Abstract
Purpose
Reproducibility of two different methods for quantifying fiber tracts by using a diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) sequence suitable for clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocols was evaluated.
Methods
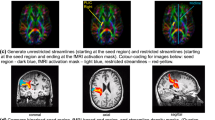
DTI of 15 subjects was used to analyze intra-rater and inter-rater reproducibility. Another 10 subjects underwent MRI twice for assessment of between-scan reliability. Ten long association tracts were defined by fiber tracking using inclusion and exclusion regions of interest (ROIs). Whole-tract analysis and tractography-based core analysis were performed, and the effect of fractional anisotropy (FA 0.15/0.30) and turning angle threshold (27°/60°) on reproducibility was evaluated. Additionally, ROI measurements were performed in the core of the tracts.
Results
For the tract-based methods, intra-rater and inter-rater reliabilities of FA and mean diffusivity (MD) measurements were excellent. Between-scan reproducibility was good or excellent in 127 of 130 of the measurements. There was no systematic difference in the reproducibility of the FA, MD, and volume measurements depending on the FA or turning angle threshold. For the cross-sectional ROI measurements, reliability showed large variation from poor to excellent depending on the tract.
Conclusions
Compared with the commonly used cross-sectional core ROI method, the tract-based analyses seem to be a more robust way to identify and measure white matter tracts of interest, and provide a novel reproducible tool to perform core analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandstack N, Kurki T, Tenovuo O. Quantitative diffusion tensor tractography of long association tracts in patients with traumatic brain injury without findings in routine MRI. Radiology. 2013;267:231–9.
Kanaan RA, Shergill SS, Barker GJ, Catani M, Ng VW, Howard R, McGuire PK, Jones DK. Tract-specific anisotropy measurements in diffusion tensor imaging. Psychiatry Res. 2006;146:73–82.
Snook L, Plewes C, Beaulieu C. Voxel based versus region of interest analysis in diffusion tensor imaging of neurodevelopment. Neuroimage. 2007;34(1):243–52.
Bisdas S, Bohning DE, Bešenski N, Nicholas JS, Rumboldt Z. Reproducibility, interrater agreement, and age-related changes of fractional anisotropy measures at 3T in healthy subjects: effect of the applied b-value. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:1128–33.
Brander A, Kataja A, Saastamoinen A, Ryymin P, Huhtala H, Öhman J, Soimakallio S, Dastidar P. Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain in a healthy adult population: normative values and measurement reproducibility at 3 T and 1.5 T. Acta Radiol. 2010;7:800–7.
Vollmar C, O’Muircheartaigh J, Barker GJ, Symms MR, Thompson P, Kumari V, Duncan JS, Richardson MP, Koepp MJ. Identical, but not the same: intra-site and inter-site reproducibility of fractional anisotropy measures on two 3.0 T scanners. Neuroimage. 2010;51:1384–94.
Mori S, Crain BJ, Chacko VP, van Zijl PCM. Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 1999;45:265–9.
Wakana S, Caprihan A, Panzenboeck MM, Fallon JH, Perry M, Gollub RL, Hua K, Zhang J, Jiang H, Dubey P, Blitz A, van Zijl P, Mori S. Reproducibility of quantitative tractography methods applied to cerebral white matter. Neuroimage. 2007;36:630–44.
Malykhin N, Concha L, Seres P, Beaulieu C, Coupland NJ. Diffusion tensor imaging tractography and reliability analysis for limbic and paralimbic white matter tracts. Psychiatry Res. 2008;164:132–42.
Danielian LE, Iwata NK, Thomasson DM, Floeter MK. Reliability of fiber tracking measurements in diffusion tensor imaging for longitudinal study. Neuroimage. 2010;49:1572–80.
Hasan KM, Kamali A, Abid H, Kramer LA, Fletcher JM, Ewing-Cobbs L. Quantification of the spatiotemporal microstructural organization of the human brain association, projection and commissural pathways across the lifespan using diffusion tensor tractography. Brain Struct Funct. 2010;214:361–73.
Kurki T, Laalo J, Oksaranta O. Diffusion tensor tractography of the uncinate fasciculus: pitfalls in quantitative analysis due to traumatic volume changes. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;38(1):46–53.
Yasmin H, Nakata Y, Aoki S, Abe O, Sato N, Nemoto K, Arima K, Furuta N, Uno M, Hirai S, Masutani Y, Ohtomo K. Diffusion abnormalities of the uncinate fasciculus in Alzheimer’s disease: diffusion tensor tract-specific analysis using a new method to measure the core of the tract. Neuroradiology. 2008;50:293–9.
Schmahmann JD, Smith EE, Eichler FS, Filley CM. Cerebral white matter neuroanatomy, clinical neurology, and neurobehavioral correlates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1142:266–309.
