Background and Purpose:
For patients with gynecologic carcinomas, irradiation of paraaortic lymph nodes (PLNs) is a routine treatment concept. Planning target volumes (PTVs) individually optimized by radiation field delineations along the big vessels permit the inclusion of at least 97% of potentially involved PLNs. However, this novel treatment technique might increase radiation-induced nephrotoxicity. Therefore, the actual incidence of kidney damage after PLN irradiation has to be assessed in order to validate the safety of this treatment concept.
Patients and Methods:
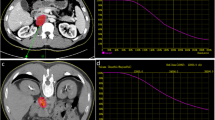
19 patients were treated with irradiation alone (50.4 Gy; 5 × 1.8 Gy/week) and monitored for up to 90 months. Functional renal parameters, namely renal plasma flow (RPF) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR), were assessed by dynamic renal scintigraphy. Additionally, patients were clinically observed (i.e., hypertension, proteinuria) and calculations of normal-tissue complication probability (NTCP) values for nonuniform kidney irradiation were performed using the Lyman-Wolbarst algorithm.
Results:
Two patients with anticipated moderate NTCP values (12.6% and 8.7%) showed slightly impaired RPF rates at 12, 24, and after 48 months of follow-up. Only one patient in the subgroup showing NTCP values > 50% (n = 9) developed a notable impairment of renal RPF. However, all patients including those with elevated complication probabilities exhibited neither impaired GFR nor clinically apparent symptoms related to a loss of functioning renal tissue from 12 to > 48 months post irradiation.
Conclusion:
Conformal irradiation of retroperitoneal lymph nodes with individual PTV delineation appears not to be associated with clinically relevant functional impairment of the kidneys.
Hintergrund und Ziel:
Die Behandlung von Patientinnen mit gynäkologischen Tumoren beinhaltet häufig die Bestrahlung der paraaortalen Lymphknoten (PLNs). Durch eine individuelle Anpassung des Planungszielvolumens (PTV) an den Verlauf der großen abdominalen Gefäße können mindestens 97% aller potentiell befallenen PLNs behandelt werden. Die dadurch z.T. vergrößerten PTVs könnten aber mit einer gesteigerten Inzidenz für eine radiogene Nephropathie einhergehen. Um die Sicherheit dieser neuen Bestrahlungstechnik zu überprüfen, wurde das tatsächliche Auftreten von radiogenen Nephropathien nach solchen PLN-Bestrahlungen untersucht.
Patienten und Methodik:
19 Patientinnen mit gynäkologischen Tumoren, die eine Bestrahlung der PLNs (50,4 Gy; 5 × 1,8 Gy/Woche) ohne Chemotherapie in der Klinik der Autoren erhielten, wurden bis zu 90 Monate nachbeobachtet. Mittels seitengetrennter Nierenclearence wurden renaler Plasmafluss (RPF) und glomeruläre Filtrationsrate (GFR) bestimmt und die Patientinnen regelmäßig klinisch untersucht (u.a. Blutdruck, Proteinurie). Außerdem wurden für jede Patientin aus den dreidimensionalen Bestrahlungsplänen für beide Nieren NTCP-Werte (Wahrscheinlichkeit von Normalgewebskomplikationen) nach dem Lyman-Wolbarst-Algorithmus berechnet.
Ergebnisse:
Zwei Patientinnen mit moderaten NTCP-Werten (12,6% und 8,7%) wiesen nach 12, 24 und 48 Monaten eine leichte Störung des RPF auf. Nur eine Patientin aus der Gruppe mit NTCP-Werten > 50% (n = 9) entwickelte eine ausgeprägtere Störung des RPF. Keine Patientin zeigte eine Störung der GFR oder klinische Symptome einer Nierenschädigung in der Zeit von 12 bis > 48 Monate nach der Bestrahlung.
Schlussfolgerung:
Die konformale Bestrahlung der PLNs mit einem individuellen, dem Verlauf der großen Gefäße angepassten PTV führte im eigenen Patientenkollektiv in keinem Fall zu einer klinisch relevanten radiogenen Nephropathie.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nevinny-Stickel, M., Poljanc, K., Forthuber, B.C. et al. Optimized Conformal Paraaortic Lymph Node Irradiation is not Associated with Enhanced Renal Toxicity. Strahlenther Onkol 183, 385–391 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-007-1657-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-007-1657-6