Background and Purpose:
Tumor hypoxia is regarded as one important underlying feature of radioresistance. The authors report on an experimental approach to improve tumor response to radiation by combining fractionated irradiation with HBOC-201, an ultrapurified polymerized hemoglobin solution, which is currently used in clinical phase II/III trials as alternative oxygen carrier and proved to be highly effective in tissue oxygenation (tpO2).
Material and Methods:
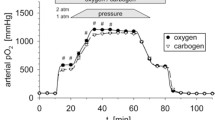
: Subcutaneously growing rhabdomyosarcoma R1H tumors of the rat were treated with either 40 Gy (2 Gy/fraction, 20 fractions in 2 weeks, ambient) followed by graded top-up doses (clamped) alone, or in combination with HBOC-201, or with HBOC-201 plus carbogen (95% O2 + 5% CO2). Local tumor control (TCD50%) and growth delay were used as endpoints. In addition, the effect of HBOC-201 alone or in combination with carbogen on the tpO2 of tumor and muscle was determined using a flexible stationary probe (Licox, GMS).
Results:
TCD50% values of 119 Gy (95% confidence interval 103;135), 111 Gy (84;138), and 102 Gy (83;120) were determined for tumors irradiated alone, in combination with HBOC-201, and with HBOC-201 plus carbogen, respectively. Although the dose-response curves showed a slight shift to lower doses when HBOC-201 or HBOC-201 plus carbogen was added, the differences in TCD50% were not statistically significant. No effect was seen on the growth delay of recurrent tumors. HBOC-201 alone did not effect tumor or muscle tpO2. In combination with carbogen the mean tpO2 of muscle raised from 23.9 mmHg to 59.3 mmHg (p < 0.05), but this effect was less pronounced than the increase in tpO2 by carbogen alone.
Conclusion:
Low-dose application of HBOC-201 does not improve the response of the rhabdomyosarcoma R1H of the rat to fractionated irradiation.
Hintergrund und Ziel:
Strategien zur Überwindung der hypoxievermittelten Radioresistenz von Tumoren sind gegenwärtig von großem klinischen und wissenschaftlichen Interesse. Eine Verbesserung der Sauerstoffverfügbarkeit im Tumor kann als Folge der gesteigerten O2-Transportkapazität durch eine Erhöhung der Hämoglobinkonzentration erreicht werden. Die zellfreie Hämoglobinlösung HBOC-201 wird erfolgreich in klinischen Phase-II/III-Studien eingesetzt und vermag die Sauerstoffversorgung von Gewebe effektiv zu erhöhen. Die vorliegende Arbeit sollte klären, ob HBOC-201 im Rahmen einer fraktionierten Strahlentherapie die Tumorhypoxie verringern und das Therapieergebnis verbessern kann.
Material und Methodik:
Eine fraktionierte Bestrahlung von subkutan wachsenden R1H-Tumoren der Ratte wurde mit täglicher, niedrigdosierter i. v. Gabe von HBOC-201 bzw. von HBOC-201 plus Carbogen (95% O2 + 5% CO2) kombiniert. Es wurden Gesamtdosen von 40 Gy fraktioniert verabreicht (2 Gy/Fraktion, 20 Fraktionen in 2 Wochen) und mit Top-up-Dosen auf Gesamtdosen aufgesättigt, die eine Bestimmung der lokalen Tumorkontrolle ermöglichten. Neben der lokalen Kontrolldosis (TCD50%) wurde die Wachstumsverzögerung der Rezidive bestimmt. Zusätzlich wurde der Effekt von HBOC-201 allein und in Kombination mit Carbogen auf die Gewebsoxygenierung (tpO2) polarometrisch bestimmt.
Ergebnisse:
Die Kombination einer fraktionierten Bestrahlung mit HBOC-201 bzw. mit HBOC-201 plus Carbogen hatte keinen statistisch signifikanten Einfluss auf die lokale Tumorkontrolle. Es wurde eine nur geringfügige Verringerung der TCD50%-Werte von 119 Gy (95%-Konfidenzintervall: 103;135) auf 111 Gy (84;138) bzw. auf 102 Gy (83;120) beobachtet. Die Wachstumsverzögerung der Rezidive wies ebenfalls keine Veränderung auf. Die Oxygenierung von Tumor- und Muskelgewebe konnte durch Carbogenatmung, nicht aber durch HBOC-201 verbessert werden.
Schlussfolgerung:
Die Wirksamkeit einer fraktionierten Tumorbestrahlung wird durch niedrigdosierte Hämoglobinlösung HBOC-201 nicht verbessert.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raabe*, A., Gottschalk*, A., Hommel, M. et al. No Effect of the Hemoglobin Solution HBOC-201 on the Response of the Rat R1H Tumor to Fractionated Irradiation. Strahlenther Onkol 181, 730–737 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-005-1418-3
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-005-1418-3



