a real-time, pre-radiation review of the RT treatment (craniospinal irradiation and boost plan) under the direct responsibility of the national coordinator center. Here we describe the centralized radiotherapy quality assurance (QA) program developed in Italy for this purpose.
Methods
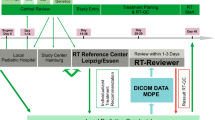
Using the software package VODCA (MSS, Hagendorn, Switzerland, www.vodca.ch), we developed a cloud platform able to handle computed tomography (CT) images and RT objects and to support the complete workflow required by the review process in the context of the SIOP PNET5 trial.
Results
All Italian centers participating in the PNET5 trial adopted the proposed QA system. 24 patients were successfully enrolled and reviewed. For 15 patients (62.5%), one or more plan revisions were requested for the craniospinal irradiation plan and for 11 patients (45.8%) plan revisions were requested for the boost. RT was delivered after the plan was centrally approved for all enrolled patients. So far, in Italy, no patients have been excluded from PNET5 due to dosimetric incompliance to the protocol or for exceeding the RT starting time limit.
Conclusion
The cloud platform successfully supported the trial workflow, producing official review documents. This efficient QA was crucial to guarantee optimized treatments and protocol compliance for all pediatric patients enrolled in the SIOP protocol.
Zusammenfassung
Zielsetzung
Die pädiatrische Strahlentherapie (RT) ist ein hochspezialisiertes Fachgebiet, welches zum korrekten Konturieren der Zielvolumina und Risikoorgane sehr viel Erfahrung erfordert. Zur Reduktion von Behandlungsversagen, das durch Ungenauigkeiten im Planungsprozess verursacht wird, und für aussagekräftige klinische Ergebnisse trotz der begrenzten Anzahl der pädiatrischen Patienten benötigt die klinische Studie SIOP PNET5MB für Medulloblastoma eine Überprüfung der kraniospinalen und Boost-Bestrahlung bereits im Bestrahlungsplanungsprozess. Die Verantwortung der Überprüfung liegt bei den nationalen Koordinierungszentren. Zu diesem Zweck wurde ein zentralisiertes Programm zu Qualitätssicherung (QA) für die RT in Italien entwickelt, welches hier beschrieben wird.
Methoden
Mit dem Softwarepaket VODCA (MSS, Hagendorn, Switzerland, www.vodca.ch) haben wir eine Cloud-Plattform entwickelt, die zum einen in der Lage ist, Computertomographie(CT)-Bilder und RT-Objekte zu verarbeiten und zum anderen den gesamten Workflow des Review-Prozesses unterstützt, der im Rahmen der SIOP-PNET5-Studie erforderlich ist.
Ergebnisse
Alle italienischen Zentren, die an der klinischen PNET5-Studie teilnahmen, führten das vorgeschlagene QA-System ein. Insgesamt wurden 24 Patienten erfolgreich rekrutiert und überprüft. Für 15 Patienten (62,5 %) wurden eine oder mehrere Revisionen des kraniospinalen Bestrahlungsplans gefordert. Für 11 Patienten (45,8 %) wurden Änderungen für den Boost-Plan gefordert. Die rekrutierten Patienten wurden ausschließlich mit den zentral genehmigten RT-Plänen behandelt. In Italien wurde bislang kein einziger Patient wegen Nichteinhaltung des dosimetrischen Protokolls oder Überschreitung des für den Patienten erforderlichen Therapiestartdatums von der PNET5-Studie ausgeschlossen.
