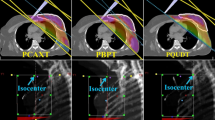
Purpose:
To compare two irradiation techniques for whole breast irradiation: tangential wedged beams (WT) versus “open” fields (without wedges) with forward planned segments (ST).
Patients and Methods:
For 20 patients two comparative 3-D plans were defined using Pinnacle P3D and analyzed with respect to dose, dose homogeneity in the target volume, and scattered dose to organs at risk. The plans of six patients were reproduced in an Alderson phantom. Measurements were performed in the planning target volume (PTV), contralateral breast, lungs, heart, thyroid gland and in mid-pelvis.
Results:
Dose distribution in the PTV was nearly identical for WT and ST with the exception of D1. Scattered doses were significantly smaller for ST. In the contralateral breast the doses per 2-Gy fraction were 7.3 cGy ± 2.1 cGy (WT), and 4.7 cGy ± 1.9 cGy (ST; p < 0.01). Similar doses were measured for lung and heart. In mid pelvis the largest difference was observed (WT: 1.0 cGy ± 0.2 cGy, ST: 0.2 cGy ± 0.1 cGy; p < 0.01).
Conclusion:
Partial volume segments can replace wedges for improved dose coverage and homogeneity in the PTV. The ST causes significantly less scattered dose to extra-target organs. This may have implications for long-term risks after exposure to low radiation doses.
Ziel:
Vergleich zweier Bestrahlungstechniken für die Brustbestrahlung: tangentiale Keilfiltertechnik (WT) versus „offene“ Felder (ohne Keil) mit vorwärts geplanten Segmenten (ST).
Patienten und Methodik:
Bei 20 Patientinnen wurden je ein Bestrahlungsplan mit Keilfiltern und ein Plan mit segmentierten Feldern erstellt und bezüglich Dosis, Dosishomogenität im Zielvolumen und Streuanteil in Risikoorganen analysiert. Die Pläne von sechs Patientinnen wurden am Alderson-Phantom reproduziert. Messungen wurden im Zielvolumen (PTV), der kontralateralen Brust, den Lungen, dem Herzen, der Schilddrüse und im kleinen Becken durchgeführt.
Ergebnisse:
Die Dosisverteilung im Planungszielvolumen (PTV) war für WT und ST nahezu identisch mit Ausnahme von D1. Der Streuanteil für Risikoorgane war für die ST signifikant geringer. In der kontralateralen Mamma betrug die Dosis pro 2-Gy-Fraktion mit der WT 7,3 cGy ± 2,1 cGy und mit der ST 4,7 cGy ± 1,9 cGy (p < 0,01). Ähnliche Ergebnisse wurden für die Dosen in Lunge und Herz gemessen. Der größte Unterschied zwischen WT und ST zeigte sich im kleinen Becken (WT 1,0 cGy ± 0,2 cGy, ST 0,2 cGy ± 0,1 cGy; p < 0,01).
Schlussfolgerung:
Teilvolumensegmente können Keile in Bezug auf Zielvolumenabdeckung und Dosishomogenität im PTV ersetzen. Die ST verursacht signifikant weniger Streuanteil außerhalb des Zielvolumens. Dies kann Einfluss auf Langzeitrisiken nach Exposition niedriger Strahlendosen haben.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ludwig, V., Schwab, F., Guckenberger, M. et al. Comparison of Wedge versus Segmented Techniques in Whole Breast Irradiation. Strahlenther Onkol 184, 307–312 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-008-1793-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-008-1793-7