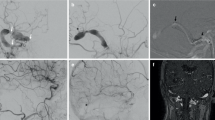
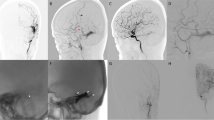
Abstract
Purpose
The objective of this study was to evaluate our 12-year experience in treating Borden type III transverse-sigmoid sinus (TSS) dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) and discuss the technical aspects of ipsilateral and contralateral transvenous embolization (TVE) approaches.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed charts of consecutive patients with TSS DAVF treated with multimodal treatment between April 2008 and March 2020. The baseline patient characteristics, imaging data, details of procedure, data sets of sinus pressure monitoring, and clinical results were systematically collected.
Results
Of 44 patients with TSS DAVF who were treated during study periods, 23 patients of Borden type III were extracted. Among the 23 patients, 18 with transfemoral TVE were included for analysis. TVE was performed using an ipsilateral approach in 8 patients and a contralateral approach in 10. Pressure monitoring data revealed that initial mean sinus pressure (43.5 mmHg vs. 29.5 mmHg; P = 0.033), maximum sinus pressure during the procedure (69.0 mmHg vs. 40.5 mmHg; P = 0.011), and sinus pressure gradient (22.5 mmHg vs. 5.5 mmHg; P = 0.021) were significantly higher in the ipsilateral approach group. The complete obliteration rate by primary embolization was 94% in our cohort with the recurrence rate of 5.6% with a median follow-up period of 57 months.
Conclusion
Our study showed the durability of TVE for patients with Borden type III TSS DAVF. TVE performed via the contralateral approach might prevent a potentially dangerous increase in intraprocedural sinus pressure and cortical venous reflux.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTA:
-
Computed tomography angiography
- CVR:
-
Cortical venous reflux
- DAVF:
-
Dural arteriovenous fistula
- DSA:
-
Digital subtraction angiography
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- MSP:
-
Mean sinus pressure
- SAD:
-
Skin-absorbed dose
- SPG:
-
Sinus pressure gradient
- TAE:
-
Transarterial embolization
- TSS:
-
Transverse-sigmoid sinus
- TVE:
-
transvenous embolization
References
Piippo A, Niemelä M, van Popta J, Kangasniemi M, Rinne J, Jääskeläinen JE, Hernesniemi J. Characteristics and long-term outcome of 251 patients with dural arteriovenous fistulas in a defined population. J Neurosurg. 2013;118:923–34.
van Dijk JM, terBrugge KG, Willinsky RA, Wallace MC. Clinical course of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with long-term persistent cortical venous reflux. Stroke. 2002;33:1233–6.
Cho WS, Han JH, Kang HS, Kim JE, Kwon OK, Oh CW, Han MH, Chung YS. Treatment outcomes of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas of the transverse and sigmoid sinuses from a single institute in Asia. J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20:1007–12.
Carlson AP, Alaraj A, Amin-Hanjani S, Charbel FT, Aletich V. Endovascular approach and technique for treatment of transverse-sigmoid dural arteriovenous fistula with cortical reflux: the importance of venous sinus sacrifice. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013;5:566–72.
Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA. A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg. 1995;82:166–79.
Miller TR, Gandhi D. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: clinical presentation and management strategies. Stroke. 2015;46:2017–25.
Bhatia KD, Lee H, Kortman H, Klostranec J, Guest W, Wälchli T, Radovanovic I, Krings T, Pereira VM. Endovascular management of Intracranial dural AVFs: transvenous approach. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2022;43:510–6.
Komiyama M, Ishiguro T, Matsusaka Y, Yasui T, Nishio A. Transfemoral, transvenous embolisation of dural arteriovenous fistula involving the isolated transverse-sigmoid sinus from the contralateral side. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2002;144:1041–6.
Kiyosue H, Tanoue S, Okahara M, Hori Y, Kashiwagi J, Sagara Y, Kubo T, Mori H. Angioarchitecture of transverse-sigmoid sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas: evaluation of shunted pouches by multiplanar reformatted images of rotational angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:1612–20.
Abecassis IJ, Meyer RM, Levitt MR, Sheehan JP, Chen CJ, Gross BA, Smith J, Fox WC, Giordan E, Lanzino G, Starke RM, Sur S, Potgieser ARE, van Dijk JMC, Durnford A, Bulters D, Satomi J, Tada Y, Kwasnicki A, Amin-Hanjani S, Alaraj A, Samaniego EA, Hayakawa M, Derdeyn CP, Winkler E, Abla A, Lai PMR, Du R, Guniganti R, Kansagra AP, Zipfel GJ, Kim LJ. Recurrence after cure in cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: a collaborative effort by the Consortium for Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Outcomes Research (CONDOR). J Neurosurg. 2021;10:1–9.
Guédon A, Saint-Maurice JP, Thépenier C, Labeyrie MA, Civelli V, Sissy CE, Eliezer M, Aymard A, Guichard JP, Houdart E. Results of transvenous embolization of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula: a consecutive series of 136 patients with 142 fistulas. J Neurosurg. 2021;28:1–9.
Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Hieshima GB, Goto K, Norman D, Newton TH. Dural fistulas involving the transverse and sigmoid sinuses: results of treatment in 28 patients. Radiology. 1987;163:443–7.
Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Hieshima GB, Mehringer CM, Hardin CW. Transvenous embolization of dural fistulas involving the transverse and sigmoid sinuses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1989;10:385–92.
Sadeh-Gonike U, Magand N, Armoiry X, Riva R, Labeyrie PE, Lamy B, Lukaszewicz AC, Lehot JJ, Turjman F, Gory B. Transarterial onyx embolization of Intracranial dural fistulas: a prospective cohort, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Neurosurgery. 2018;82:854–63.
Ambekar S, Gaynor BG, Peterson EC, Elhammady MS. Long-term angiographic results of endovascularly “cured” intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg. 2016;124:1123–7.
Tanoue S, Kiyosue H, Hori Y, Abe T, Mori H. Turn-back embolization technique for effective transvenous embolization of dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33:E88–91.
Matsuda W, Sonomura T, Honma S, Ohno S, Goto T, Hirai S, Itoh M, Honda Y, Fujieda H, Udagawa J, Takano S, Fujiyama F, Ueda S. Anatomical variations of the torcular Herophili: macroscopic study and clinical aspects. Anat Sci Int. 2018;93:464–8.
Alexander MD, Oliff MC, Olorunsola OG, Brus-Ramer M, Nickoloff EL, Meyers PM. Patient radiation exposure during diagnostic and therapeutic interventional neuroradiology procedures. J Neurointerv Surg. 2010;2:6–10.
Kohta M, Fujita A, Tanaka J, Sasayama T, Hosoda K, Kohmura E. Novel Segmentation of Placed Coils in the Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Provides a Reliable Predictor of the Long-Term Outcome in Abducens Nerve Palsy. World Neurosurg. 2018;113:e38–44.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all other staff, neurosurgeons, and radiologists of Kobe University Hospital.
Funding
The authors have no personal, financial, or institutional interest in any of the drugs, materials, and devices described in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by A. Fujita, M. Kohta. The project was directed and supervised by T. Sasayama and E. Kohmura. The first draft of the manuscript was written by A. Fujita and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscripts.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. Fujita, M. Kohta, T. Sasayama and E. Kohmura declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, A., Kohta, M., Sasayama, T. et al. Endovascular Treatment of Borden Type III Transverse-sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: a Single-center 12-year Experience. Clin Neuroradiol 33, 161–169 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-022-01197-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-022-01197-4