Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate efficacy and toxicity of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) with CyberKnife® (Accuray, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) in a selected cohort of primary, medically inoperable early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
Methods
From 2012 to 2016, 106 patients (median age 74 years, range 50–94 years) with primary NSCLC were treated with SBRT using CyberKnife®. Histologic confirmation was available in 87 patients (82%). For mediastinal staging, 92 patients (87%) underwent 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography (18-FDG-PET) and/or endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS)-guided lymph node biopsy or mediastinoscopy. Tumor stage (UICC8, 2017) was IA/B (T1a-c, 1–3 cm) in 86 patients (81%) and IIA (T2a/b, 3–5 cm) in 20 patients (19%). Depending on tumor localization, three different fractionation schedules were used: 3 fractions of 17Gy, 5 fractions of 11Gy, or 8 fractions of 7.5 Gy. Tracking was based on fiducial implants in 13 patients (12%) and on image guidance without markers in 88%.
Results
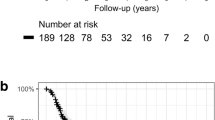
Median follow-up was 15 months (range 0.5–46 months). Acute side effects were mild (fatigue grade 1–2 in 20% and dyspnea grade 1–2 in 17%). Late effects were observed in 4 patients (4%): 3 patients developed pneumonitis requiring therapy (grade 2) and 1 patient suffered a rib fracture (grade 3). In total, 9/106 patients (8%) experienced a local recurrence, actuarial local control rates were 88% (95% confidence interval, CI, 80–96%) at 2 years and 77% (95%CI 56–98%) at 3 years. The median disease-free survival time was 27 months (95%CI 23–31 months). Overall survival was 77% (95%CI 65–85%) at 2 years and 56% (95%CI 39–73%) at 3 years.
Conclusion
CyberKnife® lung SBRT which allows for real-time tumor tracking and risk-adapted fractionation achieves satisfactory local control and low toxicity rates in inoperable early-stage primary lung cancer patients.
Zusammenfassung
Zielsetzung
Untersuchung von Wirkung und Toxizität einer stereotaktischen Bestrahlung (SBRT) bei Patienten mit Frühstadien von medizinisch inoperablen primären nichtkleinzelligen Bronchialkarzinomen (NSCLC) am CyberKnife® (Accuray, Sunnyvale, CA, US).
Methoden
Von 2012 bis 2016 wurden 106 Patienten (medianes Alter 74 Jahre, Spanne 50–94 Jahre) mit primärem NSCLC mittels SBRT am CyberKnife® behandelt. Bei 87 Patienten (82 %) war der Tumor histologisch gesichert. Zum Ausschluss mediastinaler Lymphknotenmetastasen erhielten 92 Patienten (87 %) eine 18Fluorodeoxyglukose-Positronenemissionstomographie (18FDG-PET) und/oder einen endobronchialen Ultraschall (EBUS) mit Lymphknotenbiopsie oder eine Mediastinoskopie. Das Tumorstadium (UICC8, 2017) war bei 86 Patienten IA/B (T1a–c, 1–3 cm) und bei 20 (19 %) IIA (T2a/b, 3–5 cm). Abhängig von der Tumorlokalisation wurden drei Fraktionierungsschemata verwendet: 3 × 17 Gy, 5 × 11 Gy, 8 × 7,5 Gy. Für das Tracking wurden 13 Patienten (12 %) Marker-Seeds implantiert, in 88 % erfolgte die Bestrahlung bildgesteuert ohne Marker.
Ergebnisse
Das mediane Follow-up betrug 15 Monate (Spanne 0,5–46 Monate). Akute Nebenwirkungen waren mild (Fatigue Grad 1–2 in 20 %, Atemnot Grad 1–2 in 17 %). Spättoxizitäten zeigten sich bei 4 Patienten (4 %): 3‑mal eine Pneumonitis (Grad 2),1-mal eine Rippenfraktur (Grad 3). Bei 9/106 Patienten (8 %) trat ein Lokalrezidiv auf, die lokale Kontrollrate betrug 88 % (95 %-Konfidenzintervall [KI] 80–96 %) nach 2 und 77 % (95 %-KI 56–98 %) nach 3 Jahren. Das mediane krankheitsfreie Überleben war 27 Monate (95 %-KI 23–31 Monate). Das Gesamtüberleben betrug 77 % (95 %-KI 65–85 %) nach 2 und 56 % (95 %-KI 39–73 %) nach 3 Jahren.
