Background and Purpose:
The objective of this investigation was a direct comparison of the dosimetry of CT-based and radiograph- based postplanning procedures for seed implants.
Patients and Methods:
CT- and radiograph-based postplans were carried out for eight iodine-125 (125I) seed implant patients with a commercial treatment-planning system (TPS). To assess a direct comparison of the dosimetric indices (D90, V100, V400), the radiograph-based seed coordinates were transformed to the coordinate system of the CT postplan. Afterwards, the CT-based seed positions were replaced by the radiograph-based coordinates in the TPS and the dose distribution was recalculated.
Results:
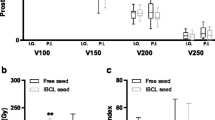
The computations demonstrated that the radiograph-based dosimetric values for the prostate (D p 90, V p 100, and Vp400) were on average lower than the values of the CT postplan. Normalized to the CT postplan the following mean values were found: D p 90: 90.6% (standard deviation [SD]: 9.0%), V p 100: 86.1% (SD: 14.7%), and V p 400: 79.4% (SD: 14.4%). For three out of the eight patients the D p 90 decreased to 90% of the initial CT postplan values. The reason for this dosimetric difference is supposed to be evoked by an error of the reconstruction software used. It was detected that the TPS algorithm assigned some sources to wrong coordinates, partly out of the prostate gland.
Conclusion:
The radiograph-based postplanning technique of the investigated TPS should only be used in combination with CT postplanning. Furthermore, complex testing procedures of reconstruction algorithms are recommended to minimize calculation errors.
Hintergrund und Ziel:
Das Ziel dieser Untersuchung war es, die Dosimetrie zweier häufig angewandter Nachplanungsverfahren bei Seed-Implantationen, die Computertomographie und die Röntgenbildrekonstruktion, direkt miteinander zu vergleichen.
Patienten und Methodik:
Die CT-Nachplanungen und Röntgenbildrekonstruktionen wurden in einem Kollektiv von acht Patienten mit Iod-125-(125I-)Implantaten anhand eines kommerziellen Seed-Planungssystems durchgeführt. Um eine direkte Evaluation der dosimetrischen Parameter (D90, V100, V400) zu erreichen, wurden die Koordinaten der Seeds aus den Röntgenbildrekonstruktionen in das Koordinatensystem der CT-Nachplanung transformiert. Im Planungssystem wurden die Seed-Koordinaten der CT-Nachplanung durch die Seed-Positionen der Röntgenfilmrekonstruktionen ersetzt, und die Dosisverteilung wurde erneut berechnet.
Ergebnisse:
Die Berechnungen ergaben, dass die auf Röntgenbildrekonstruktionen basierenden Werte der Prostata für D p 90, V p 100 und V p 400 im Mittel unter denen der CT-basierten Nachplanungen lagen. Auf die Werte der CT-Nachplanungen normiert stellten sich die Ergebnisse wie folgt dar: D p 90: 90,6% (Standardabweichung [SD]: 9,0%), V p 100: 86,1% (SD: 14,7%) sowie V p 400: 79,4% (SD: 14,4%). Bei drei der acht Patienten lag der D p 90-Wert unter 90% der Dosen der ursprünglichen CT-Nachplanung. Als Erklärung für die Diskrepanz der Dosimetrie in diesen Fällen werden Ungenauigkeiten im Rekonstruktionsalgorithmus der verwendeten Planungssoftware angenommen. Es zeigte sich, dass einzelnen Seeds fehlerhafte Koordinaten, teilweise sogar außerhalb der Prostata, zugeordnet worden waren.
Schlussfolgerung:
Der Rekonstruktionsalgorithmus des verwendeten Planungssystems sollte nur in Verbindung mit einer CTNachplanung verwendet werden. Des Weiteren wird eine gründliche Überprüfung verwendeter Algorithmen empfohlen, um Fehler bei der Rekonstruktionsberechnung zu minimieren.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siebert, FA., Kohr, P. & Kovács, G. Comparison of CT- and Radiograph-Based Post-Implant Dosimetry for Transperineal 125I Prostate Brachytherapy Using Single Seeds and a Commercial Treatment-Planning Software. Strahlenther Onkol 182, 96–101 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-006-1465-4
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-006-1465-4