Aims:
To provide a schematized and graduated CT reference series of the mediastinum showing CT-detectable lymph node areas of lung cancer patients to support 3-D treatment planning and documentation for adjuvant irradiation of the mediastinum.
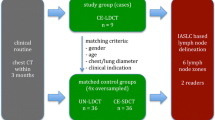
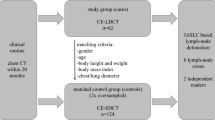
Patients and Methods: Cross sections of mediastinal structures from one male individual were schematized and overlaid with a 1 cm2 reference grid. Mediastinal CT scans of 100 consecutive patients with histologically proven lung cancer and CT-detectable lymph nodes were evaluated. For each patient the outlines of all identifiable nodes were transferred into the schematized CT series according to their localization in relation to anatomical landmarks. The outlines were centered in a predefined way into relevant squares of the reference grid. The number of patients with nodes projecting to individual CT cross sections was determined. Further, the number and percentage of patients locating to positive grid squares were analyzed.
Results: A differentiated pattern of CT-detectable lymph nodes was confirmed. Along the longitudinal axis the CT-detectable nodes followed a Gaussian distribution with its maximum (89% of all patients) at the level of the tracheal bifurcation. At different transverse levels closely circumscribed central areas with node positive grid squares were identified harboring up to 72% of the patients (locating to the front of the trachea, the bifurcation and below the carina). Peripheral areas showed only sporadically node positive grid squares, usually representing less than 5% of the patients.
Conclusions: These schematized and graduated CT cross sections show areas of CT-detectable lymph node spread from the view of 3-D planning. They are of additional help to individualize mediastinal target volumes and/or dose distributions, particularly when administering adjuvant irradiation to patients without mediastinal lymph node involvement. Classifying mediastinal structures by using a grid square easily allows to describe and document target volumes and dose distributions per cross section.
Ziel:
Erstellung einer schematisierten und mit einem Planquadratnetz versehenen CT-Referenzserie des Mediastinums mit Darstellung der Häufigkeitsverteilung computertomographisch nachweisbarer Lymphknoten bei Patienten mit Bronchialkarzinom als Beitrag zur 3-D-Planung einer adjuvanten Mediastinalbestrahlung.
Patienten und Methode: Die CT-Bildserie des Mediastinums einer männlichen Person wurde schematisiert und mit einem in den Bildmaßstab integrierten Planquadratnetz (1 cm2/Quadrat) versehen. Anschließend wurden die CT-Bildserien von 100 konsekutiven Patienten mit Bronchialkarzinom und computertomographisch nachweisbaren nodalen Befunden ausgewertet. Für jeden Patienten wurden die Umrisse aller identifizierbaren Lymphknoten maßstabsgerecht und in anatomischer Relation in die schematisierte Referenzserie übertragen. Die Lymphknotenkonturen wurden dabei in vordefinierter Weise auf ihre Schwerpunkte reduziert und diese einem oder mehreren Planquadraten zugeordnet. Für die longitudinale Häufigkeitsverteilung wurde die Anzahl der Patienten mit nodalen Befunden in den einzelnen Querschnittebenen und für die Häufigkeitsverteilung in der Fläche der Querschnittsebenen der Prozentsatz nodal positiver Planquadrate ermittelt.
Ergebnisse: Es bestätigte sich ein differenziert gewichtetes Verteilungsmuster der im CT nachweisbaren nodalen Befunde. Ihre Häufigkeitsverteilung entlang der longitudinalen Mediastinalachse folgt annähernd einer Gauss'schen Kurve mit Maximum (89% der Patienten) in Höhe der Trachealbifurkation. In den verschiedenen Schnittebenen zeigte die Querverteilung zentral größere umschriebene Areale mit bis zu 72% nodal positiver Planquadrate (prätracheal, präbifurkal, subkarinal), peripher hingegen nur sporadisch kleinere Areale mit nodal positiven Planquadraten unter 5%.
Schlussfolgerungen: Die schematisierten und mit einem Planquadratnetz versehenen Querschnitte der CT-Referenzserie zeigen die erhobenen Befunde direkt in der für die 3-D-Planung spezifischen Sichtweise. Sie sind eine zusätzliche Hilfe für eine Nuancierung des mediastinalen Zielvolumens bei der adjuvanten Bestrahlung mediastinal nodal negativer Patienten. Die Einteilung in Planquadrate erlaubt eine einfache Kennzeichnung und Dokumentation von Zielvolumen und Dosisverteilung pro Querschnitt durch Angabe der Planquadratkoordinaten.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: August 29, 2001; accepted: January 22, 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slanina, J., Laubenberger, J. CT-Based Study on Potential Mediastinal Lymph Node Spread of Patients with Lung Cancer Contribution to 3-D Treatment Planning for Adjuvant Radiotherapy of the Mediastinum. Strahlenther Onkol 178, 199–208 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-002-0936-5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-002-0936-5