Purpose:
To explore the potential of helical tomotherapy (HT) in the treatment of nasopharynx cancer.
Patients and Methods:
Six T1–4 N1–3 patients were considered. A simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) technique was planned with inversely optimized conventional intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT; dynamic multileaf collimator using the Eclipse-Helios Varian system) and HT. The prescribed (median) doses were 54 Gy, 61.5 Gy, and 64.5 Gy delivered in 30 fractions to PTV1 (planning target volume), PTV2, and PTV3, respectively. The same constraints for PTV coverage and for parotids, spinal cord, mandible, optic structures, and brain stem were followed in both modalities. The planner also tried to reduce the dose to other structures (mucosae outside PTV1, larynx, esophagus, inner ear, thyroid, brain, lungs, submental connective tissue, bony structures) as much as possible.
Results:
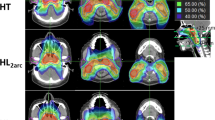
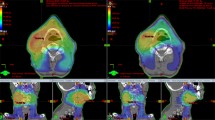
The fraction of PTV receiving > 95% of the prescribed dose (V95%) increased from 97.6% and 94.3% (IMRT) to 99.6% and 97% (HT) for PTV1 and PTV3, respectively (p < 0.05); median dose to parotids decreased from 30.1 Gy for IMRT to 25.0 Gy for HT (p < 0.05). Significant gains (p < 0.05) were found for most organs at risk (OARs): mucosae (V30 decreased from 44 cm3 [IMRT] to 18 cm3 [HT]); larynx (V30: 25 cm3 vs. 11 cm3); thyroid (mean dose: 48.7 Gy vs. 41.5 Gy); esophagus (V45: 4 cm3 vs. 1 cm3); brain stem (D1%: 45.1 Gy vs. 37.7 Gy).
Conclusion:
HT improves the homogeneity of dose distribution within PTV and PTV coverage together with a significantly greater sparing of OARs compared to linac five-field IMRT.
Ziele:
Untersuchung des Potentials der helikalen Tomotherapie (HT) beim Nasopharynxkarzinom.
Patienten und Methodik:
Sechs T1–4 N1–3-Patienten wurden einbezogen. Eine Technik des simultanen integrierten Boost (SIB) wurde geplant mit invers optimierter konventioneller intensitätsmodulierter Radiotherapie (IMRT; dynamischer Multileaf-Kollimator des Eclipse-Helios Varian-Systems) und mit HT. Die verschriebenen (medianen) Strahlungsdosen waren 54 Gy, 61,5 Gy und 64,5 Gy, die in 30 Fraktionen auf die Planungszielvolumina PTV1, PTV2 bzw. PTV3 gegeben wurden. Bei beiden Modalitäten, HT und IMRT, wurden für die PTV-Erfassung sowie für Parotiden, Rückenmark, Kiefer, optischen Apparat und Stammhirn dieselben Begrenzungen eingehalten. Der Planer versuchte auch, die Strahlungsdosis auf andere Regionen (Mukosa außerhalb von PTV1, Larynx, Ösophagus, Innenohr, Schilddrüse, Hirn, Lunge, Bindegewebe und Knochen unterhalb des Kinns) so stark wie möglich zu reduzieren.
Ergebnisse:
Der PTV-Anteil, der mehr als 95% der verschriebenen Strahlungsdosis (V95%) erhielt, erhöhte sich für PTV1 und PTV3 von 97,6% bzw. 94,3% (IMRT) auf 99,6% bzw. 97% (HT) (p < 0,05); die mediane Dosis der Parotiden verminderte sich von 30,1 Gy bei IMRT auf 25,0 Gy bei HT (p < 0,05). Signifikante Vorteile (p < 0,05) zeigten sich für die meisten Risikoorgane: Mukosa (V30-Verminderung von 44 cm3 [IMRT] auf 18 cm3 [HT]), Larynx (V30: 25 cm3 vs. 11 cm3), Schilddrüse (mittlere Strahlungsdosis: 48,7 Gy vs. 41,5 Gy), Ösophagus (V45: 4 cm3 vs. 1 cm3), Stammhirn (D1%: 45,1 Gy vs. 37,7 Gy).
Schlussfolgerung:
Verglichen mit der Linac-5-Felder-IMRT verbessert HT die Homogenität der Dosisverteilung innerhalb des PTV und die PTV-Erfassung bei signifkant besserer Schonung von Risikoorganen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiorino, C., Dell'Oca, I., Pierelli, A. et al. Simultaneous Integrated Boost (SIB) for Nasopharynx Cancer with Helical Tomotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 183, 497–505 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-007-1698-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-007-1698-x