Schlussfolgerung
Durch Tumor-Tracking in Echtzeit und risikoadaptierte Fraktionierung führt die CyberKnife®-SBRT der Lunge bei inoperablen primären NSCLC-Patienten im Frühstadium zu einer guten lokalen Kontrolle bei niedrigen Toxizitätsraten.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang JY, Senan S, Paul MA, Mehran RJ, Louie AV, Balter P, Groen HJ, McRae SE, Widder J, Feng L et al (2015) Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus lobectomy for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Oncol 16:630–637
Palma D, Visser O, Lagerwaard FJ, Belderbos J, Slotman B, Senan S (2011) Treatment of stage I NSCLC in elderly patients: a population-based matched-pair comparison of stereotactic radiotherapy versus surgery. Radiother Oncol 101:240–244
Guckenberger M, Andratschke N, Alheit H, Holy R, Moustakis C, Nestle U, Sauer O (2014) Definition of stereotactic body radiotherapy: principles and practice for the treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 190:26–33
Palma D, Visser O, Lagerwaard FJ, Belderbos J, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2010) Impact of introducing stereotactic lung radiotherapy for elderly patients with stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a population-based time-trend analysis. J Clin Oncol 28:5153–5159
Palma DA, Senan S (2013) Improving outcomes for high-risk patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: insights from population-based data and the role of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy. Clin Lung Cancer 14:1–5
Chang JY, Cox JD (2010) Improving radiation conformality in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol 20:171–177
Nuyttens JJ, van de Pol M (2012) The CyberKnife radiosurgery system for lung cancer. Expert Rev Med Devices 9:465–475
Lagerwaard FJ, Verstegen NE, Haasbeek CJ, Slotman BJ, Paul MA, Smit EF, Senan S (2012) Outcomes of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy in patients with potentially operable stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:348–353
Colinet B, Jacot W, Bertrand D, Lacombe S, Bozonnat MC, Daures JP, Pujol JL (2005) A new simplified comorbidity score as a prognostic factor in non-small-cell lung cancer patients: description and comparison with the Charlson’s index. Br J Cancer 93:1098–1105
Pasic A, Brokx HA, Comans EF, Herder GJ, Risse EK, Hoekstra OS, Postmus PE, Sutedja TG (2005) Detection and staging of preinvasive lesions and occult lung cancer in the central airways with 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography: a pilot study. Clin Cancer Res 11:6186–6189
Rami-Porta R, Bolejack V, Crowley J, Ball D, Kim J, Lyons G, Rice T, Suzuki K, Thomas CF Jr., Travis WD et al (2015) The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for the revisions of the T descriptors in the forthcoming eighth edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 10:990–1003
Chan MK, Werner R, Ayadi M, Blanck O (2015) Comparison of 3D and 4D Monte Carlo optimization in robotic tracking stereotactic body radiotherapy of lung cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 191:161–171
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
Essler M, Wantke J, Mayer B, Scheidhauer K, Bundschuh RA, Haller B, Astner ST, Molls M, Andratschke N (2013) Positron-emission tomography CT to identify local recurrence in stage I lung cancer patients 1 year after stereotactic body radiation therapy. Strahlenther Onkol 189:495–501
Falkson CB, Vella ET, Yu E, El-Mallah M, Mackenzie R, Ellis PM, Ung YC (2017) Radiotherapy With Curative Intent in Patients With Early-stage, Medically Inoperable, Non-Small-cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review. Clin Lung Cancer. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2016.10.008
Guckenberger M, Allgauer M, Appold S, Dieckmann K, Ernst I, Ganswindt U, Holy R, Nestle U, Nevinny-Stickel M, Semrau S et al (2013) Safety and efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage 1 non-small-cell lung cancer in routine clinical practice: a patterns-of-care and outcome analysis. J Thorac Oncol 8:1050–1058
Kishan AU, Lee P (2016) Radiation therapy for stage I nonoperable or medically inoperable lung cancer. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 37:716–726
