Abstract
Purpose
Limbic encephalitis (LE) is an immune-related disease with limbic symptoms, variable and asymmetric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) aspects and antibody profiles. This study investigated the diagnostic value of quantitative relaxation times T2 (qT2) and MRI signal intensities (SI) in LE.
Methods
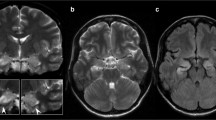
The prospective 3T-MRI study included 39 epilepsy patients with initially suspected LE and 20 healthy controls. Values and asymmetry indices of qT2, T2-weighted (T2-w) and proton density (PD)-w SI of manually delineated and automatically segmented amygdala and hippocampus were measured. Additionally, two raters made a blinded visual analysis on FLAIR (fluid attenuation inversion recovery) and T2-w images.
Results
According to diagnostic guidelines, 22 patients had probable LE and 17 patients had possible LE. The qT2 was higher (p < 0.01) in patients than in controls (mean ± SD, amygdala 98 ± 7 ms vs. 90 ± 5 ms, hippocampus 101 ± 7 ms vs. 92 ± 3 ms), but was not different between probable and possible LE or between sides (left and right). The PD-w SI and T2-w SI were lower in patients than in controls but were not different between patient subgroups or between sides. Diagnostic performance of visual analysis was relatively poor.
Conclusions
Epilepsy patients with suspected LE had elevated qT2 in amygdala and hippocampus, whereas the expected T2-w SI increase was not found; however, the diagnostic value of qT2 remains questionable since it did not discriminate probable from possible LE.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FLAIR:
-
Fluid attenuation inversion recovery
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- LE:
-
Limbic encephalitis
- LI:
-
Laterality index
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
- PD:
-
Proton density
- PD-w:
-
Proton density weighted
- qT2:
-
Quantified T2-relaxation time
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- SI:
-
Signal intensity
- T2-w:
-
T2-weighted
- TE:
-
Echo time
- TR:
-
Repetition time
- VGKC:
-
Voltage-gated potassium channel
References
Kelley BP, Patel SC, Marin HL, Corrigan JJ, Mitsias PD, Griffith B. Autoimmune encephalitis: pathophysiology and imaging review of an overlooked diagnosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017;38:1070–8.
da Rocha AJ, Nunes RH, Maia AC Jr, do Amaral LL. Recognizing autoimmune-mediated encephalitis in the differential diagnosis of limbic disorders. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36:2196–205.
Bien CG, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie. S1-Leitlinie: Immunvermittelte Erkrankungen der grauen ZNS-Substanz sowie Neurosarkoidose. 2012. https://www.dgn.org/leitlinien/2396-ll-32-2012-immunvermittelte-erkrankungen-der-grauen-zns-substanz-sowie-neurosarkoidose. Accessed 31 Aug 2017.
Dalmau J, Rosenfeld MR. Autoimmune encephalitis update. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16:771-8.
Graus F, Saiz A, Dalmau J. Antibodies and neuronal autoimmune disorders of the CNS. J Neurol. 2010;257:509–17.
Bien CG, Vincent A, Barnett MH, Becker AJ, Blümcke I, Graus F, Jellinger KA, Reuss DE, Ribalta T, Schlegel J, Sutton I, Lassmann H, Bauer J. Immunopathology of autoantibody-associated encephalitides: clues for pathogenesis. Brain. 2012;135:1622–38.
Dalmau J, Bataller L. Clinical and immunological diversity of limbic encephalitis: a model for paraneoplastic neurologic disorders. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006;20:1319–35.
Mittal MK, Rabinstein AA, Hocker SE, Pittock SJ, Wijdicks EF, McKeon A. Autoimmune encephalitis in the ICU: analysis of phenotypes, serologic findings, and outcomes. Neurocrit Care. 2016;24:240–50.
Gultekin SH, Rosenfeld MR, Voltz R, Eichen J, Posner JB, Dalmau J. Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis: neurological symptoms, immunological findings and tumour association in 50 patients. Brain. 2000;123(Pt 7):1481–94.
Dalmau J, Lancaster E, Martinez-Hernandez E, Rosenfeld MR, Balice-Gordon R. Clinical experience and laboratory investigations in patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:63–74.
Vincent A. Autoimmune channelopathies: new antibody-mediated disorders of the central nervous system. F1000 Biol Rep. 2009;1:61.
Tüzün E, Dalmau J. Limbic encephalitis and variants: classification, diagnosis and treatment. Neurologist. 2007;13:261–71.
Pittock SJ, Kryzer TJ, Lennon VA. Paraneoplastic antibodies coexist and predict cancer, not neurological syndrome. Ann Neurol. 2004;56:715–9.
Nunez-Enamorado N, Camacho-Salas A, Belda-Hofheinz S, Cordero-Castro C, Simon-De Las Heras R, Saiz-Diaz R, Martinez-Sarries FJ, Martinez-Menendez B, Graus F. Fast and spectacular clinical response to plasmapheresis in a paediatric case of anti-NMDA encephalitis. Rev Neurol. 2012;54:420–4.
