Abstract
Objective
Restoration of a normal profile of spinal column by complete or almost complete reduction, stabilization achieved by instrumentation and fusion of the lumbosacral intervertebral segment.
Alleviation or at least marked reduction of pain and neurologic deficits present before surgery.
Indications
High grade, that means usually spondylolisthesis grade IV according to Meyerding or spondyloptosis.
Patients with progression of slip.
Contraindications
Osteopenia.
Spondylolistheses which do not necessitate an opening of the spinal canal.
Possibility of adequate anterior access to the lumbosacral disk.
Surgical Technique
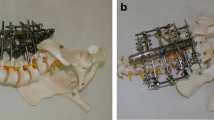
Posterior decompression and resection of the sacral dome, reduction of L5 over the sacrum and posterior interbody fusion L5/S1 with two autogenous bi- or tricortical bone grafts harvested from the iliac crest.
Results
Between January 1995 and January 1998, we used the described technique in eleven patients. Six patients had a grade IV spondylolisthesis and five a spondyloptosis. Previous surgery had been done in four patients.
A complete or almost complete reduction was possible in ten patients. No pseudarthrosis nor loss of correction were seen. Neurologic deficits improved in five of six patients. All patients noted an improvement of symptoms.
Postoperative complications in previously operated patients: one dura lesion, one deficit of the S1 nerve root diagnosed postoperatively, and one inadequate reduction. Postoperative complications in the remaining seven, not previously operated patients: one instability of the adjacent segment and a transient irritation of the L5 nerve root in two patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boxall D, Bradford DS, Winter RB, Moe JH. Management of severe spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1979;61:479–95.
Cloward RB. The treatment of ruptured lumbar intervertebral discs by vertebral body fusion. Indications, operative technique, after care. J Neurosurg 1953;10:154–68.
Cloward RB. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion updated. Clin Orthop 1985;193:16–9.
Denis F, Amstrong GWD, Searls K, Matta L. Acute thoracolumbar burst fractures in the absence of neurologic deficit. Clin Orthop 1984;189:142–9.
Harms JG, Jeszenszky D. Die posteriore, lumbale, interkorporelle Fusion in unilateraler transforaminaler Technik. Operat Orthop Traumatol 1998;10:90–102.
Klöckner C, Räder L, Wörsdörfer O. Management of infected osteosyntheses following operative stabilisation of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1997;79:Suppl II:159.
Meyerding HW. Spondylolisthesis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1932;54:371–7.
Noack W, Kirgis A. Posterior Reduction and Anterior Intervertebral Fusion in Lumbar Spondylolisthesis 1994;3:60–76.
Seitsalo S, Osterman K, Hyvarinen H, Tallroth K, Schlenzka D, Poussa M. Progression of spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. A long-term follow-up of 272 patients. Spine 1991;16:417–21.
Taillard W. Le spondylolisthésis chez l’enfant et l’adolescent (étude de 50 cas). Acta Orthop Scand 1954;24:115–44.
Wegener C, Weber U, Schöndorf TH, Franz K. Sekundäre Gefäßerkrankungen bei Spondylolisthesis. Z Orthop 1980;118:337–50.
Wiltse LL, Newman PH, Macnab I. Classification of spondylolisis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop 1976;117:23–9.
Wiltse LL, Winter RB. Terminology and measurement of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1983;65:768–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klöckner, C. Surgery for severe spondylolisthesis and spondyloptosis. Orthop Traumatol 10, 47–59 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00065-002-1036-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00065-002-1036-x