Murray P, Franks K, Hanna GG (2017) A systematic review of outcomes following Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy in the treatment of early stage primary lung cancer. Br J Radiol. doi:10.1259/bjr.20160732
Bahig H, Filion E, Vu T, Roberge D, Lambert L, Bouchard M, Lavoie C, Doucet R, Nadeau DB, Chalaoui J et al (2015) Excellent cancer outcomes following patient-adapted Robotic lung SBRT but a case for caution in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Technol Cancer Res Treat 14:667–676
Bibault JE, Prevost B, Dansin E, Mirabel X, Lacornerie T, Lartigau E (2012) Image-guided robotic stereotactic radiation therapy with fiducial-free tumor tracking for lung cancer. Radiat Oncol 7:102
Factor OB, Vu CC, Schneider JG, Witten MR, Schubach SL, Gittleman AE, Catell DT, Haas JA (2014) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a small academic hospital experience. Front Oncol 4:287
Heal C, Ding W, Lamond J, Wong M, Lanciano R, Su S, Yang J, Feng J, Arrigo S, Markiewicz D et al (2015) Definitive treatment of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer with stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy in a community cancer center setting. Front Oncol 5:146
Kelley KD, Benninghoff DL, Stein JS, Li JZ, Byrnes RT, Potters L, Knisely JP, Zinkin HD (2015) Medically inoperable peripheral lung cancer treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Radiat Oncol 10:120
van der Voort van Zyp NC, Prevost JB, Hoogeman MS, Praag J, van der Holt B, Levendag PC, van Klaveren RJ, Pattynama P, Nuyttens JJ (2009) Stereotactic radiotherapy with real-time tumor tracking for non-small cell lung cancer: clinical outcome. Radiother Oncol 91:296–300
Guckenberger M (2015) Dose and fractionation in stereotactic body radiation therapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: lessons learned and where do we go next? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 93:765–768
Guckenberger M, Klement RJ, Allgauer M, Andratschke N, Blanck O, Boda-Heggemann J, Dieckmann K, Duma M, Ernst I, Ganswindt U et al (2016) Local tumor control probability modeling of primary and secondary lung tumors in stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 118:485–491
Guckenberger M, Klement RJ, Allgauer M, Appold S, Dieckmann K, Ernst I, Ganswindt U, Holy R, Nestle U, Nevinny-Stickel M et al (2013) Applicability of the linear-quadratic formalism for modeling local tumor control probability in high dose per fraction stereotactic body radiotherapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol 109:13–20
Nyman J, Hallqvist A, Lund JA, Brustugun OT, Bergman B, Bergstrom P, Friesland S, Lewensohn R, Holmberg E, Lax I (2016) SPACE – A randomized study of SBRT vs conventional fractionated radiotherapy in medically inoperable stage I NSCLC. Radiother Oncol 121:1–8
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, Michalski J, Straube W, Bradley J, Fakiris A, Bezjak A, Videtic G, Johnstone D et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA 303:1070–1076
Videtic GM, Hu C, Singh AK, Chang JY, Parker W, Olivier KR, Schild SE, Komaki R, Urbanic JJ, Timmerman RD et al (2015) A randomized phase 2 study comparing 2 stereotactic body radiation therapy schedules for medically inoperable patients with stage I peripheral non-small cell lung cancer: NRG oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 93:757–764
Patel Z, Retrouvey M, Vingan H, Williams S (2014) Tumor track seeding: a new complication of fiducial marker insertion. Radiol Case Rep 9:928
Mendiratta-Lala M, Sheiman R, Brook OR, Gourtsoyianni S, Mahadevan A, Siewert B (2014) CT-guided core biopsy and percutaneous fiducial seed placement in the lung: can these procedures be combined without an increase in complication rate or decrease in technical success? Eur J Radiol 83:720–725
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
S. Temming, M. Kocher, E. Stoelben, L. Hagmeyer, D.-H. Chang, K. Frank, K. Hekmat, J. Wolf, W.W. Baus, R. Semrau, C. Baues, and S. Marnitz declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Temming, S., Kocher, M., Stoelben, E. et al. Risk-adapted robotic stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 194, 91–97 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-017-1194-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-017-1194-x