Kraus MF, Susmaras T, Caughlin BP, Walker CJ, Sweeney JA, Little DM. White matter integrity and cognition in chronic traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain. 2007;130(10):2508–19.
Niogi SN, Mukherjee P, Ghadar J, Johnson C, Kolster RA, Sarkar R, Lee H, Meeker M, Zimmerman RD, Manley GT, McCandliss BD. Extent of microstructural white matter injury in postconcussive syndrome correlates with impaired cognitive reaction time: a 3T diffusion tensor imaging study of mild traumatic brain injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(5):967–73.
Rutgers DR, Toulgoat F, Cazejust J, Fillard P, Lasjaunias P, Ducreux D. White matter abnormalities in mild traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:514–9.
Salmond CH, Menon DK, Chatfield DA, Williams GB, Pena A, Sahakian BJ, Pickard JD. Diffusion tensor imaging in chronic head injury survivors: correlations with learning and memory indices. Neuroimage. 2006;29:117–24.
Wang JY, Abdi H, Bakhadirov K, Diaz-Arrastia R, Devous MD. A comprehensive reliability assessment of quantitative diffusion tensor tractography. Neuroimage. 2012;60:1127–38.
Bonekamp D, Nagae LM, Degaonkar M, Matson M, Abdalla WMA, Barker PB, Mori S, HorskaÌa A. Diffusion tensor imaging in children and adolescents: reproducibility, hemispheric, and age-related differences. Neuroimage. 2007;34:733–42.
Borich MR, Wadden KP, Boyd LA. Establishing the reproducibility of two approaches to quantify white matter tract integrity in stroke. Neuroimage. 2012;59:2393–400.
Hong YH, Sung JJ, Kim SM, Park KS, Lee KW, Chang KH, Song IC. Diffusion tensor tractography-based analysis of the pyramidal tract in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuroimaging. 2008;18:282–7.
Partridge SC, Mukherjee P, Berman JI, Henry RG, Miller SP, Lu Y, Glenn OA, Ferriero DM, Barkovich AJ, Yigneron DB. Tractography-based quantitation of diffusion tensor imaging parameters in white matter tracts of preterm new-borns. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;22:467–74.
Wang S, Melhem ER. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and primary lateralsclerosis: the role of diffusion tensor imaging and other advanced MR-based techniques as objective upper motor neuron markers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1064:61–77.
Netsch T, van Muiswinkel A. Quantitative evaluation of image-based distortion correction in diffusion tensor imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2004;23(7):789–98.
Rohde GK, Barnett AS, Basser PJ, Marenco S, Pierpaoli C. Comprehensive approach for correction of motion and distortion in diffusion-weighted MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2004;51:103–14.
Shrout P, Fleiss J. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979;2:420–8.
Portney L, Watkins M, editors. Foundations of clinical research: applications to practice. 2nd ed. Norwalk: Appleton & Lange; 2000.
Hermoye L, Saint-Martin C, Cosnard G, Lee S-K, Kim J, Nassogne M-C, Menten R, Clapuyt P, Donohue PK, Hua K, Wakana S, Jiang H, van Zijl PCM, Mori S. Pediatric diffusion tensor imaging: normal database and observation of the white matter maturation in early childhood. Neuroimage. 2006;29(2):493–504.
Heiervang E, Behrens TE, Mackay CE, Robson MD, Johansen- Berg H. Between session reproducibility and between subject variability of diffusion MR and tractography measures. Neuroimage. 2006;33:867–77.
Alexander AL, Lee JE, Wu YC, Field AS. Comparison of diffusion tensor imaging measurements at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T with and without parallel imaging. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2006;16:299–309.
Ling J, Merideth F, Caprihan A, Pena A, Teshiba T, Mayer AR. Head Injury or head motion? Assessment and quantification of motion artifacts in diffusion tensor imaging studies. Hum Brain Mapp. 2011;33(1):50–62.
Chung S, Courcot B, Sdika M, Moffat K, Rae C, Henry RG. Bootstrap quantification of cardiac pulsation artifact in DTI. Neuroimage. 2010;49:631–40.
Ni H, Kavcic V, Zhu T, Ekholm S, Zhong J. Effects of number of diffusion gradient directions on derived diffusion tensor imaging indices in human brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(8):1776–81.
Rankin G, Stokes M. Reliability of assessment tools in rehabilitation: an illustration of appropriate statistical analyses. Clin Rehabil. 1998;12(3):187–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brandstack, N., Kurki, T., Laalo, J. et al. Reproducibility of Tract-based and Region-of-Interest DTI Analysis of Long Association Tracts. Clin Neuroradiol 26, 199–208 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0349-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0349-8