Gresa-Arribas N, Titulaer MJ, Torrents A, Aguilar E, McCracken L, Leypoldt F, Gleichman AJ, Balice-Gordon R, Rosenfeld MR, Lynch D, Graus F, Dalmau J. Antibody titres at diagnosis and during follow-up of anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: a retrospective study. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:167–77.
Moscato EH, Jain A, Peng X, Hughes EG, Dalmau J, Balice-Gordon RJ. Mechanisms underlying autoimmune synaptic encephalitis leading to disorders of memory, behavior and cognition: insights from molecular, cellular and synaptic studies. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;32:298–309.
Petit-Pedrol M, Armangue T, Peng X, Bataller L, Cellucci T, Davis R, McCracken L, Martinez-Hernandez E, Mason WP, Kruer MC, Ritacco DG, Grisold W, Meaney BF, Alcalá C, Sillevis-Smitt P, Titulaer MJ, Balice-Gordon R, Graus F, Dalmau J. Encephalitis with refractory seizures, status epilepticus, and antibodies to the GABAA receptor: a case series, characterisation of the antigen, and analysis of the effects of antibodies. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:276–86.
Leypoldt F, Wandinger K‑P, Bien CG, Dalmau J. Autoimmune encephalitis. Eur Neurol Rev. 2013;8:31–7.
Titulaer MJ, McCracken L, Gabilondo I, Armangué T, Glaser C, Iizuka T, Honig LS, Benseler SM, Kawachi I, Martinez-Hernandez E, Aguilar E, Gresa-Arribas N, Ryan-Florance N, Torrents A, Saiz A, Rosenfeld MR, Balice-Gordon R, Graus F, Dalmau J. Treatment and prognostic factors for long-term outcome in patients with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: an observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:157–65.
Urbach H, Soeder BM, Jeub M, Klockgether T, Meyer B, Bien CG. Serial MRI of limbic encephalitis. Neuroradiology. 2006;48:380–6.
Wagner J, Witt J‑A, Helmstaedter C, Malter MP, Weber B, Elger CE. Automated volumetry of the mesiotemporal structures in antibody-associated limbic encephalitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. 2015;86:735–42.
Wagner J, Schoene-Bake JC, Malter MP, Urbach H, Huppertz HJ, Elger CE, Weber B. Quantitative FLAIR analysis indicates predominant affection of the amygdala in antibody-associated limbic encephalitis. Epilepsia. 2013;54:1679–87.
Irani SR, Bera K, Waters P, Zuliani L, Maxwell S, Zandi MS, Friese MA, Galea I, Kullmann DM, Beeson D, Lang B, Bien CG, Vincent A. N‑methyl-D-aspartate antibody encephalitis: temporal progression of clinical and paraclinical observations in a predominantly non-paraneoplastic disorder of both sexes. Brain. 2010;133:1655–67.
Florance NR, Davis RL, Lam C, Szperka C, Zhou L, Ahmad S, Campen CJ, Moss H, Peter N, Gleichman AJ, Glaser CA, Lynch DR, Rosenfeld MR, Dalmau J. Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis in children and adolescents. Ann Neurol. 2009;66:11–8.
Kotsenas AL, Watson RE, Pittock SJ, Britton JW, Hoye SL, Quek AM, Shin C, Klein CJ. MRI findings in autoimmune voltage-gated potassium channel complex encephalitis with seizures: one potential etiology for mesial temporal sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014;35:84–9.
Graus F, Titulaer MJ, Balu R, Benseler S, Bien CG, Cellucci T, Cortese I, Dale RC, Gelfand JM, Geschwind M, Glaser CA, Honnorat J, Höftberger R, Iizuka T1, Irani SR, Lancaster E, Leypoldt F, Prüss H, Rae-Grant A, Reindl M, Rosenfeld MR, Rostásy K, Saiz A, Venkatesan A, Vincent A, Wandinger KP, Waters P, Dalmau J. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:391–404.
Essig M, Knopp MV, Schoenberg SO, Hawighorst H, Wenz F, Debus J, van Kaick G. Cerebral gliomas and metastases: assessment with contrast-enhanced fast fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery MR imaging. Radiology. 1999;210:551–7.
Khan NL, Jeffree MA, Good C, Macleod W, Al-Sarraj S. Histopathology of VGKC antibody-associated limbic encephalitis. Neurology. 2009;72:1703–5.
Kotsarini C, Griffiths PD, Wilkinson ID, Hoggard N. A systematic review of the literature on the effects of dexamethasone on the brain from in vivo human-based studies: implications for physiological brain imaging of patients with intracranial tumors. Neurosurgery. 2010;67:1799–815. discussion 1815.
Cole AJ. Status epilepticus and periictal imaging. Epilepsia. 2004;45(Suppl 4):72–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A.-H. Schievelkamp, A. Jurcoane, T. Rüber, L. Ernst, A. Müller, B. Mädler, H.H. Schild, E. Hattingen and declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schievelkamp, AH., Jurcoane, A., Rüber, T. et al. Limbic Encephalitis in Patients with Epilepsy—is Quantitative MRI Diagnostic?. Clin Neuroradiol 29, 623–630 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-018-0705-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-018-0705-1