Schlussfolgerung
Die Cloud-Plattform unterstützt den Studienworkflow erfolgreich und ist darüber hinaus in der Lage, offizielle Überprüfungsdokumente zu erstellen. Diese effiziente QA war entscheidend, um sicherzustellen, dass alle Patienten, die in die PNET5-Studie aufgenommen wurden, eine optimale Behandlung erhielten, und dass die Protokolle eingehalten wurden.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrie C, Hoffstetter S, Gomez F, Moncho V, Doz F, Alapetite C et al (1999) Impact of targeting deviations on outcome in medulloblastoma: Study of the French Society of Pediatric Oncology (SFOP). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45(2):435–439
Halperin EC, Laurie F, FitzGerald TJ (2002) An evaluation of the relationship between the quality of prophylactic cranial radiotherapy in childhood acute leukemia and institutional experience: a Quality Assurance Review Center—Pediatric Oncology Group Study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53(4):1001–1004
Ohri N, Shen X, Dicker A, Doyle LA, Harrison AS, Showalter TN (2013) Radiotherapy protocol deviations and clinical outcomes: a meta-analysis of cooperative group clinical trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 6(105):387–393
Goodman KA (2013) Quality assurance for radiotherapy: a priority for clinical trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 6(105):376–377
Fairchild A, Straube W, Laurie F, Followill D (2013) Does quality of radiation therapy predict outcomes of multicenter cooperative group trials. A literature review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87:246–260
Eich HT, Engenhart-Cabillic R, Hansemann K, Lukas P, Schneeweiss A, Seegenschmiedt H et al (2008) Quality control of involved field radiotherapy in patients with early-favorable (Hd10) and early-unfavorable (Hd11) Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: an analysis of the German Hodgkin study group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71(5):1419–1424
Miralbell R, Fitzgerald TJ, Laurie F, Kessel S, Glicksman A, Friedman HS, Urie M, Kepner J (2006) Radiotherapy in pediatric medulloblastoma: quality assessment of Pediatric Oncology Group Trial 9031. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 5(64):1325–1330
Eich HT, Mueller RP, Schneeweiss A, Hansemann K, Smerau R, Willich N et al (2004) Initiation of a teleradiotherapeutic network for patients in German lymphoma studies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58(3):805–808
Dharmarajan KV, Friedman DL, FitzGerald T, McCarten KM, Constine LS, Chen L et al (2015) Radiotherapy quality assurance report from children’s oncology group AHOD0031. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 91(5):1065–1071
Laprise N, Hanusik R, Fitzgerald TJ, Rosen N, White K (2009) Developing a multi-institutional PACS archive and designing processes to manage the shift from a film to a digital-based archive. J Digit Imaging 1(22):15–24
Fitzgerald TJ (2010) Quality of radiotherapy reporting in randomized controlled trials of Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: in regard to Bekelman and Yahalom. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1(77):315–316
Mendenhall NP, Meyer J, Williams J, Tebbi C, Kessel S, Laurie F et al (2005) The impact of central quality assurance review prior to radiation therapy on protocol compliance: POG 9426, a trial in pediatric Hodgkin’s disease. Blood 106:753
SIOP Europe Brain Tumor Committee PNET Working Group (2011) An international prospective study on clinically standard-risk medulloblastoma in children older than 3 to 5 years with low-risk biological profile (PNET 5 MB-LR) or average-risk biological profile (PNET 5 MB-SR). NCT02066220, https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02066220?cond=PNET+5&rank=1
Kortmann RD, Timmermann B, Kühl J, Willich N, Flentje M, Meisner C, Bamberg M (1999) HIT ’91 (prospective, co-operative study for the treatment of malignant brain tumors in childhood): accuracy and acute toxicity of the irradiation of the craniospinal axis. Results of the quality assurance program. Strahlenther Onkol 175(4):162–169
Freeman CR, Taylor RE, Kortmann RD, Carrie C (2002) Radiotherapy for medulloblastoma in children: a perspective on current international clinical research efforts. Med Pediatr Oncol 39(2):99–108
Carrie C, Muracciole X, Gomez F, Habrand JL, Benhassel M, Mege M et al (2005) Conformal radiotherapy, reduced boost volume, hyperfractionated radiotherapy, and online quality control in standard-risk medulloblastoma without chemotherapy: Results of the French M‑SFOP 98 protocol. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63(3):711–716
Coles CE, Hoole AC, Harden SV, Burnet NG, Twyman N, Taylor RE, Kortmann RD, Williams MV (2003) Quantitative assessment of inter-clinician variability of target volume delineation for medulloblastoma: quality assurance for the SIOP PNET 4 trial protocol. Radiother Oncol 69(2):189–194
Halperin E (1996) Impact of radiation technique upon the outcome of treatment for medulloblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 36:233–239
Mirabell R, Bleher A, Huguenin P, Ries G, Kann R, Mirimanoff R, Notter M, Nouet P, Bieri S, Thum P, Toussi H (1997) Pediatric medulloblastoma: Radiation treatment technique and patterns of failure. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:523–529
Acknowledgements
We deeply thank Associazione Bianca Garavaglia Onlus for making this whole project possible. We thank Piergiorgio Venuti from the company Secure Online Desktop for his valuable contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
S. Meroni, C. Cavatorta, S. Barra, F. Cavagnetto, G. Scarzello, A. Scaggion, E. Pecori, B. Diletto, O. Alessandro, M. Massimino, S. Gianolini, E. Pignoli, and L. Gandola declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meroni, S., Cavatorta, C., Barra, S. et al. A dedicated cloud system for real-time upfront quality assurance in pediatric radiation therapy. Strahlenther Onkol 195, 843–850 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-019-01469-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-019-01469-y